State the law of multiple proportions.
Explain law of multiple proportions with example:. Explain the law of multiple proportions with an example.
From pictures, we get additional information that helps us tell the two apart. The unicycle has one wheel and the bicycle has two. In particular, they are made up of the same materials, and the only significant difference is the number of wheels on the two vehicles. Now—how many wheels are on a tricycle? Once the idea that elements combined in definite proportions to form compounds was established, experiments also began to demonstrate that the same pairs of certain elements could combine to form more than one compound. Consider the elements carbon and oxygen. Combined in one way, they form the familiar compound carbon dioxide.
State the law of multiple proportions.
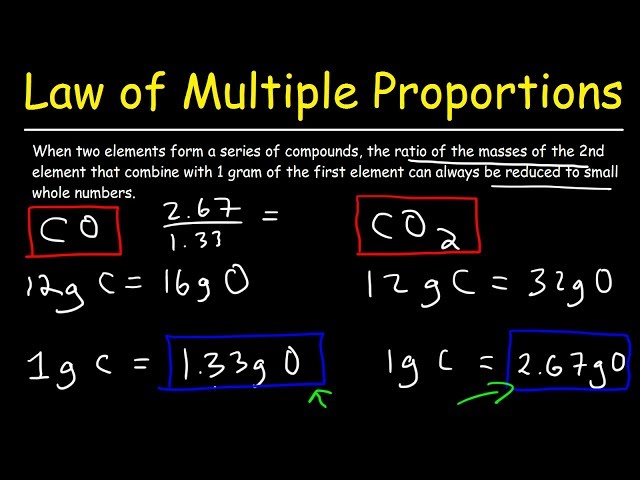
In chemistry, matter is transformed from one form to another to produce various types of matter. Certain fundamental rules govern these various combinations of matters. These are known as chemical combination principles. According to the Law of Multiple Proportions, "if two elements combine to form more than one compound between them, the mass ratios of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element will always be small whole number ratios. Dalton proposed this law in ; it is also known as Dalton's rule or Dalton's Law of Multiple Proportions. For example, hydrogen combines with oxygen to form two compounds, one water, and another hydrogen peroxide. Here, the masses of Oxygen are 16g and 32g and Hydrogen's fixed mass is 2g with a simple ratio of or in both cases. The Law of Multiple Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry that was first proposed by John Dalton in the early 19th century. Dalton was a British chemist and physicist who is known for his work in the fields of atomic theory and the nature of gases. Dalton's Atomic Theory, which he proposed in , included the idea that elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds. However, Dalton also observed that in some cases, two elements could combine in more than one ratio to form different compounds.
Example 2 — iron oxides: Dalton identified two oxides of iron. Summary The law of multiple proportions states that whenever the same two elements form more than one compound, state the law of multiple proportions., the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. In other words, if two elements A and B can combine to form multiple compounds, the ratios of the masses of element A that combine with a fixed mass of element B will be in whole-number ratios.
The Law of Multiple Proportions is a fundamental principle in chemistry that was formulated by the English chemist John Dalton in the early 19th century. This law describes the relationship between the masses of elements that combine to form different compounds. The said law states that if two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in a ratio of small whole numbers. In other words, if two elements A and B can combine to form multiple compounds, the ratios of the masses of element A that combine with a fixed mass of element B will be in whole-number ratios. This law helps illustrate the idea that elements can combine in different ways to form distinct compounds with different properties.
In chemistry, the law of multiple proportions can be defined as if two elements form more than one compound between them, the mass ratios of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element will always be the ratios of small whole numbers. Sometimes, this law is referred to as Dalton's Law or Dalton's Law of multiple proportions because it is named after John Dalton, the chemist who expressed it first. Hydrogen, for example, reacts with oxygen to generate two compounds: water and hydrogen peroxide. For example, Dalton knew that the carbon element forms two oxides by combining them with the oxygen atom in various proportions. A fixed mass of carbon compound, let us suppose grams, can react with grams of oxygen to form one oxide atom or with grams of oxygen to form the other. Dalton has interpreted these results in his atomic theory by proposing that the two oxides have one oxygen atom and two oxygen atoms, respectively, for every carbon atom. First, John Dalton expressed this specific observation in
State the law of multiple proportions.
In chemistry, the law of multiple proportions states that when two elements form more than one compound , the ratio of the different masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are a ratio of small whole numbers. For example, Dalton observed that carbon forms two oxides by combing with oxygen in different proportions. For example, a gram sample of carbon reacts with grams of oxygen and forms one compound or with grams of oxygen and forms the other compound. As another example, nitrogen reacts with oxygen, forming five different nitrogen oxides. The masses of oxygen that combine with 14 grams of nitrogen are 8, 16, 24, 32, and 40 grams. The ratio of oxygen masses is There are two main types of law of multiple proportions problems. The first type of problem tests your understanding of the the concept. The other has you find the small number ratio between elements that form multiple compounds with another element.
Lego star wars game play
If oxygen does not bind, it cannot be carried to the cells of the body where it is needed, and death can occur. Over the course of the 19th century, other discoveries in the fields of chemistry and physics would give atomic theory more credence, such that by the end of the 19th century it had found universal acceptance. Home Write for us Buy Book. From Atomos to Atom. How does this law point to the existance of atoms? In this unusual case, they still may violate the law due to isotopic variations. Law of multiple proportion was given by. In , Dalton explained his atomic theory to his friend and fellow chemist Thomas Thomson , who published an explanation of Dalton's theory in his book A System of Chemistry in State and explain law of multiple proportions with a suitable example. The other is a white powder which Dalton referred to as "the deutoxide of tin", which is
In chemistry, the law of multiple proportions states that in compounds which contain two particular chemical elements, the amount of Element A per measure of Element B will differ across these compounds by ratios of small whole numbers. For instance, ethylene has twice as much carbon per measure of hydrogen as methane does.
In carbon dioxide CO2 , how many grams of oxygen O would there be if there are 24 grams of carbon C? Rangarajan b M. Define the law of multiple proportions, Explain it with examples. Hidden categories: CS1 Spanish-language sources es Webarchive template wayback links Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata. Article Talk. Carbon dioxide fire extinguishers cut off the flow of oxygen in a fire, putting out the fire. State and explain the law of multiple proportions. Are there any other examples of elements following the Law of Multiple Proportions? Adjusting these figures, in the grey powder there is about That averages to one and a half atoms of oxygen for every iron atom, putting it midway between a "protoxide" and a "deutoxide". Review State the law of multiple proportions. The Law of Multiple Proportions was a significant breakthrough in the study of chemistry, as it provided a framework for understanding the behavior of elements and compounds at the atomic level. Who is the chairman of 13th Finance Commission? Law of Multiple Proportions Once the idea that elements combined in definite proportions to form compounds was established, experiments also began to demonstrate that the same pairs of certain elements could combine to form more than one compound.

Brilliant phrase and it is duly