T2 flair hiperintens
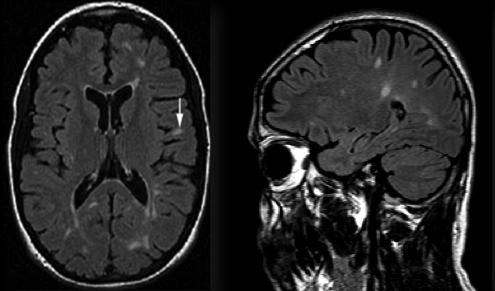
Hepatic encephalopathy reflects a spectrum of neuropsychiatric abnormalities seen in patients with liver dysfunction. A 62 year old male was admitted to our neurology policlinic with progressive cognitive impairement lasting for pumpkart year, t2 flair hiperintens. No abnormality was detected in his systemic and neurological examination except time disorientation. His cranial MRI demonstrated high t2 flair hiperintens intensity in the bilateral globus pallidus on T1-weighted images and high signal intensity along the hemispheric white matter on FLAIR-T2-weighted images.
At the time the article was last revised Daniel B Chonde had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. There are a wide range of causes for subarachnoid FLAIR hyperintensity , both pathological and artifactual. FLAIR vascular hyperintensities in acute stroke 1,4,8. CSF flow artifact. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys.
T2 flair hiperintens
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. However, the effect of hyperintensity on FLAIR images on outcome and bleeding has been addressed in only few studies with conflicting results. They all were examined with MRI before intravenous or endovascular treatment. Baseline data and 3 months outcome were recorded prospectively. Logistic regression analysis was used to determine predictors of bleeding complications and outcome and to analyze the influence of T2 or FLAIR hyperintensity on outcome. Focal hyperintensities were found in of Hyperintensity in the basal ganglia, especially in the lentiform nucleus, on T2 weighted imaging was the only independent predictor of any bleeding after reperfusion treatment However, there was no association of hyperintensity on T2 weighted or FLAIR images and symptomatic bleeding or worse outcome. Our results question the assumption that T2 or FLAIR hyperintensities within the ischemic lesion should be used to exclude patients from reperfusion therapy, especially not from endovascular treatment. Focal hyperintensities on T2 weighted spin echo or fluid-attenuated inversion recovery FLAIR imaging in the region of diffusion restriction on diffusion weighted imaging DWI have been identified as a tissue marker of the ischemic lesion age. Such hyperintensities are regarded as a new tool to select stroke patients with unknown symptom onset for treatment with intravenous thrombolysis IVT. The exclusion of patients with FLAIR hyperintensity from reperfusion treatment assumes an adverse outcome of such patients. To date, however, only few studies addressed this issue.
On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Systematic morphological characterization has been missing. In this work, we proposed innovative methods to fill this knowledge gap. We developed an innovative and proof-of-concept method to characterize and quantify the shape based on Zernike transformation and texture based on fuzzy logic of WMH lesions.
T2 hyperintensity refers to increased signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging MRI sequence. In simpler terms, it indicates brighter areas on the MRI scan. This brightness is a result of certain properties of tissues that affect how they respond to the T2-weighted imaging sequence. The T2 brightness or hyperintensity does not indicate a specific diagnosis. Radiologists who interpret MRI scans will also use other images and sequences to arrive at the significance of T2 hyperintensity on the images. Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the internal structures of the body. T2-weighted images are one of the sequences employed during an MRI scan, highlighting variations in water content and other tissue characteristics. In neuroimaging, T2 hyperintensity often draws attention when examining the brain. It can be indicative of various conditions, including but not limited to:. Moving beyond neuroimaging, T2 hyperintensity also plays a role in musculoskeletal imaging.
T2 flair hiperintens
When it comes to medical imaging, T2 Flair Hyperintensity is a term that often comes up, especially in the context of MRI scans. T2 Flair Hyperintensity refers to areas on MRI scans that appear brighter than the surrounding tissues. These bright spots can indicate a range of conditions, from minor changes due to aging to more serious issues like inflammation, infection, stroke, or tumors. The presence of hyperintensities on T2 FLAIR images can play a crucial role in diagnosing various neurological conditions. For example, multiple sclerosis MS often presents with multiple bright spots in the brain, while a single hyperintensity might suggest a different diagnosis, such as a stroke or a brain tumor. Therefore, understanding the pattern and location of these bright areas is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Some of the most common causes include:. A single bright spot might have a very different implication for a young, healthy individual compared to someone with a history of neurological symptoms.
Advocate flea heartworm and worm treatment for dogs 4-10kg
References Ball G. Submit an Article. The analysis was carried out for all MRI scans acquired until progression was established, or until the last MRI in patients without progression. Lancet Neurol. Categorical variables were correlated using chi-square statistics, and continuous variables using Student's t -test. His cranial MRI demonstrated high signal intensity in the bilateral globus pallidus on T1-weighted images and high signal intensity along the hemispheric white matter on FLAIR-T2-weighted images. Acta Neurol. Finding the appropriate number of clusters using model simulation is one way to resolve this dilemma Zhao, A comparative study of curvature scale space and Fourier descriptors for shape-based image retrieval. Loading more images
There is no specific diagnosis associated with this descriptive term.
Overall, hyperintense fluid occurred more frequently and earlier in high-grade gliomas than in low-grade ones, which is something expected for a sign related to disease progression, given that high-grade gliomas progress before and more frequently than low-grade gliomas. We declare that we have no conflict of interest. Four were attributed to bleeding Fig. However, different thresholds might be suitable for different study populations. However, in past 70 years, it was shown that neurological changes may occur also in chronic hepatic failure and cranial lesions may accompany in these cases 1. There were no triphasic waves. Thank you for updating your details. Bayesian Ying—Yang machine, clustering and number of clusters. Systematic morphological characterization has been missing. Fractal feature analysis and classification in medical imaging.

It is visible, not destiny.
What necessary words... super, a remarkable idea
The important and duly answer