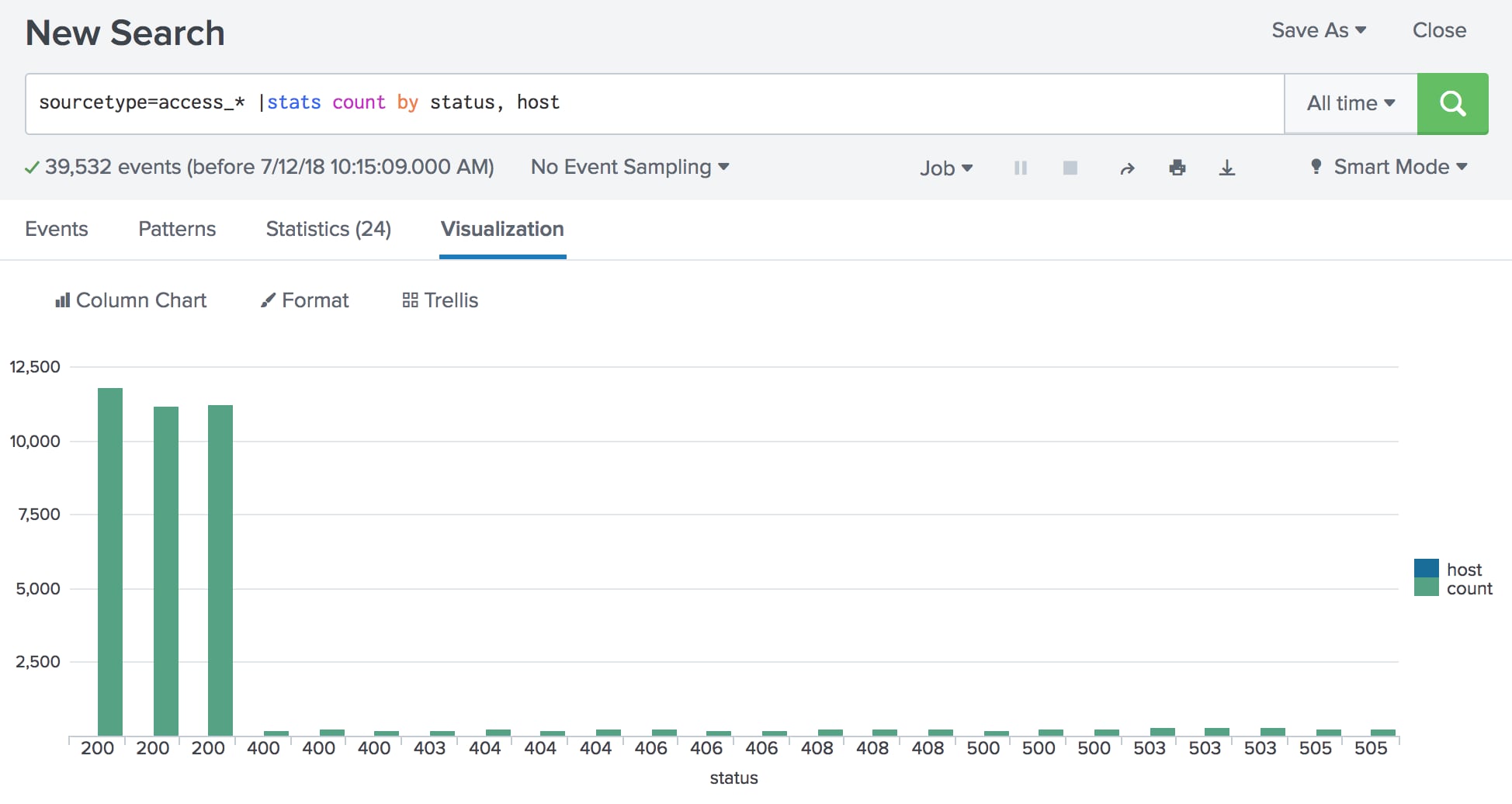
Splunk count by time
They make pulling data from your Splunk environment quick and easy to understand. But what if you wanted to take your STATS command one step further and splunk count by time a time breakdown of that data? However, it is important to note that there are a few key differences with timechart:. Understanding these differences will prepare you to use the timechart command in Splunk without confusing the use cases.
