Dorsal raphe nucleus
Thank you for visiting nature.
Pharmacological experiments have shown that the modulation of brain serotonin levels has a strong impact on value-based decision making. The serotonin and dopamine systems also have reciprocal functional influences on each other. However, the specific mechanism by which serotonin affects value-based decision making is not clear. To understand the information carried by the DRN for reward-seeking behavior, we measured single neuron activity in the primate DRN during the performance of saccade tasks to obtain different amounts of a reward. We found that DRN neuronal activity was characterized by tonic modulation that was altered by the expected and received reward value.
Dorsal raphe nucleus
The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is a heterogeneous brainstem nucleus located in the midbrain and pons. Via widespread projections, which target a multitude of brain areas, its neurons utilize many transmitters to control various physiological functions, including learning, memory and affect. Accordingly, the DRN has been strongly associated with brain dysfunction, especially mood disorders such as depression, but also Alzheimer's disease. The DRN's most abundant transmitter, serotonin, has received the most attention in studies on both normal brain function and disease, and lately its involvement in the regulation of neuroplasticity has been under particular scrutiny. This chapter begins with a systematic overview of what we currently know about the anatomy of the DRN and its neurons, including their ascending projections. It continues with a review of the transmitters of the DRN, followed by a discussion on the connection between the DRN and neuroplasticity. Special emphasis is put on serotonin and its central role in neuroplasticity, which is proving to be of high priority in unraveling the full picture of the cellular mechanisms and their interconnections in the etiology of major depression and Alzheimer's disease. Abstract The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is a heterogeneous brainstem nucleus located in the midbrain and pons. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review.
Increasing evidences implicate that reward processing involves DRN neurons Although 5-HT neurons have been reported to form local connections Weissbourd dorsal raphe nucleus al. Structure and function of the brain serotonin system.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Harvard Dataverse. Molecular and anatomical organization of the dorsal raphe nucleus. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN represents one of the most sensitive reward sites in the brain. However, the exact relationship between DRN neuronal activity and reward signaling has been elusive. In this review, we will summarize anatomical, pharmacological, optogenetics, and electrophysiological studies on the functions and circuit mechanisms of DRN neurons in reward processing. The DRN is commonly associated with serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT , but this nucleus also contains neurons of the neurotransmitter phenotypes of glutamate, GABA and dopamine. Pharmacological studies indicate that 5-HT might be involved in modulating reward- or punishment-related behaviors. Recent optogenetic stimulations demonstrate that transient activation of DRN neurons produces strong reinforcement signals that are carried out primarily by glutamate.
Dorsal raphe nucleus
