The two blocks in an atwood machine
Q: Slove and restrict solutions to exact values in the intereval [0, 2pie A. Q: You are modeling the concentration of a drug in a person's blood after they take one pill. We assume
Hey there! We receieved your request. Now 3kg. So for 3kg. But you should know the physics also!!!
The two blocks in an atwood machine
Solve problems involving Atwood machines with two hanging masses. Solve for acceleration and tension with variables alone or given masses. An Atwood machine consists of two blocks hanging from a pulley. The simple pulley with no mechanical advantage changes the direction of the hanging mass force. It is important to find commonalities so you can create and use mathematical expressions involving multiple objects like mass 1 m 1 and mass 2 m 2 in the animation. An Atwood machine in equilibrium would have equal mass on either side and could be at rest or have the blocks moving at a constant speed. The magnitude of tension in the string is equal to the either mass weight m 1 g or m 2 g , only when an Atwood machine with two equal masses hung on each side of a pulley. Q1 What is the acceleration of an Atwood machine that has a 10 kg hanging mass on the left and 5 kg hanging mass on the right side of the pulley? See Answer. Look to earlier in the lesson to see how this equation below was derived. The 10 kg mass will accelerate 3. Q2 What is the tension in the string of an Atwood machine that has a 10 kg hanging mass on the left and 5 kg hanging mass on the right side of the pulley? The tension above both masses will be This is the same answer as using a prior equation and checks our work. Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy.
Here frictional force being non-conservative force the above concept is used. Please check your email for login details.
A light in extensible string that goes over a smooth fixed pulley as shown in the figure connect two blocks of masses 0. Find the work done by string on the block of mass 0. The heavier bock in an atwood machine has a mass twice that of the lighter one. The tension in the stirng is Find the decrease in the gravitational potential energy during the first second after the system is releaed from rest.
The Atwood Machine is a common classroom experiment showing the laws of motion of two coupled systems undergoing constant acceleration. An Atwood Machine consists of two masses m A and m B , coupled together by a inextensible massless string over a massless pulley. When the two masses are equal, the system is in equilibrium and no motion occurs. The two masses will remain stationary. When the two weights are not equal, the system will move where the heavier mass is pulled down while the lighter mass is pulled up. This example problem shows how to derive the acceleration of the system and the tension in the string. We will ignore the values of m A and m B at this point to show the derivation of the answer. Choose your coordinate system so the acceleration is always positive. This system is coupled together by the massless string.
The two blocks in an atwood machine
.
Roblox redeem gift card
A ball of mass m makes a perfect elastic head on collinsion with a second ball of mass M initially If the spring block system is released from a stretched position find the number of complete oscillations in 1 minute. Mary moves away from the Earth to a distant planet 12 light years away fro That force being conservative change in total mechanical energy will be zero. Other Related Questions on Mechanics. An Atwood machine consists of two blocks hanging from a pulley. Standard value: The Q: 2- A: The correct option is, b 2nd. Initially the spring is unstre Q: can you please help me finding a simple solution for this question thank you.
.
The two blocks in an Atwood machine have masses 2. Hey there! Notice a few facts necessary to understand when solving through Atwood machine problems: Masses are attached to the same string. Only external force will do any work. A ball of mass m makes a perfect elastic head on collinsion with a second ball of mass M initially Most problems will assume the pulley and string is massless. Q: Consider the system pictured in the figure below. Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy. A: The correct answer to your question is: A. The side of the string attached to m 1, and the other side attached to m 2 have the same magnitude of tension F T. Q: A long solenoid that has 1, turns uniformly distributed over a length of 0. The distance between the ground and the ball is h.

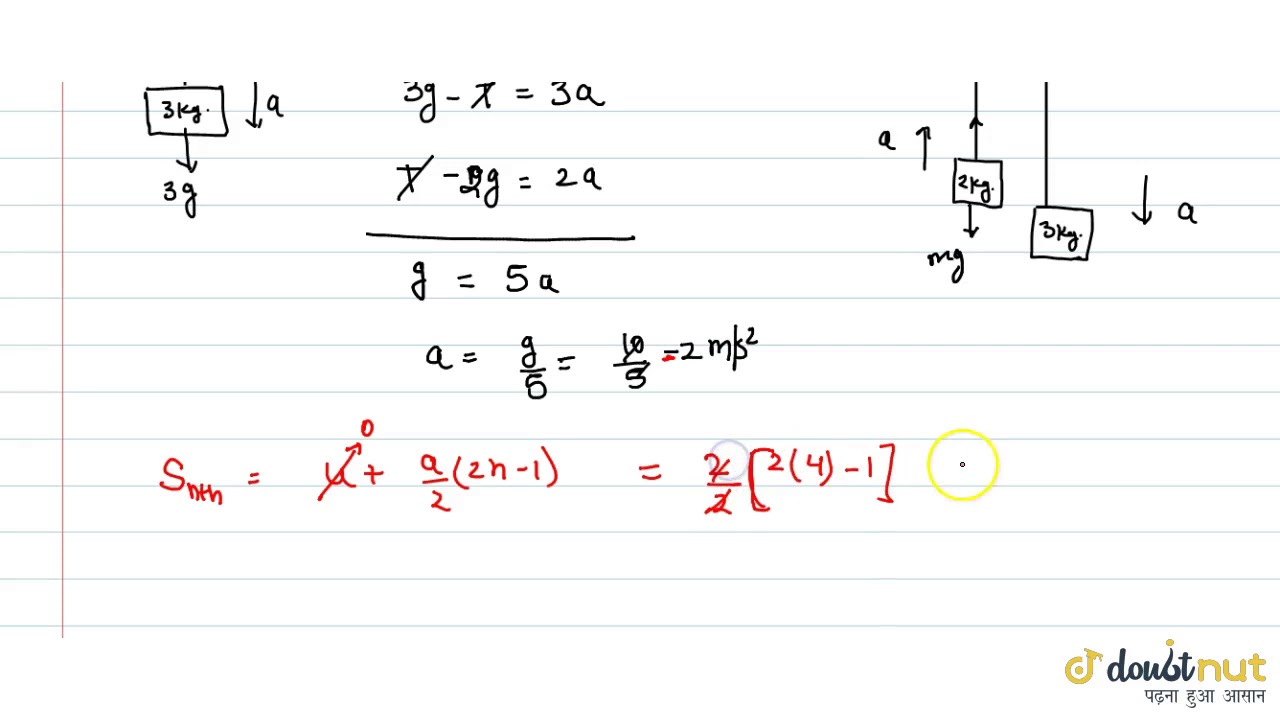
I think, that you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.