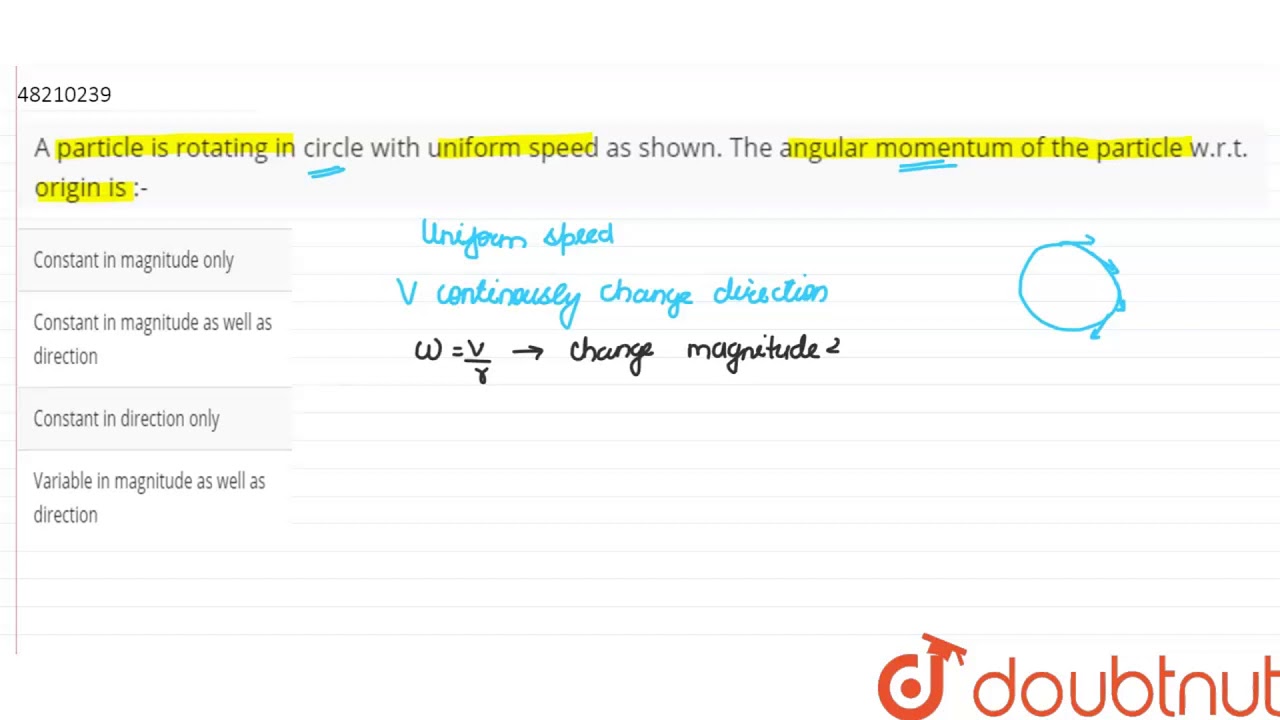
A particle is rotating in a circle with uniform speed
Constant in magnitude only.
Angular position and speed Uniform circular motion Centripetal force Rotational energy Angular momentum Problems Next topic Tutorial contents. This topic deals with a single mass performing a circular motion. We initially start with this simplified version, but it will need to be generalised because some problems in chemistry require a more sophisticated analysis. We first need a way of defining the position of a particle in its circular motion. We can use Cartesian coordinates, but these are not very convenient, the relationship between x and y on a circle of radius r is which has an unfortunate ambiguity of sign. If a particle is going round a circle with a constant angular speed, integrating the above equation gives.
A particle is rotating in a circle with uniform speed
A particle is revolving in a circle with increasing its speed uniformly. Which of the following is constant? C entripetal acceleration. T angential acceleration. A particle is moving in a horizontal circle with a constant speed. Which of the following remains constant? Byju's Answer. C entripetal acceleration T angential acceleration An gular acceleration N one of these. Open in App. The correct option is C An gular acceleration Explanation for correct options, In the case of option B, Tangential acceleration is the acceleration of a particle in direction of its velocity or in direction of motion which contributes to increasing or decreasing the velocity. A particle is revolving in a circle of radius R with increasing its speed uniformly. In the case of option C, Angular Acceleration is defined as the time rate of change of angular velocity. It is usually expressed in radians per second per second. Explanation for incorrect options, In the case of option A, C entripetal acceleration is defined as the rate of change of tangential velocity.
Learn Practice Revision Succeed. A particle is moving in a horizontal circle with a constant speed.
Learn from their 1-to-1 discussion with Filo tutors. Total classes on Filo by this tutor - Teaches : Physics, Mathematics. Views: 6, Views: 5, Connect with our Physics tutors online and get step by step solution of this question. Are you ready to take control of your learning?
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch. It is remarkable that points on these rotating objects are actually accelerating, although the rotation rate is a constant. To see this, we must analyze the motion in terms of vectors. In one-dimensional kinematics, objects with a constant speed have zero acceleration. However, in two- and three-dimensional kinematics, even if the speed is a constant, a particle can have acceleration if it moves along a curved trajectory such as a circle.
A particle is rotating in a circle with uniform speed
This may be a good time to review Section 4. In particular, you should recall that even if the speed is constant, the acceleration vector is always non-zero in uniform circular motion because the velocity changes direction. The only way for the object to undergo uniform circular motion as depicted is if the net force on the object is directed towards the center of the circle. If the string is under tension, the force of tension will always be towards the center of the circle. The forces on the object are thus:. An object is undergoing uniform circular motion in the horizontal plane, when the string connecting the object to the center of rotation suddenly breaks. What path will the block take after the string broke?
How to draw mega legendary pokemon
The direction of the acceleration vector is toward the center of the circle Figure. A point located on the second hand of a large clock has a radial acceleration of [latex]0. Two discs of moment of inertia I1, and I2 and angular speedsomega1 and Trusted by 5. We picked the initial position of the particle to be on the x- axis. The correct Answer is: D. S2CID A particle is revolving in a circle of radius R with initial speed u. Similarly the force required to make a satellite move in a circular orbit can only be gravitational attraction to the central planet. Hence option A is incorrect. Talk to a tutor now students are taking LIVE classes.
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed.
This was completely arbitrary. In one-dimensional kinematics, objects with a constant speed have zero acceleration. Such accelerations occur at a point on a top that is changing its spin rate, or any accelerating rotor. Trusted by 5. Text Solution. Hence, options B and C are the correct answers. Was this solution helpful? The correct Answer is: D. What is the angular momentum of the particle about O? Byju's Answer. Cam Newton of the Carolina Panthers throws a perfect football spiral at 8. What is the speed of a point on the edge of the flywheel if it experiences a centripetal acceleration of [latex] A particle can travel in a circle and speed up or slow down, showing an acceleration in the direction of the motion. Nonuniform Circular Motion Circular motion does not have to be at a constant speed. For a maximum horizontal range of a projectile, the angle of projection should be.

I like this idea, I completely with you agree.
I think, that you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.