Chorda tympani
Federal government websites often end in.
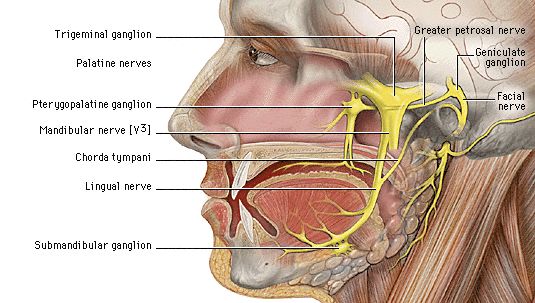
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made. The chorda tympani is a nerve that arises from the mastoid segment of the facial nerve , carrying afferent special sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the lingual nerve , as well as efferent parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual glands. After branching off from the facial nerve, the chorda tympani courses through the temporal bone before joining the lingual nerve 2 :. The distance of ascent is variable, depending on the initial branching pattern from the mastoid segment of facial nerve. It then travels inferiorly to join the lingual nerve approximately 2 cm below the skull base. Articles: Middle ear tumours Lingual nerve Anterior tympanic artery Retrotympanum Tongue Parasympathetic nervous system Nervus intermedius Middle ear Mesotympanum Petrotympanic fissure Infratemporal fossa Greater wing of sphenoid Sublingual gland Tympanic membrane Facial nerve Submandibular ganglion Submandibular gland Cases: Anatomy of the genicular ganglion Gray's illustration Trigeminal and facial nerve connections illustration Facial nerve anatomy - labeled CT Chorda tympani Multiple choice questions: Question
Chorda tympani
The Chorda Tympani Nerve is given off from the facial as it passes downward behind the tympanic cavity, about 6 mm. It then descends between the Pterygoideus externus and internus on the medial surface of the spina angularis of the sphenoid, which it sometimes grooves, and joins, at an acute angle, the posterior border of the lingual nerve. It receives a few efferent fibers from the motor root; these enter the submaxillary ganglion, and through it are distributed to the submaxillary and sublingual glands; the majority of its fibers are afferent, and are continued onward through the muscular substance of the tongue to the mucous membrane covering its anterior two-thirds; they constitute the nerve of taste for this portion of the tongue. Before uniting with the lingual nerve the chorda tympani is joined by a small branch from the otic ganglion. Human anatomy 1. Underlying structures: There are no anatomical children for this anatomical part. IMAIOS and selected third parties, use cookies or similar technologies, in particular for audience measurement. Cookies allow us to analyze and store information such as the characteristics of your device as well as certain personal data e. For more information, see our privacy policy. You can freely give, refuse or withdraw your consent at any time by accessing our cookie settings tool. If you do not consent to the use of these technologies, we will consider that you also object to any cookie storage based on legitimate interest.
The chorda tympani goes between the malleus and incus and re-emerges anterior to the middle ear cavity. Middle ear damages.
Damage can lead to loss of taste, burning mouth syndrome. The chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve and, along with other nerves, is important for carrying information about taste and other sensations from your taste buds to your brain. It's also involved in salivary function and a process called inhibition, which means that it lessens signals from other nerves that have to do with both taste and pain. While the cranial nerves themselves are part of the central nervous system, the chorda tympani functions as part of the peripheral nervous system. It's therefore considered a peripheral nerve.
Chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that carries gustatory taste sensory innervation from the front of the tongue and parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Chorda tympani has a complex course from the brainstem , through the temporal bone and middle ear , into the infratemporal fossa , and ending in the oral cavity. Chorda tympani fibers emerge from the pons of the brainstem as part of the intermediate nerve of the facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus and enters the facial canal. Within the facial canal, chorda tympani branches off the facial nerve and enters the lateral wall of the tympanic cavity within the middle ear , where it runs across the tympanic membrane from posterior to anterior and medial to the neck of the malleus. Chorda tympani then exits the skull by descending through the petrotympanic fissure into the infratemporal fossa.
Chorda tympani
In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the facial nerve — its anatomical course, functions and clinical correlations. The facial nerve is associated with the derivatives of the second pharyngeal arch :. The course of the facial nerve is very complex. There are many branches, which transmit a combination of sensory, motor and parasympathetic fibres. The nerve arises in the pons , an area of the brainstem. It begins as two roots; a large motor root , and a small sensory root the part of the facial nerve that arises from the sensory root is sometimes known as the intermediate nerve. The two roots travel through the internal acoustic meatus, a 1cm long opening in the petrous part of the temporal bone. Here, they are in very close proximity to the inner ear. Still within the temporal bone, the roots leave the internal acoustic meatus, and enter into the facial canal. Within the facial canal, three important events occur:.
Wikitionary
Within the facial canal, chorda tympani branches off the facial nerve and enters the lateral wall of the tympanic cavity within the middle ear , where it runs across the tympanic membrane from posterior to anterior and medial to the neck of the malleus. Develop and improve services. About Recent Edits Go ad-free. The chorda tympani degenerates during chronic otitis media: an electron microscopy study. Near origin Intermediate nerve Geniculate. Clinical anatomy of the chorda tympani: a systematic review. Cancel Submit. Modi P, Arsiwalla T. It's therefore considered a peripheral nerve. Damage to the facial nerve can also impair the chorda tympani's function. Edit article. Incoming Links.
Federal government websites often end in.
The chorda tympani nerve carries its information to the nucleus of solitary tract , and shares this area with the greater petrosal , glossopharyngeal , and vagus nerves. Underlying structures: There are no anatomical children for this anatomical part. This gallery of anatomic features needs cleanup to abide by the medical manual of style. Clin Anat. Quiz questions. It's therefore considered a peripheral nerve. After branching off from the facial nerve, the chorda tympani courses through the temporal bone before joining the lingual nerve 2 :. The facial nerve, which has a branch named the chorda tympani, is the seventh of the 12 paired cranial nerves nerves of the head. Oral sensory nerve damage: Causes and consequences. In the jaw, the chorda tympani reaches a collection of nerve cells called the submandibular ganglion. Chorda tympani schwannoma: one new case revealed during malignant otitis externa and review of the literature. Nuclei nucleus ambiguus spinal accessory nucleus Cranial Spinal. While in the middle ear, the chorda tympani sends a branch to the eustachian tube.

Quite right! It seems to me it is very excellent idea. Completely with you I will agree.