Why do mentos cause soda to explode
Skip to content.
What causes Coke to explode when Mentos are added to it? One would think that there must be a chemical reaction that causes the Coke and Mentos reaction to be so attractive and satisfying. The gas tries to escape and form bubbles around any irregular surface, called a nucleation site. Mentos also have nucleation sites because they are not as smooth as they appear. When added to Coke, the dissolved gas pushes the liquid out of the container at a super-fast speed in the form of bubbles. The candies simply catalyze the release of gas from the Coke bottle. Therefore, the chemical reaction between Coke and Mentos, in reality, is a physical reaction.
Why do mentos cause soda to explode
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in. Already have an account? Log in here. The chemical reactions involved in dropping mentos candies into a bottle of diet coke make quite the spectacle! Soda geysters, which can reach as high as ten meters, were a popular subject for viral videos in the early 's, but the science behind the spectacle remained a mystery until Many people speculated that the geyser was the result of an acid base reaction , given the low pH of soda. However, none of the ingredients in mentos are basic, and the experiment works to some degree with any type of soda and any type of candy. Mentos candies are not as smooth as they appear to the naked eye.
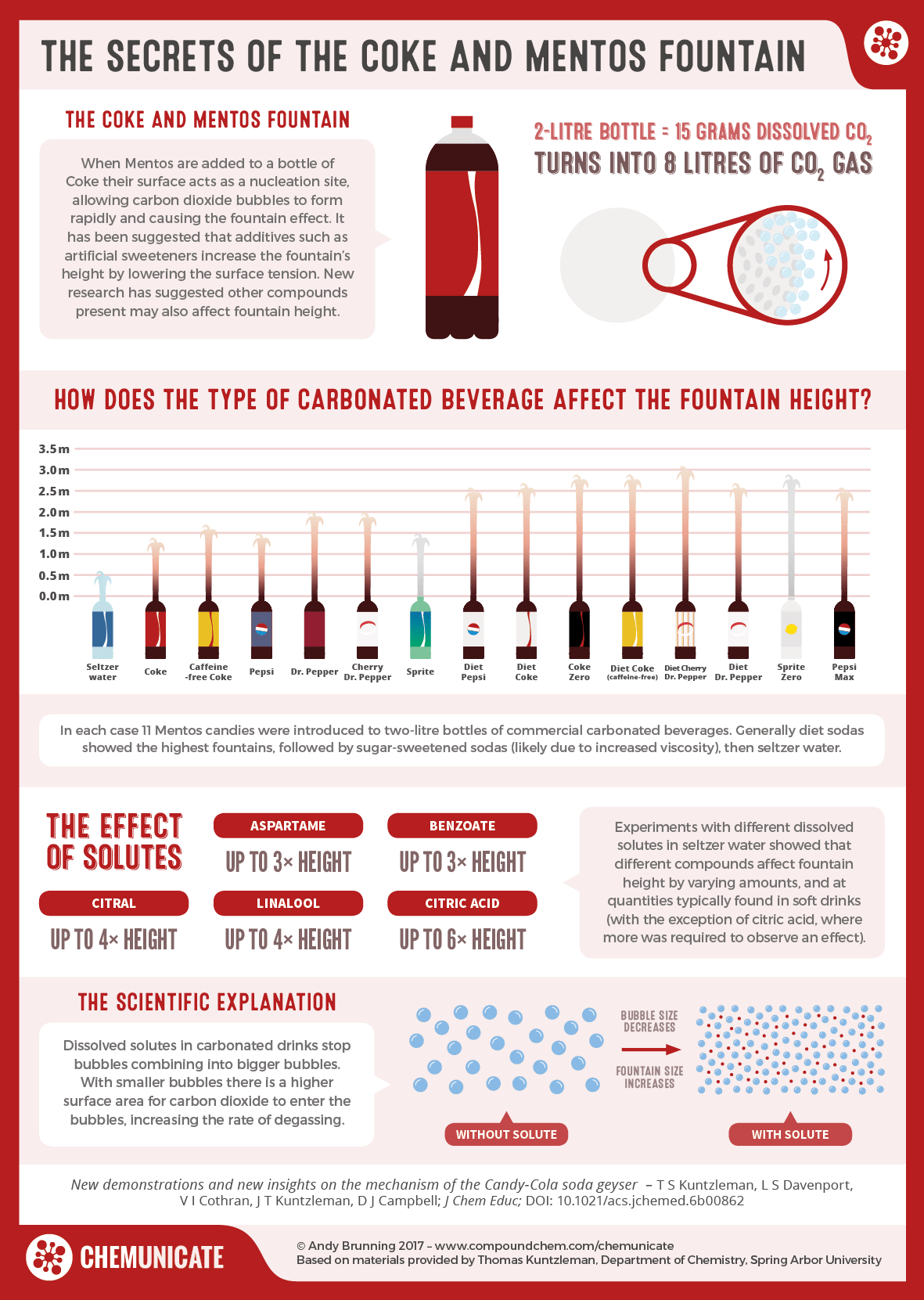
Carbonated sodas contain elevated levels of carbon dioxide under pressure.