The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains. Here we used single-cell RNA sequencing, in situ hybridization, anatomical tracing, and spatial correlation analysis to map the transcriptional and spatial profiles of cells from the mouse DRN. Our analysis of 39, single-cell transcriptomes revealed at least 18 distinct neuron subtypes and 5 serotonergic neuron subtypes with distinct molecular and anatomical properties, including a serotonergic neuron subtype that preferentially innervates the basal ganglia. Our study lays out the molecular organization of distinct serotonergic and non-serotonergic subsystems, and will facilitate the design of strategies for further dissection of the DRN and its diverse functions. Keywords: dorsal raphe nucleus; mouse; neuromodulation; neuroscience; serotonin; single cell RNAseq. Abstract The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. Publication types Research Support, N.
The walking dead season 1 พากย์ ไทย ep 1
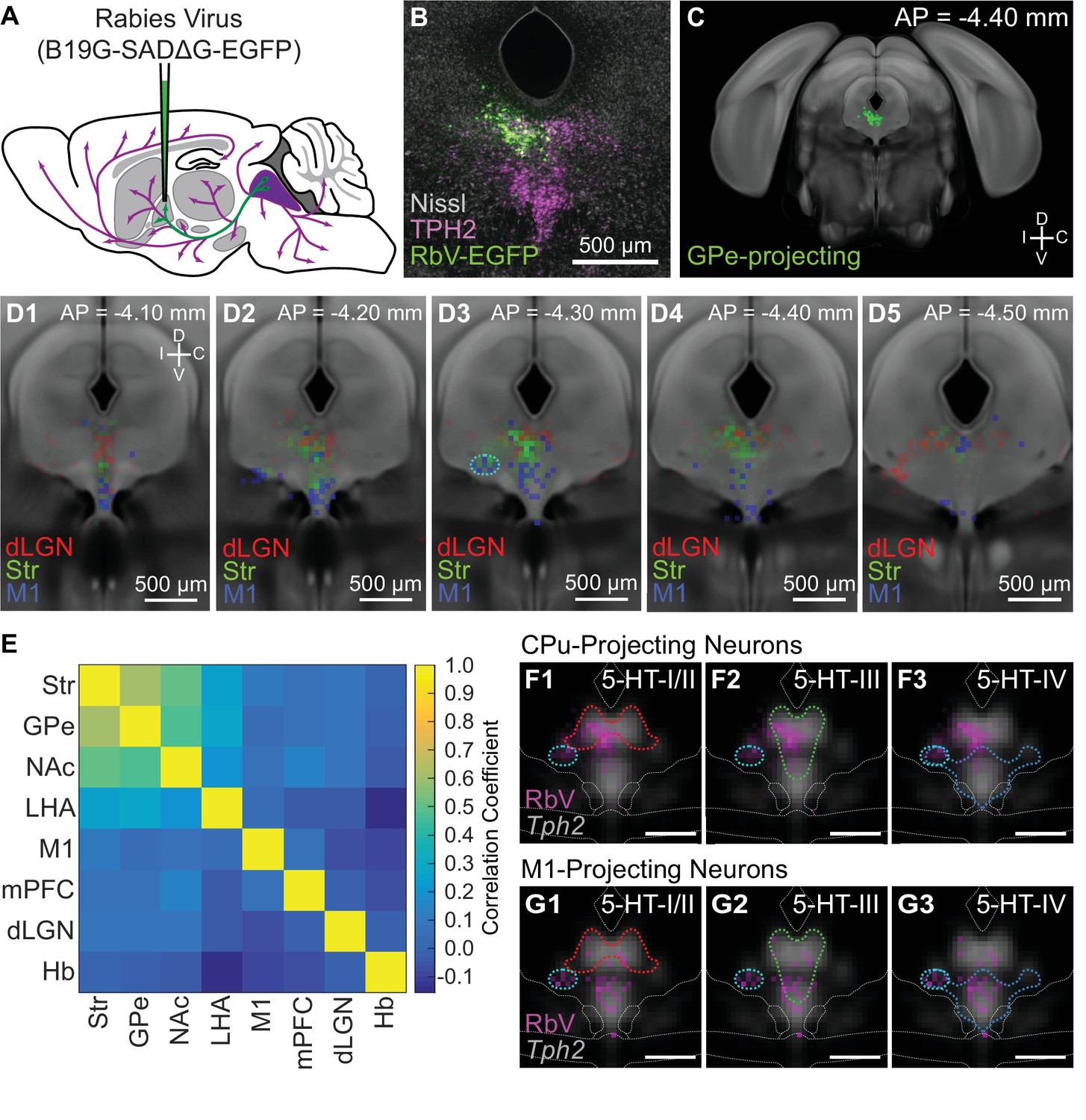
Genes used to identify major neuronal cell types by their neurotransmitters are labeled in red. Fine alignment of each 2D histogram along the dorsal-ventral axis was adjusted manually using Tph2 ISH images as the reference. Van Bockstaele EJ Biswas A Pickel VM Topography of serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus that send axon collaterals to the rat prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens Brain Research — Spatial reconstruction of single-cell gene expression data. Mice were deeply anesthetized with isoflurane and transcardially perfused with 5—10 ml chilled 0. Red: Huang dataset batch 1. The interaction of the 5-HT system with the dopamine system has been documented in the frontal cortex and basal ganglia nuclei, which form part of the nigrostriatal, mesocortical, and mesolimbic dopamine pathways. Therefore, our results support the hypothesis that the Str-projecting DRN 5-HT neuron subpopulation is molecularly heterogeneous, and is comprised of at least 2 transcriptionally distinct 5-HT neuron subtypes. Ultrasensitive fluorescent proteins for imaging neuronal activity. Mice were deeply anesthetized with isoflurane and transcardially perfused with 5—10 ml chilled 0.
Federal government websites often end in.
Varga, V. In addition, the authors demonstrate that at least 2 distinct 5-HT neuronal types project to the striatum. An analysis of serotonin secretion in hypothalamic regions based on 5-hydroxytryptophan accumulation or push-pull perfusion. We also found enriched genes for both clusters despite their similarities, and that cells in both clusters had comparable read depth and gene detection rates see Author response image 1. Exclusion of PCs from the calculation of the 2-dimensional UMAP embedding abolished the separation of cells by dataset and batch Author response image 8. The analysis was also performed only for restricted periods of the task, which were determined tentatively. It also avoids restraint-associated inescapable stress that may change the activity of DRN neurons and 5-HT signalling 42 , Genes differentially expressed between 5-HT neuron subtypes were used as the target list, and all genes expressed in the 5-HT neuron dataset were used for the background list. Stimulation of medial prefrontal cortex serotonin 2C [5-HT 2C ] receptors attenuates cocaine-seeking behavior. Richmond, B. Whole-brain axonal projection mapping revealed that DR serotonin neurons co-expressing vesicular glutamate transporter-3 preferentially innervate the cortex, whereas those co-expressing thyrotropin-releasing hormone innervate subcortical regions in particular the hypothalamus.

I think, that you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I apologise, that I can help nothing. I hope, to you here will help.