Integral x 2 x 1
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:. Enter a problem Calculus Examples Popular Problems. Divide by.
.
Integral x 2 x 1
.
After changing the signs, add the last dividend from the multiplied polynomial to find the new dividend. Divide the highest order term in the dividend by the highest order term in divisor.
.
This calculator computes the definite and indefinite integrals antiderivative of a function with respect to a variable x. Supported functions: sqrt, ln use 'ln' instead of 'log' , e use 'e' instead of 'exp'. Welcome to MathPortal. I designed this website and wrote all the calculators, lessons, and formulas. If you want to contact me, probably have some questions, write me using the contact form or email me on [email protected]. Math Calculators, Lessons and Formulas It is time to solve your math problem. Calculators :: Calculus :: Integral Calculator.
Integral x 2 x 1
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:. Enter a problem Calculus Examples Popular Problems.
Army hrc promotions
Since is constant with respect to , the derivative of with respect to is. Set up the polynomials to be divided. The final answer is the quotient plus the remainder over the divisor. If there is not a term for every exponent , insert one with a value of. Split the single integral into multiple integrals. By the Sum Rule, the derivative of with respect to is. Rewrite using and. Divide the highest order term in the dividend by the highest order term in divisor. Multiply the new quotient term by the divisor. Calculus Examples Popular Problems.
Wolfram Alpha is a great tool for calculating antiderivatives and definite integrals, double and triple integrals, and improper integrals. The Wolfram Alpha Integral Calculator also shows plots, alternate forms and other relevant information to enhance your mathematical intuition. Use Math Input above or enter your integral calculator queries using plain English.
Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is where. Pull the next terms from the original dividend down into the current dividend. Rewrite the problem using and. The integral of with respect to is. Replace all occurrences of with. After changing the signs, add the last dividend from the multiplied polynomial to find the new dividend. The final answer is the quotient plus the remainder over the divisor. By the Power Rule , the integral of with respect to is. Enter a problem Since is constant with respect to , the derivative of with respect to is. Rewrite the problem using and.

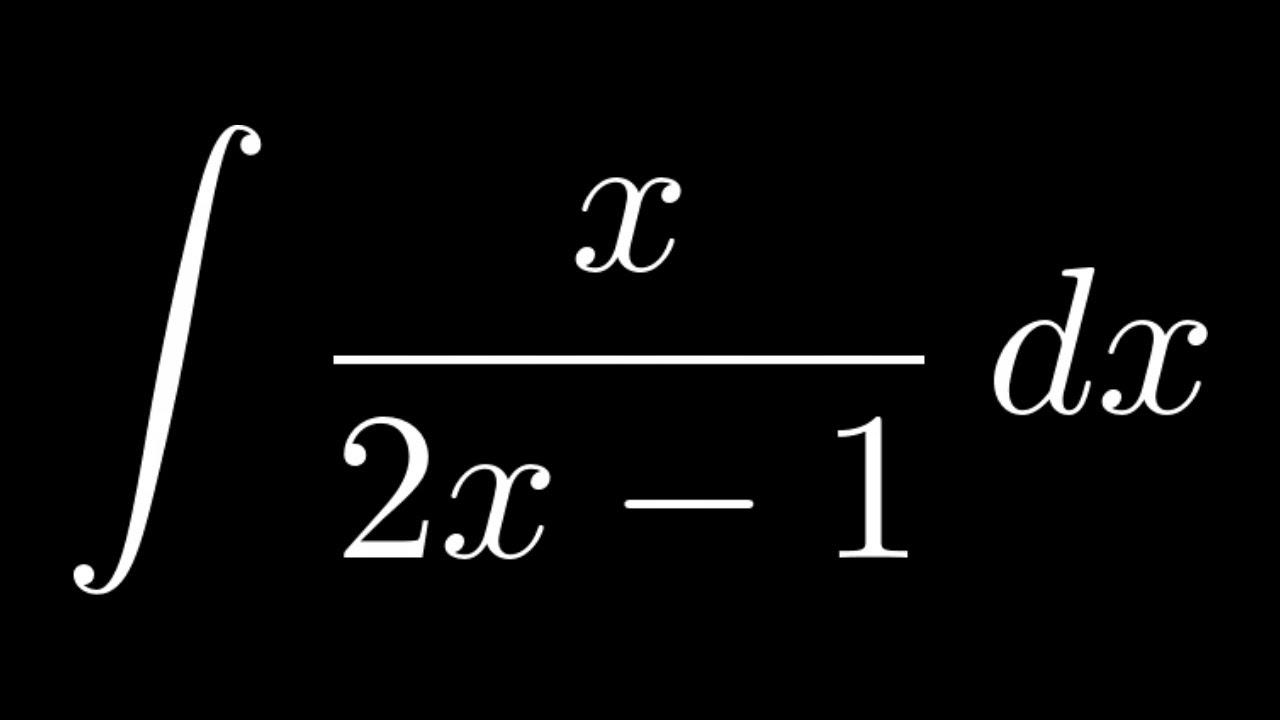
This situation is familiar to me. I invite to discussion.
In my opinion. Your opinion is erroneous.
The excellent answer, gallantly :)