A soda geyser is a physical reaction between a carbonated beverage, usually Diet Coke , and Mentos mints that causes the beverage to be expelled from its container. The candies catalyze the release of gas from the beverage, which creates an eruption that pushes most of the liquid up and out of the bottle. The tubes of candies were threaded onto a pipe cleaner and dropped into the soft drink to create a geyser. At the end of the s, the manufacturer of Wintergreen Lifesavers increased the size of the mints, and they no longer fit in the mouth of soda bottles. Science teachers found that Mentos candies had the same effect when dropped into a bottle of any carbonated soft drink.
Drop a few Mentos into a two-liter bottle of soda, and a geyser of foam erupts rapidly, sometimes reaching heights of 15 feet or more. First made famous by chemistry teacher Lee Marek on the Letterman show in , the phenomena sparked hundreds of homed videos and an episode of Discovery Channel's "Mythbusters. The bubbles in a bottle of soda are caused by molecules of dissolved carbon dioxide. Generally, water molecules like to stay next to each other, which prevents any dissolved gases from collecting. However, when offered a surface, called a nucleation site, dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide can gather, eventually forming a bubble. The sides of a bottle serve this purpose. When the bubble gets big enough, it breaks surface tension with the side of the bottle and floats up. A bottle of soda that gets shaken up releases the gas bubbles into the solution, making the soda supersaturated with carbon dioxide. This causes the carbon dioxide to get released quicker when you open it, causing a foamy explosion. Mentos candies accelerate this reaction through two primary means.
Why do mentos cause soda to explode
By Science Buddies. If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today. Key concepts Chemistry Physics Materials science Carbonation Physical reactions Explosions Introduction Have you ever seen the Diet Coke and Mentos experiment that is all over the Internet and wondered what makes the reaction work? You might think that there is some ingredient in a Mentos candy that causes a chemical reaction with the soda pop, like the way baking soda reacts with vinegar. But the amazing eruption that takes place when Mentos are dropped into Diet Coke or other brands of diet soda pop is not a chemical reaction at all! Instead it is a physical reaction.
Wood minecraft houses
Modal Gallery Close. Home Courses. Whether the soda is warm or cold, the process of forming bubbles occurs slowly. Hidden categories: Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Use mdy dates from November All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from June Commons category link from Wikidata Articles containing video clips. University of Hawaii at Hilo. Volcanic gas is dissolved in magma; at the surface of the earth, it escapes to the atmosphere. When you are ready, remove the card and let all the Mentos drop into the soda at once and quickly move out of the way. Tape the tube together on the side. Gases are dissolved in magma at pressures many thousands of times atmospheric pressure. If you try this project with regular Coke, the eruption should still happen but its sugary content may make cleaning more difficult. Archived from the original on July 27, However, if there are sharp edges or fine particles in the liquid, these have surfaces that allow the CO 2 molecules to start bubble formation more easily these are called nucleation points. This pressure effect of gases and liquids also has a more dangerous aspect as well: when scuba divers go to great depths in the ocean, they are breathing air, or specialized gas mixtures, at four or more times atmospheric pressure. What do you notice from the videos? One would think that there must be a chemical reaction that causes the Coke and Mentos reaction to be so attractive and satisfying.
Mentos and Coke — a combination that has fascinated us for years, leaving us mesmerized by the explosive reaction that ensues. But why does this happen? What is it about these seemingly harmless candies and soda that causes such a dramatic chemical reaction?
Archived from the original on May 7, However, experiments have shown that some dissolved solids that increase the surface tension of water such as sugars also increase fountain heights. A soda geyser is a physical reaction between a carbonated beverage, usually Diet Coke , and Mentos mints that causes the beverage to be expelled from its container. Davenport, Victoria I. Make a Mentos-and-Soda Fountain! Join Brilliant The best way to learn math and computer science. If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. When you open the Coke container, the pressure is reduced to 15 psi , and the CO 2 immediately begins to leave the Coke. Why do you think all of this is important? By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today. Bibcode : JChEd.. The candies simply catalyze the release of gas from the Coke bottle. Diet Coke makes a better spectacle than regular Coca-Cola because both aspartame and benzonatate a preservative used in artificially sweetened drinks lower surface tension more than sugar does. The soda company puts carbon dioxide in the soda to make the soda fizzy. The warm one will release bubbles of CO 2 much faster, because a warm gas is more energetic.

Rather, rather