Apollo 11 rocket diagram
Traveling to the Moon and returning required three unique and technologically advanced pieces of spacecraft, apollo 11 rocket diagram, from the Saturn V rocket, to the Command Module, Columbiaand the Lunar Module, Eagle. Click a link below to learn more about each technological feat that made it possible to land an American on the Moon.
The Apollo missions were the answer to a challenge issued by President John F. Kennedy to put a man on the moon. But just to get there, scientists had to build a powerful rocket. And to actually land on the moon and return the astronauts safely, NASA had to develop new spacecraft and a new type of rocket. NASA ultimately decided on a solution that consisted of three parts: A lunar lander known as the lunar module would put humans on the moon.
Apollo 11 rocket diagram
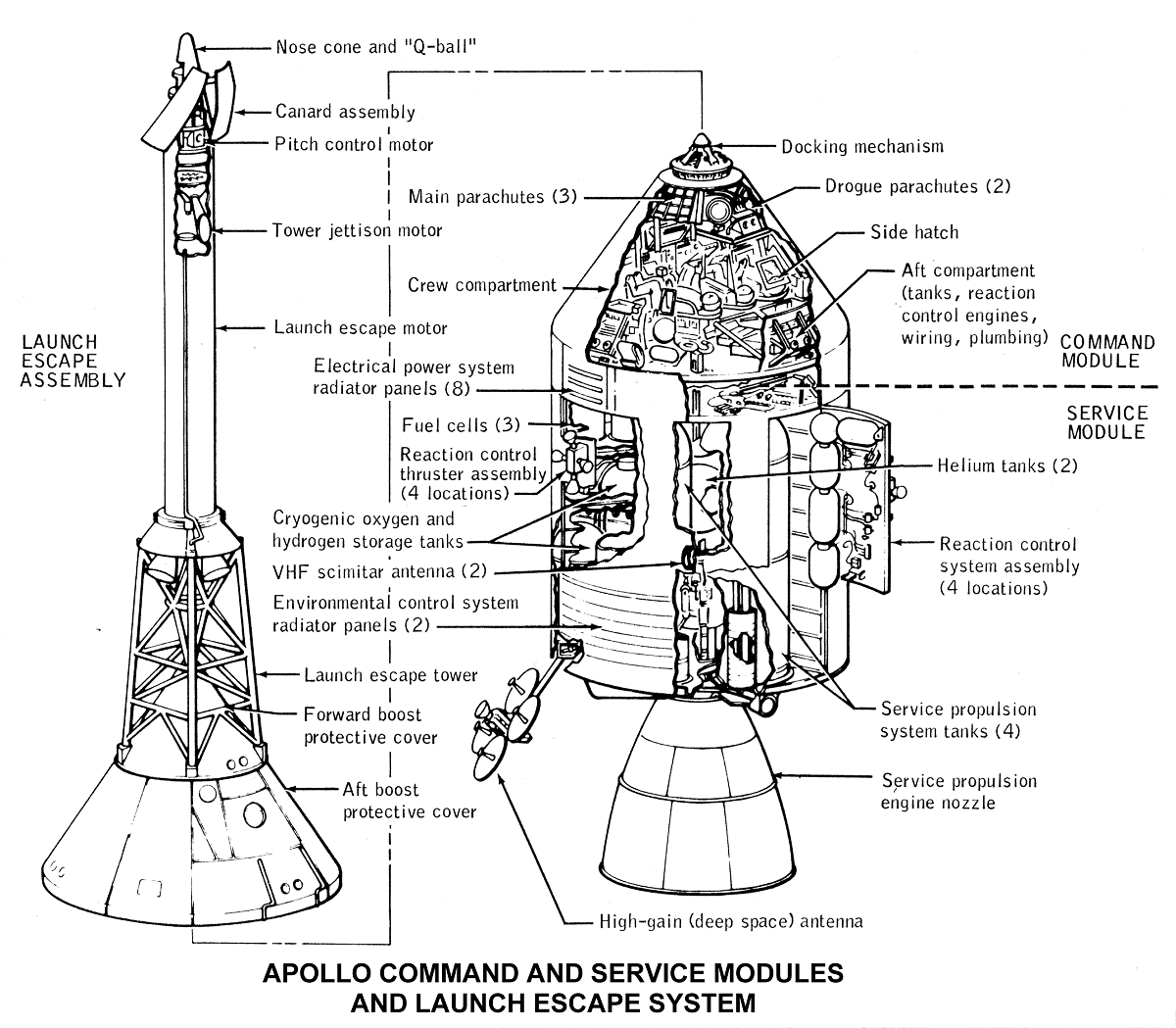
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program 's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the s and returning them safely to Earth. Two additional components complemented the spacecraft stack for space vehicle assembly: a spacecraft—LM adapter SLA designed to shield the LM from the aerodynamic stress of launch and to connect the CSM to the Saturn launch vehicle and a launch escape system LES to carry the crew in the command module safely away from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch emergency. The design was based on the lunar orbit rendezvous approach: two docked spacecraft were sent to the Moon and went into lunar orbit. After the lunar excursion, the two craft rendezvoused and docked in lunar orbit, and the CSM returned the crew to Earth. The command module was the only part of the space vehicle that returned with the crew to the Earth's surface. The LES was jettisoned during launch upon reaching the point where it was no longer needed, and the SLA remained attached to the launch vehicle's upper stage. Larger Saturn Vs launched two uncrewed CSMs on high Earth orbit test flights, the CSM on one crewed lunar mission, the complete spacecraft on one crewed low Earth orbit mission, and eight crewed lunar missions. The major part of the Apollo spacecraft was a three-man vehicle designed for Earth orbital, translunar, and lunar orbital flight, and return to Earth. This consisted of a command module supported by a service module , built by North American Aviation later North American Rockwell. The command module was the control center for the Apollo spacecraft and living quarters for the three crewmen. It contained the pressurized main crew cabin, crew couches, control and instrument panel, Primary Guidance, Navigation and Control System , communications systems, environmental control system, batteries, heat shield , reaction control system to provide attitude control , forward docking hatch, side hatch, five windows, and a parachute recovery system. The service module was unpressurized and contained a main service propulsion engine and hypergolic propellant to enter and leave lunar orbit, a reaction control system to provide attitude control and translational capability, fuel cells with hydrogen and oxygen reactants, radiators to dump waste heat into space, and a high gain antenna. The oxygen was also used for breathing, and the fuel cells produced water for drinking and environmental control. On Apollo 15, 16 and 17 it also carried a scientific instrument package, with a mapping camera and a small sub-satellite to study the Moon.
