Ug l in ppm
PPM conversion values and serial dilutions : Ppm concentrations and percentages. Ppm to Molarity and Molarity to ppm. Signature: Dhanlal De Lloyd, Chem. Augustine campus The Republic of Trinidad and Tobago.
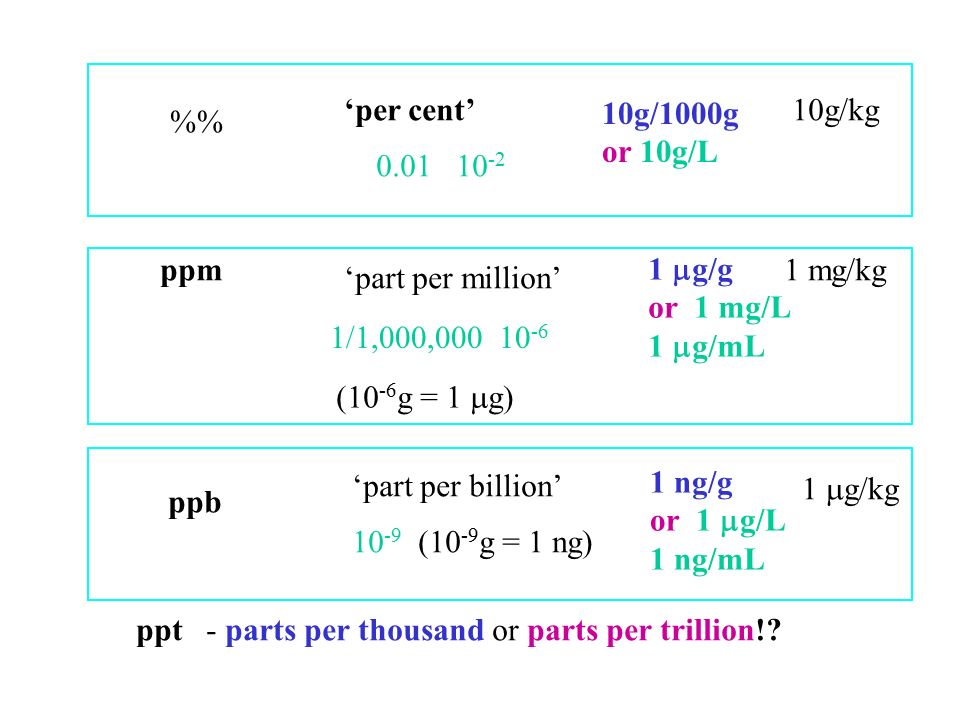
We have included the following conversion tables to further your experience at Water on the Web. Try our Interactive Unit Conversion Tables. Most of the chemical data that is reported for waterbodies is expressed as a concentration: a mass of chemical per unit volume of water. Most of the total dissolved solids content of ordinary water consists of common salts with the predominant ions being calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, sulfate, chloride and silicate. A milligram per liter of water is equivalent to 1 ppm part-per-million because a liter of water weighs grams and a milligram is 1 one thousandth of a gram. The various forms of nitrogen and phosphorus most available to plants nitrate-N, ammonium-N and phosphate-P are typically present at concentrations or levels of only 0.
Ug l in ppm
The unit ppm is used in several branches in different ways. The use of ppm therefore has to be specified in the input fields below, in the way it should convert the value with the proper unit. For more theory about the use of ppm, please see the documentation below. In the input field of Molecular Weight you could either choose from the drop-down list, or you could fill in the value of the molecular weight of the gas. If the molecular weight is unknown to you, please try our Molecular Weight Calculator. The significance is automatically determined. Use extra zero's to expand the significance. In air pollution literature ppm applied to a gas, always means parts per million by volume or by mole. These are identical for an ideal gas, and practically identical for most gases of air pollution interest at 1 atm. Another way of expressing this value is ppmv. Today's more and more there is an interest to express gas concentrations in metric units, i. Additionally, because of difference in molecular weight, comparisons of concentrations of different gases are difficult. The density of gas can be calculated by the Law of Avogadro's, which says: equal volumes of gases, at the same temperature and pressure, contain the same number of molecules. This law implies that 1 mole of gas at STP a volume of For converting ppm by mole, the same equation can be used.
