Valence shell of nitrogen
Skip to main content. Table of contents. A Review of General Chemistry 5h 9m.
Nitrogen is present in almost all proteins and plays important roles in both biochemical applications and industrial applications. Nitrogen forms strong bonds because of its ability to form a triple bond with itself and other elements. Thus, there is a lot of energy in the compounds of nitrogen. Before years ago, little was known about nitrogen. Now, nitrogen is commonly used to preserve food and as a fertilizer. Nitrogen is found to have either 3 or 5 valence electrons and lies at the top of Group 15 on the periodic table.
Valence shell of nitrogen
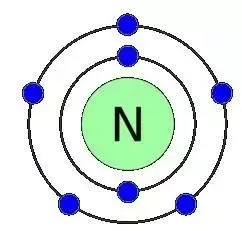
Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons. The thing to remember about main-group elements is that the group number gives you the element's number of valence electrons. In your case, nitrogen, "N" , is located in group 1color red 5 , which means that it has color red 5 valence electrons. Each nitrogen molecule consists of two atoms of nitrogen that are bonded by a triple covalent bond. This is a direct consequence of the fact that each nitrogen atom has 5 valence electrons. Each atom can thus complete its octet by sharing three electrons. Another thing to mention here is the fact that nitrogen's 5 valence electrons causes the atom to form 3- anions. This is the case because adding 3 electrons to nitrogen's valence shell will give it a complete octet. What is the number of valence electrons in nitrogen? Chemistry Electron Configuration Valence Electrons. Stefan V.
Atomic Structure.
The number of valence electrons is the number of electrons in the outer shell, that the atom uses for bonding. There is a quick way of identifying the number of valence electrons - it is the same as the Group number not for d-block elements , though. Nitrogen is in Group 5, so it has 5 outer shell electrons. How many valence electrons does nitrogen have? Doc Croc. Jun 8,
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. This allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. The 1 s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. However, this pattern does not hold for larger atoms.
Valence shell of nitrogen
Nitrogen , a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14, is a colorless liquid, gas, or solid. At normal temperature and pressure, two atoms of nitrogen bind together to form colorless and odorless dinitrogen N 2 gas. In chemical laboratory, dinitrogen can be prepared by treating an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite. Valence electrons are the total number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom i. The valence electrons for a neutral atom are always definite, it cannot be varied more or less in any condition for a particular atom and may or may not be equal to its valency. Valency is defined as the total number of electrons an atom can lose, gain, or share at the time of bond formation to get a stable electronic configuration i. The valency of an atom can be variable in different compounds or chemical reactions due to the different bonding circumstances. There are four simple steps to find out the valence electrons for nitrogen atom which are:. Step 1: Find the Atomic Number.
Julieth diaz
R and S of Fischer Projections. Oxidizing Agent. Diazo Replacement Reactions. You can reuse this answer Creative Commons License. Nitrogen is a non-metal element that occurs most abundantly in the atmosphere; nitrogen gas N 2 comprises Monosaccharides - Kiliani-Fischer. Orbital Diagram:Excited States. Diazo Sequence Groups. Phenol Acidity. How many valence electrons does hydrogen have? Triple bonds are very hard to break, so they keep their full valence shell instead of reacting with other compounds or atoms. Thomas, Jacob. Condensation Chemistry 2h 9m. Kumada Coupling Reaction.
Nitrogen is present in almost all proteins and plays important roles in both biochemical applications and industrial applications.
Acid Chloride Nomenclature. In aqueous solution, ammonia forms the ammonium ion, which we described above, and it has special amphiprotic properties. Carbocation Intermediate Rearrangements. It is found in abundance in the atmosphere and among many living organisms. Monosaccharides - Drawing Fischer Projections. Reaction Mechanism. Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids. Each atom can thus complete its octet by sharing three electrons. Double Elimination. Isoelectric Point. E2 Mechanism. Amines 1h 43m. They can be useful, yet dangerous.

Completely I share your opinion. It is excellent idea. I support you.
It is the truth.
It is delightful