The lunar modules, such as Eagle from Apollo 11, not only got astronauts to the moon safely, but also provided critical backup oxygen and rations.
Published: 14 June You are reading in The technology it took to get to the Moon — Part of Space. The success of the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon, and the safety of the astronauts, relied on engineering, ingenuity and technology. When US President John F Kennedy was assured by his advisors that the United States would be capable of landing astronauts on the Moon in less than ten years, the nation had precisely 15 minutes of human spaceflight experience. With such limited experience, one of the first things the Americans had to decide was how to get to the Moon and back.
Kennedy on May 25, perform a crewed lunar landing and return to Earth. Additional flight objectives included scientific exploration by the lunar module, or LM, crew; deployment of a television camera to transmit signals to Earth; and deployment of a solar wind composition experiment, seismic experiment package and a Laser Ranging Retroreflector. During the exploration, the two astronauts were to gather samples of lunar-surface materials for return to Earth. They also were to extensively photograph the lunar terrain, the deployed scientific equipment, the LM spacecraft, and each other, both with still and motion picture cameras. Two hours, 44 minutes and one-and-a-half revolutions after launch, the S-IVB stage reignited for a second burn of five minutes, 48 seconds, placing Apollo 11 into a translunar orbit. The S-IVB stage separated and injected into heliocentric orbit four hours, 40 minutes into the flight. Later, on July 17, a three-second burn of the SPS was made to perform the second of four scheduled midcourse corrections programmed for the flight. The launch had been so successful that the other three were not needed.
Apollo 11 rocket diagram
Traveling to the Moon and returning required three unique and technologically advanced pieces of spacecraft, from the Saturn V rocket, to the Command Module, Columbia , and the Lunar Module, Eagle. Click a link below to learn more about each technological feat that made it possible to land an American on the Moon. When President Kennedy proclaimed that Americans would put a human on the Moon by the end of the decade, there wasn't a rocket that could get someone there. The engineering feat of the Saturn V rocket made it possible for astronauts to travel to the Moon. During the journey to and from the Moon, Columbia —its interior space about as roomy as a large automobile—served as main quarters for the astronauts, a place for working and living.
Ogx thick and full biotin shampoo
To rejoin the command module, the astronauts fired the ascent-stage rocket engine and lifted off, leaving the descent stage on the Moon. The first stage shot the rocket up about 42 miles 68 kilometers and the second stage carried the rocket even closer to orbit. The top of the lunar module from the viewpoint of the astronauts. Prior to the tragic fire in January in which three astronauts died, there were two hatches on the Apollo command module requiring 90 seconds to open. Kennedy to put a man on the moon. The command module was the only part of the spacecraft that would return to Earth. The thin, gold-colored films are used in "blankets" of up to 25 layers. Why March is the best month to see the northern lights. However, there were significant differences. The televised Moon landing was an incredible milestone in broadcasting, the result of years of planning and technological development. The ascent stage then was programmed to crash into the Moon. The popular conception may be that it was all rocket fuel and slide rulers, but you can't get to the Moon and back without some pretty hefty gear.
Published: 14 June You are reading in The technology it took to get to the Moon — Part of Space.
The SLA was made from 1. Capable of multiple restarts, this engine placed the Apollo spacecraft into and out of lunar orbit, and was used for mid-course corrections between the Earth and the Moon. While the Command Module was more like a cannonball than a plane, there was still a degree of control for the occupants. Today, the command modules for all of the Apollo missions are on display at various museums. Finally, the lunar module—stored in protective casing during the launch—would be the part of the spacecraft to actually land on the Moon. Sitting atop the Saturn V rocket was the Apollo spacecraft, which had three components: the service module, the command module spacecraft and the lunar module spacecraft. A window over the Commander's head aids docking with the Command Module. Objects and stories Discover unique and compelling stories—from objects that have changed our world to the intriguing personal histories that lie behind them. The astronauts wore an inner garment beneath the main suit with water-filled tubes sewn in to stop the astronauts from over-heating. The descent engine's thrust is 44, Newtons lbs maximum, and the ascent engine's thrust is 15, Newtons lbs. We now know that the Soviets were following a similar technological route for getting to the Moon. The third stage placed the Apollo spacecraft into Earth orbit and pushed it toward the moon.

I think, that you are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
What necessary words... super, a brilliant phrase
It agree, very amusing opinion