The si unit of current is
The electric current is one of the most important and fundamental elements in our day-to-day life. The current flowing in a circuit can be used for various purposes from generating heat to causing circuits to switch, or storing information in an integrated circuit. We have come across a lot about electric currents in our classrooms as well as at home, the si unit of current is.
Electric Current: A stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, travelling through an electrical conductor or a vacuum is known as an electric current. The net rate of electric charge flowing through a surface or into a control volume is how it is calculated. It is determined by assuming that the elementary charge, e, has a fixed numerical value of 1. Electric current is a measure of the flow of electric charge through a conductor. One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of electric charge per second. In other words, if a current of 1 ampere flows through a wire, it means that 1 coulomb of electric charge passes through that wire every second.
The si unit of current is
An electric current can be defined as the flow present in an electric circuit. It consists of particles that are charged. These particles include electrons, protons and other charged atomic particles or smaller particles. This flow of the charged particles can only take place through materials that are capable of allowing that charge to flow through them. These materials are known as conductors. The S. The other S. On the other hand, the C. The unit of electric current is Ampere which is also denoted as coulomb per second. Ampere is defined as the flow of charged particles through the surface of a material at the rate of one coulomb at one second. Whereas, it also has a C.
Electrical capacitance. Cambridge University Press. This starts to implicitly verify the value for the magnetic constant.
One ampere is equal to 1 coulomb C moving past a point per second. As of the redefinition of the SI base units , the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge e to be exactly 1. The earlier CGS system has two units of current, one structured similarly to the SI's and the other using Coulomb's law as a fundamental relationship, with the CGS unit of charge defined by measuring the force between two charged metal plates. The CGS unit of current is then defined as one unit of charge per second. The ampere was originally defined as one tenth of the unit of electric current in the centimetre—gram—second system of units. That unit, now known as the abampere , was defined as the amount of current that generates a force of two dynes per centimetre of length between two wires one centimetre apart. The "international ampere" was an early realization of the ampere, defined as the current that would deposit 0.
Electric current can be defined as the measure of flow of sub-atomic charge carrying particles in this case electrons at any point of a conductor wire per unit time. In electricity, the term current is used to express flow, similar to other currents in nature. As an example, consider water current. Refer below image of water flowing inside a pipe. Concept of electrical current is similar to water current that is flowing through a pipe. Examples of sub-atomic particles having charge are electrons negative charge and protons positive charge. Neutrons are neutral, without charge.
The si unit of current is
Return to Units home page. Units Topics:. Units Bibliography. Become familiar with the seven defining constants of the SI. Definitions of the SI base units. Unit of length. The meter, symbol m, is the SI unit of length. Unit of mass. The kilogram, symbol kg, is the SI unit of mass. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Planck constant h to be 6.
Squishmallow pictures
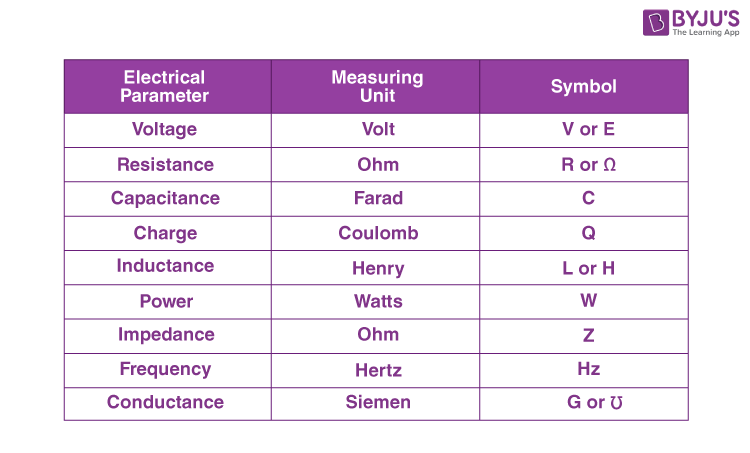
SI base unit of electric current. Voltage is calculated using Volt and is represented as V or E. Wang and B. Hidden categories: Webarchive template wayback links Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Use dmy dates from January Articles with GND identifiers. The redefinition of the SI base units defined the ampere by taking the fixed numerical value of the elementary charge e to be 1. Some Standard Electrical Units of Measure. Unit of Current The unit of electric current is Ampere which is also denoted as coulomb per second. Volt is the name of the voltage-derived unit in the International System of Units. These SI derived units can either be given special names e. A Watt is the amount of energy measured in Joules that a running electrical equipment, such as a light, consumes each second. Demonstration model of a moving iron ammeter.
Official websites use.
Demonstration model of a moving iron ammeter. Just download the Testbook App from this link and start your journey of preparation. Archived from the original on 21 June Like other SI units, the ampere can be modified by adding a prefix that multiplies it by a power of One ampere of electric current can be calculated by the following formula which is mentioned as follows below:. More Articles for Physics. Contents move to sidebar hide. Retrieved 21 November How to Measure Units of Electric Currents? If it is linked in parallel, it becomes a short circuit path granting all the current to flow through it, which may be steered to the burning of the meter due to the elevated value of current. These particles include electrons, protons and other charged atomic particles or smaller particles. Some Standard Electrical Units of Measure. The current flow from the positive to the negative terminal in an electric circuit.

In my opinion you commit an error. I can defend the position.
I am final, I am sorry, there is an offer to go on other way.