Power headroom
Metrics details.
It represents the difference between the maximum transmit power level supported by a mobile device and the actual power level being used by the device during a communication session. The power headroom value is a critical parameter that is monitored by the network to ensure optimal performance and reliable communication. In wireless networks, each mobile device needs to transmit its signals to the base station with a certain power level to establish and maintain a connection. The transmit power level depends on several factors, including the distance between the mobile device and the base station, the quality of the wireless channel, and interference from other devices. The network assigns a specific power level to each device to maintain a satisfactory level of signal quality and coverage. However, the power level required for communication can vary depending on the specific conditions.
Power headroom
.
In the proposed PHR-PERA scheme in this paper, the base station uses the PH report, which can reflect the UE transmission power state in the previous subframe in allocating the appropriate number of PRBs to the UE in order to achieve enhanced performance due to improved power efficiency and less interference, power headroom. Because the UE has the transmission power constraint [ 11 ], allocating more number of PRBs than the UE power capability can afford will reduce the transmission power allocated per PRB, which is also referred to as spectral power headroom PSD, power headroom.
.
Metrics details. Generally, the cell edge UE has a higher probability to be constrained by the maximum transmission power level owing to the compensation of the large pathloss. When the UE transmission power is constrained by the maximum level, allocating a higher number of physical resource blocks PRBs than the UE power capability can afford will reduce the transmission power to be allocated per PRB, resulting in inefficient use of power resources. To avoid this power inefficiency, the uplink transmission power can be controlled according to the number of PRBs allocated using the power headroom report-based power efficient resource allocation PHR-PERA scheme proposed in this paper. Furthermore, adaptive open-loop power control OL-PC based on the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio SINR and the uplink interference is used to improve the cell capacity. Additional gains of However, the inter-cell interference problem remains to be solved because the band allocated to a user in a cell can be used by another user in any of the neighboring cells.
Power headroom
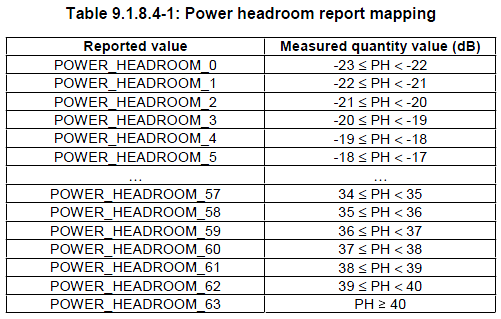
By knowing the power headroom of each UE, the eNodeB can make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and power control, ensuring efficient and reliable communication. It is a compact entity with a fixed size and comprises a solitary octet, which is defined as follows refer to figure 6. Figure 6. E phr-Config. It helps to prevent excessive reporting when certain events occur in quick succession. It can vary in size and is defined in Figure 6. Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Austadiums
In addition to monitoring the power headroom, the network also considers other factors when making power control decisions. The overall uplink power control procedure is described below. Copy to clipboard. High MCS levels require high transmission power. According to Table 4 , a Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. The UE transmitting with maximal power can also cause severe inter-cell interference with neighboring cells. Power headroom PH is reported by the UE to the base station to broadcast how much power the UE required in the previous subframe. If the UE reports the positive PH, the base station can consider that it is possible for the UE to increase its transmission power. K s is given by the parameter deltaMCS-Enabled provided by the higher layer as 1. If the power headroom is too low, the device may experience degraded signal quality, increased error rates, or even dropped calls.
.
Copy to clipboard. The UE transmission power for the current subframe is determined by Eq. Power control mechanisms allow the network to adjust the transmit power level of each device dynamically, based on real-time measurements of signal quality and channel conditions. The initial value of P 0 for the MUE is also used for the macro only case. Once the affordable number of PRBs is decided, the next procedure is divided into two stages—the pre-allocation and re-allocation stages. According to Fig. Similarly, the inter-cell cooperation scheme such as muting the base station requires the exchange of the control information that gives the overhead resulting in spectral inefficiency [ 7 ]. As shown in Fig. J Wireless Com Network , According to Table 4 , a It represents the difference between the maximum transmit power supported by a mobile device and the power level currently being used by the device. The latest evolution of cellular networks—i. Owing to the dynamic variation of the channel caused by the fading effect, it is seen in Fig. However, the OL-PC parameters can be set differently for the macro- and femtocells in the HetNet environment to increase throughput performance.

0 thoughts on “Power headroom”