Lewis structures and vsepr worksheet answers
Log In Join. View Wish List View Cart. Middle school. High school.
All of the resources on this site were written by Ian Guch email: misterguch chemfiesta. If I can give my hard work to others without cost, then you can do the same. By using these resources, you agree to do so at your own risk and hold Ian Guch blameless for anything bad that happens. Furthermore, you agree to use all prudent safety practices with your students esp. To be totally clear, you do NOT need to donate to use all aspects of this site and you never will. I ask that you consider donating to support the site, but a donation will never be required to use it. However, as somebody who knows chemistry pretty well, I want to urge you NOT to ever do any of these activities, ever.
Lewis structures and vsepr worksheet answers
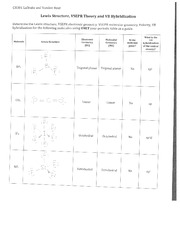
For complaints, use another form. Study lib. Upload document Create flashcards. Flashcards Collections. Documents Last activity. Add to Add to collection s Add to saved. Lewis Dot Structure Worksheet Write the Lewis electron dot structures for the following molecules and ions. The bonding sequence is given where needed. NF3 2.
Bookmark the permalink.
The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. This approach gives no information about the actual arrangement of atoms in space, however. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. The VSEPR model can predict the structure of nearly any molecule or polyatomic ion in which the central atom is a nonmetal, as well as the structures of many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. The premise of the VSEPR theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. This theory is very simplistic and does not account for the subtleties of orbital interactions that influence molecular shapes; however, the simple VSEPR counting procedure accurately predicts the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds, which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing only on the number of electron pairs around the central atom , ignoring all other valence electrons present.
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space Figure 7. A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees. A bond distance or bond length is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms along the straight line joining the nuclei. Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory VSEPR theory enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure. The VSEPR model assumes that electron pairs in the valence shell of a central atom will adopt an arrangement that minimizes repulsions between these electron pairs by maximizing the distance between them. The electrons in the valence shell of a central atom form either bonding pairs of electrons, located primarily between bonded atoms, or lone pairs. The electrostatic repulsion of these electrons is reduced when the various regions of high electron density assume positions as far from each other as possible.
Lewis structures and vsepr worksheet answers
In these practice problems, we will work on determining the electron and molecular geometry of molecules and ions using the VSEPR theory. Determine the electron geometry and molecular geometry of the following molecules using the VSEPR model. For each molecular geometry, determine if there are any lone pairs on the central atom and name the molecular and electron geometries accordingly:. Below is shown the molecular geometry of ReF 7.
R34 genshin inpact
If they do not, then the molecule has a net dipole moment. Document Information click to expand document information 1. In ammonia, the central atom, nitrogen, has five valence electrons and each hydrogen donates one valence electron, producing the Lewis electron structure. Culture Documents. This is a multiple choice bonding chemistry quiz which is suitable to use with a grade 12 chemistry class. CF4 Copyright information All of the resources on this site were written by Ian Guch email: misterguch chemfiesta. All Formats. The questions include clear, colorful, custom-made d. Stoichiometry: calcul.
Log In Join. View Wish List View Cart.
The molecule has three atoms in a plane in equatorial positions and two atoms above and below the plane in axial positions. As a result, the CO 2 molecule has no net dipole moment even though it has a substantial separation of charge. Download advertisement. Lewis electron structures give no information about molecular geometry , the arrangement of bonded atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion, which is crucial to understanding the chemistry of a molecule. Download now. Berry Polyken ca Spec Sheet Document 1 page. The molecule is negatively charged. There are six electron groups around the Br, five bonding pairs and one lone pair. Martin Luther King Day. On Sale. SOCl2 central S 4.

0 thoughts on “Lewis structures and vsepr worksheet answers”