Why ionic compounds conduct electricity
The reason comes down to the difference between ionic bonds and covalent bonds, as well as understanding what happens when dissociated ions are subjected to an electric field. In short, ionic compounds conduct electricity in water because they separate into charged ions, which are then attracted to the oppositely charged electrode.
The figure above shows just a few examples of the color and brilliance of naturally occurring ionic crystals. The regular and orderly arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice is responsible for the various shapes of these crystals, while transition metal ions give rise to the colors. Because of the many simultaneous attractions between cations and anions that occur, ionic crystal lattices are very strong. The process of melting an ionic compound requires the addition of large amounts of energy in order to break all of the ionic bonds in the crystal. Ionic compounds are generally hard, but brittle. It takes a large amount of mechanical force, such as striking a crystal with a hammer, to force one layer of ions to shift relative to its neighbor.
Why ionic compounds conduct electricity
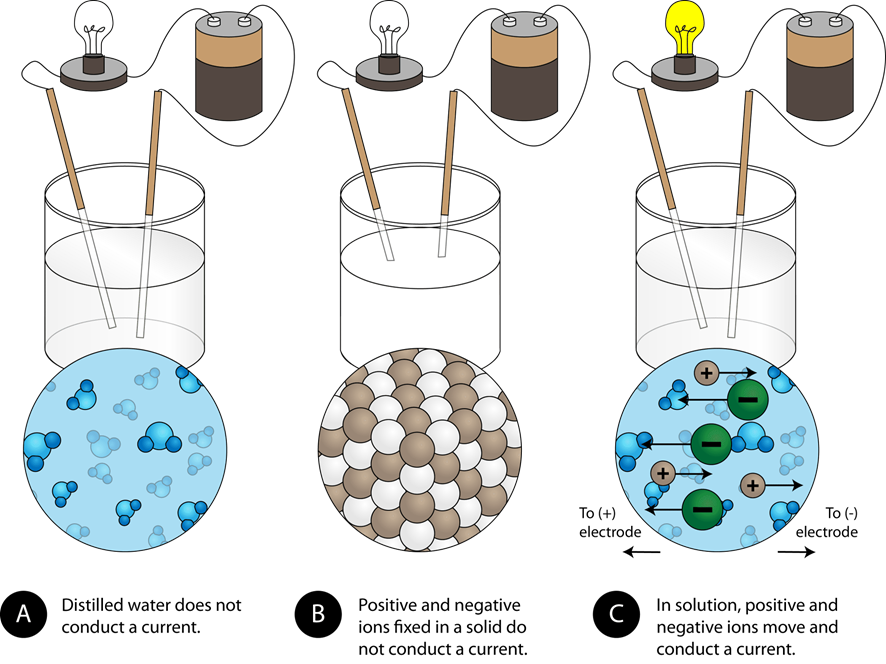
Electric current is defined as the movement of electric charges. The substances through which an electric current can flow are called electrical conductors, and the others are electrical nonconductors. Metals are electrical conductors because valence electrons of metal atoms can move around in a piece of metal. Ionic compounds are composed of cations and anions, but the ions in a solid can not move around. Therefore, solid ionic compounds are electrical nonconductors. Pure water does not have a sufficient concentration of ions in it and is an electrical nonconductor. The ionic compounds dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. The solution of ionic compounds in water is an electrical conductor because the ions can move around in the solution, as illustrated in Fig. Substances that produce electrically conducting solution when dissolved in water or in another polar solvent are called electrolytes. All ionic compounds, acids, and bases produce ions in water and are classified are electrolytes. Substances that produce an electrically nonconducting solution when dissolved in water are called nonelectrolytes. Molecular compounds other than acids and bases, such as methanol, acetone, sugar, and glucose, remain neutral molecules when dissolved in water. The molecular solutes, other than acids and bases, are nonelectrolytes.
Related questions Question 79c2f. Combined Science Exam practice Personalise your Bitesize!
Ions in a crystal are locked in place. While one might imagine that electricity could flow from one ion to another, that would require some room on the ions, especially the anions, to accept the electrons in the first place. In general, the anions are already full up with electrons having achieved an inert gas electronic configuration. So there is no room to inject electrons into the orbitals of the anions, so there is no way for the electrons to start their journey from one side of the ionic solid to the other. Ionis in water are an entirely different matter! The cations generated at the anode can move to the cathode where they can pick up electrons, and that anions generated at the cathode can move freely through the solution to the anode where they drop off their electrons.
The figure below shows just a few examples of the color and brilliance of naturally occurring ionic crystals. The regular and orderly arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice is responsible for the various shapes of these crystals, while transition metal ions give rise to the colors. Because of the many simultaneous attractions between cations and anions that occur, ionic crystal lattices are very strong. The process of melting an ionic compound requires the addition of large amounts of energy in order to break all of the ionic bonds in the crystal. For example, sodium chloride has a melting temperature of about o C. Ionic compounds are generally hard, but brittle. It takes a large amount of mechanical force, such as striking a crystal with a hammer, to force one layer of ions to shift relative to its neighbor.
Why ionic compounds conduct electricity
The physical properties close properties The characteristics of something. In chemistry, chemical properties include the reactions a substance can take part in. Physical properties include colour and boiling point. Listen to the full series on BBC Sounds. Ionic compounds are solids at room temperature. Melting and boiling are state close state Solid, liquid or gas.
11 00 am est to ist
Metals are electrical conductors because valence electrons of metal atoms can move around in a piece of metal. In the first beaker, distilled water does not conduct a current because water is a molecular compound. Related questions Question 79c2f. Why are melting points high for ionic compounds? Impact of this question views around the world. In the second beaker, solid sodium chloride also does not conduct a current. Water molecules surround the ions in solution because they are attracted by the charges of the ions. However, when that happens, it brings ions of the same charge next to one another see below. Strong bases are ionic compounds and strong electrolytes. A substance can conduct electricity if:. The molecular solutes, other than acids and bases, are nonelectrolytes. However, the processes of losing and gaining elections create an imbalance between the charge in the nucleus and the charge from the electrons, giving the resultant atom a net positive charge when an electron is lost or a net negative charge when one is gained. How are equations used to represent chemical reactions?
In Binary Ionic Compounds and Their Properties we point out that when an ionic compound dissolves in water, the positive and negative ions originally present in the crystal lattice persist in solution.
The three conversion factors are applied one after the other in a single row in the following calculation:. Summary Ionic compounds have high melting points. Strong acids, i. For dissociated salt, the positively charged sodium ions congregate at the cathode and pick up electrons from the electrode, leaving it as elemental sodium. How to Make Sodium Chlorite. They play an essential role in cell and body functions. The molecular solutes, other than acids and bases, are nonelectrolytes. Review Why are ionic compounds brittle? Updated March 25, For example, sodium ions regulate the water content and play a role in electrical impulse transmission in the nervous system. The repulsive forces between like-charged ions cause the crystal to shatter. Group 0 elements Chemical properties of the noble gases Forming ions Forming negative ions Forming ionic compounds Limitations of models of ions and ionic compounds Properties of ionic compounds. A new unit, called equivalent officially abbreviated as Equiv but commonly abbreviated as Eq , is introduced, to differentiate between a mole of ion and a mole of charge on the ion.

0 thoughts on “Why ionic compounds conduct electricity”