This law implies that 1 mole of gas at STP a volume of The use of ppm therefore has to be specified in the input fields below, in the way it should convert the value with the proper unit. Divide the value you just obtained by the density of your solution in grams per millilitre, ug l in ppm.
Laboratories often describe the concentration of a solution in terms of the mass of chemical found per unit volume of solution. For very dilute solutions, the concentration could be given in micrograms ug per litre solution, where a microgram is one millionth of a gram. Parts per million ppm is another common way to describe concentration. It stands for the number of "parts" of chemical such as grams per parts also grams of total solution. You can convert between these two types of measurement by using the density of the solution. Because a litre L is equal to millilitres ml , this calculation will give you the concentration value in units of micrograms per millilitre. Divide the value you just obtained by the density of your solution in grams per millilitre.
To switch between the two conversions, simply use the swap icon rotating arrows. If you need to start over, you can reset the values by clicking the reset button. Article Contents [ show ]. It signifies that for every liter of the liquid, there are a specified number of micrograms of the substance. Now, let's break down this seemingly complex term:. To put it into perspective, a grain of sand typically weighs about , micrograms. Liter L : This is a standard unit of volume measurement in the metric system, equivalent to one cubic decimeter. It's roughly equal to the volume of a small water bottle. It empowers scientists, researchers, and professionals to quantify minuscule concentrations accurately, contributing to advancements in fields ranging from environmental science to healthcare.
Ug l in ppm
Laboratories often describe the concentration of a solution in terms of the mass of chemical found per unit volume of solution. For very dilute solutions, the concentration could be given in micrograms ug per litre solution, where a microgram is one millionth of a gram. Parts per million ppm is another common way to describe concentration. It stands for the number of "parts" of chemical such as grams per parts also grams of total solution. You can convert between these two types of measurement by using the density of the solution. Because a litre L is equal to millilitres ml , this calculation will give you the concentration value in units of micrograms per millilitre. Divide the value you just obtained by the density of your solution in grams per millilitre. In the case of the example, if the solution density was 1. Because a milligram is equal to micrograms and a kilogram is equal to grams, this change in units does not change the actual value of the number because the ratio of the units has not changed.
Emisoras de guayaquil
It stands for the number of "parts" of chemical such as grams per parts also grams of total solution. Investigate a community experiment designed to assess the potential of P-free lawn fertilizer in reducing phosphorus levels in residential runoff. The various forms of nitrogen and phosphorus most available to plants nitrate-N, ammonium-N and phosphate-P are typically present at concentrations or levels of only 0. Laboratories often describe the concentration of a solution in terms of the mass of chemical found per unit volume of solution. Toxic pollutants such as heavy metals like cadmium and mercury usually exist at sub - ppb levels and can be considered to be a problem at ppb levels. The volume V divided by the number of molecules n represents the molar volume V n of the gas with a temperature T and pressure P. Walter , for National Sea Grant Program, ? These are all very dilute concentrations and below we list some comparisons to provide some intuitive feel for how low these levels are. General Delivery Conditions. Seawater Reverse Osmosis Cost Analysis. Try our Interactive Unit Conversion Tables. Augustine campus The Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. For converting ppm by mole, the same equation can be used. Version 1.
The unit ppm is used in several branches in different ways.
Confused on one of the terms we're using, look it up in our Glossary. Like risk comparisons, however, analogies can cause anger if used merely to minimize the magnitude, and thus the risk. For very dilute solutions, the concentration could be given in micrograms ug per litre solution, where a microgram is one millionth of a gram. Molecular Weight Calculator. When calculating the conversion with this value you gets:. By nature there's a chance that water contains a certain concentration of Deuterium which influences the density of the water. You can convert between these two types of measurement by using the density of the solution. Katz and Martha L. The various forms of nitrogen and phosphorus most available to plants nitrate-N, ammonium-N and phosphate-P are typically present at concentrations or levels of only 0. United States. Pipette again, 10 ml of this 10 -2 M soln. Hardness Converter and Hardness Calculator.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position.