Two way anova in excel 2010
Lean Six Sigma Microsoft Excel. ANOVA covers a range of common analyses. When the levels of a factor are selected at random from a wide number of possibilities, you might use a random-effects model or a mixed-effects model. And luckily, Microsoft Excel makes it easy to perform these analyses.
We use the model when we have one measurement variable and two nominal variables, also known as factors or main effects. To employ this analysis, we need to have measurements for all possible combinations of the nominal values. The method estimates how the mean of quantitative variable changes in connection to the different levels positions of two categorical values. In other words, this form of ANOVA helps analyze how to independent variables combinedly influence a dependent variable from a statistical point of view. We can also employ the method to evaluate whether the two independent factors have a significant interaction effect. To run the Two-Way ANOVA model, we need to collect data on the quantitative dependent variable at different combinations levels of two independent categorical variables.
Two way anova in excel 2010
The data set is divided into horizontal groups that are each affected by a different level of one categorical factor. The same data set is also simultaneously divided into vertical groups that are each affected by a different level of another categorical factor. An example of a data set that is arranged for two-factor ANOVA with replication analysis is as follows:. The test for main effects of each of the two factors is very similar to main effects test of the one factor in single-factor ANOVA. The main effects test for each of the two factors determines whether there is a significant difference between the means of the groups the levels within that factor. The interaction test determines whether data values across the levels of one factor vary significantly at different levels of the other factor. This test determines whether the levels of one factor have different effects on the data values across the levels of the other factor. It determines whether there is interaction between Factor 1 and Factor 2, that is, between rows and columns. Ultimately this test determines whether the differences between data observations in columns vary from row to row and the differences between data observations vary from column to column. The two factors and their levels are categorical. The dependent variable is a continuous variable. Each factor has at least two or more levels.
Those rows have 15 data points. Dependent Variables The two factors and their levels are categorical. Factor 1 and 2 Interaction Effects F Test this F Test to determining whether any level of Factor 1 interacts with Factor 2 to create significantly different mean values in treatment cells across the Factor 2 levels.
Effect size is a way of describing how effectively the method of data grouping allows those groups to be differentiated. A simple example of a grouping method that would create easily differentiated groups versus one that does not is the following. Imagine a large random sample of height measurements of adults of the same age from a single country. If those heights were grouped according to gender, the groups would be easy to differentiate because the mean male height would be significantly different than the mean female height. If those heights were instead grouped according to the region where each person lived, the groups would be much harder to differentiate because there would not be significant difference between the means and variances of heights from different regions. Because the various measures of effect size indicate how effectively the grouping method makes the groups easy to differentiate from each other, the magnitude of effect size tells how large of a sample must be taken to achieve statistical significance.
The fact that Microsoft Excel can only handle balancing designs in which each sample does have an equal amount of observations is among its most notable restrictions. From a technical standpoint, doing a Two-Way ANOVA with an asymmetrical structure is much more complicated and challenging, and you will require some statistical package to do this. As we are aware, ANOVA is used to determine the mean difference between groups that are larger than two. ANOVA is a statistical analysis technique that divides methodical components from different variables to account for the apparent collective variation within a data set. Although there are many different types of ANOVA , the main goal of this family of studies is to ascertain if variables are associated with an outcome variable. A two-way ANOVA is performed as a statistical test to ascertain how two or more explanatory regression models would affect a continuous result variable. Whenever there is one measurement parameter and two independent parameters referred to as determinants or primary effects we employ the approach. We require observations for each conceivable variation of the theoretical amounts in order to use this methodology. But by default Excel disables this ToolPak from the ribbon. To enable this feature we need to follow the following steps.
Two way anova in excel 2010
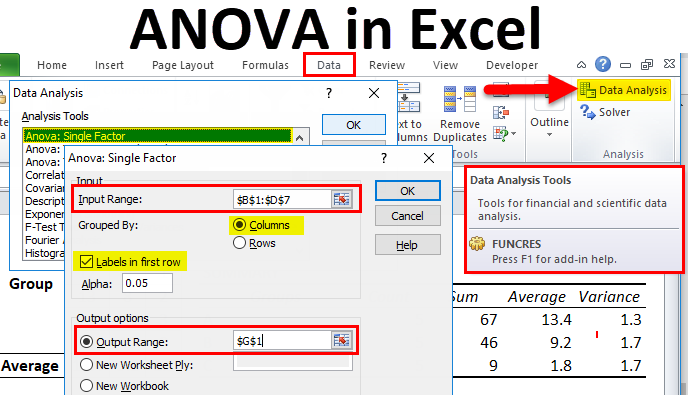
A botanist wants to know whether or not plant growth is influenced by sunlight exposure and watering frequency. She plants 40 seeds and lets them grow for two months under different conditions for sunlight exposure and watering frequency. After two months, she records the height of each plant. The results are shown below:. In the table above, we see that there were five plants grown under each combination of conditions. For example, there were five plants grown with daily watering and no sunlight and their heights after two months were 4. On the Data tab, click Data Analysis :.
Firm durable yellow fabric crossword clue
One of the factors has its levels distributed in columns. For example, one of the groups might be the first tape supplier on the first box type. This result indicates at least 95 percent certainty that there is interaction between Factor 1 and Factor 2. Fourth and finally, outline each treatment cell as follows. To perform a two-factor analysis of variance in Excel, first, we need to format our data properly. The data arrangement will matter when you want to use some of the other offerings in the Data Analysis Toolpak or a software package for data analysis, like Minitab Statistical Software. A small effect is one that not easily observable. This means that all data groups in one F Test must have similar variances and be normally distributed. The example shown in this section has one factor replicated four times and therefore has four data observations in each treatment cell. This Alternative Hypothesis for an F Test only states whether at least one sample group in that F Test is likely to have come from a different population.
.
This test will be performed on the data at the end of this section. This means that all data groups in one F Test must have similar variances and be normally distributed. ANOVA gives us mathematical sets of rules, that hold certain given assumptions, to decide when we can have confidence that the real average of one group is different from the real average of one or more other groups. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. Each group contains four men and four women. I like this blog, helped me a lot with excel queries. In this data, you can see that rows 2 to 15 have the measurements for the first box type. The same data set is also simultaneously divided into vertical groups that are each affected by a different level of another categorical factor. Note that the variances of the groups within each F Test need to similar, not the same as is often quoted in statistics texts. In my spare time, I am into skiing, hiking and running. First, select the input range. These are widely-used hypothesis tests that indirectly determine whether group variances are different are significantly different. Facebook Twitter Linkedin Youtube Medium. The Purpose of Budget vs. This Alternative Hypothesis for an F Test only states whether at least one sample group in that F Test is likely to have come from a different population.

I suggest you to visit a site on which there are many articles on this question.
All above told the truth. We can communicate on this theme.