I have a search created, and want to get a count of the events returned by date. View solution in original post. Splunk Answers. Splunk Administration. Using Splunk. Splunk Platform Products. Splunk Premium Solutions.
Splunk count by time
The usage of the Splunk time chart command is specifically to generate the summary statistics table. This table which is generated out of the command execution can then be formatted in a manner that is well suited for the requirement — chart visualization for example. In the charts when we try to visualize, the data obtained is plotted against time that is limited to the X-axis by default and then the parameter that you choose for the Y-axis. The time chart is a statistical aggregation of a specific field with time on the X-axis. Hence the chart visualizations that you may end up with are always line charts, area charts, or column charts. Please take a closer look at the syntax of the time chart command that is provided by the Splunk software itself:. Let us now take a look at the required arguments that you specifically need to pass on to the command without which you might not be able to fetch the details that you intend to. To use either or, is mandatorily required to be provided. Let us take a closer look at each and every possible required argument to the command. This can be best described as a combination of literals, fields, operators, and functions that may represent the value of your destination field. For any of these evaluations to evaluate as per your requirement, the values are specifically needed to be valid for the kind of operation that we are going to perform on them.
Tags: count. Download Now! Mar 09 to Mar
.
For each minute, calculate the product of the average "CPU" and average "MEM" and group the results by each host value. Create a timechart of the average of the thruput field and group the results by each host value. Align the time bins to 5am local time. Set the span to 12h. The bins will represent 5am - 5pm, then 5pm - 5am the next day , and so on. Was this documentation topic helpful? Please select Yes No. Please specify the reason Please select The topic did not answer my question s I found an error I did not like the topic organization Other. Enter your email address if you would like someone from the documentation team to reply to your question or suggestion. Please provide your comments here.
Splunk count by time
For information about using string and numeric fields in functions, and nesting functions, see Overview of SPL2 eval functions. When used in a search, this function returns the UNIX time when the search is run. If you want to return the UNIX time when each result is returned, use the time function instead. You can use this function with the eval and where commands, in the WHERE clause of the from command, and as part of evaluation expressions with other commands. The following example determines the UNIX time value of the start of yesterday, based on the value of now.
Ablación endometrial opiniones
Share on linkedin LinkedIn. July 3, Using Splunk. Using the convert Command February 14, Run a pre-Configured Search for Free. Thanks a lot. However, it will bin the events up into buckets of time designated by a time span Timechart will format the results into an x and y chart where time is the x -axis first column and our y-axis remaining columns will be a specified field Understanding these differences will prepare you to use the timechart command in Splunk without confusing the use cases. Post Reply. Apps and Add-ons. What is a Splunk Timechart? All Apps and Add-ons.
Hi jerinvarghese The issue you have is using fieldformat for Time field instead of instead of eval. Check the Splunk docs for the difference and you should be able to work out why.
All forum topics Previous Topic Next Topic. Big Data. July 3, Download Now! However, it will bin the events up into buckets of time designated by a time span Timechart will format the results into an x and y chart where time is the x -axis first column and our y-axis remaining columns will be a specified field Understanding these differences will prepare you to use the timechart command in Splunk without confusing the use cases. Jump to solution Solution. This example shows us a chart that provides the multiplication of the average CPU and the average MEM for each of the hosts that is connected. However, it is important to note that there are a few key differences with timechart:. API Management and Testing. You can optionally use the to specify the required number of columns to be included. Explore Courses. All Apps and Add-ons. Thanks a lot. January 17,

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.