Sigma bond and pi bond examples
When you hear the words sigma and pi bond, you might think of Greek life in college.
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two atomic orbitals on different atoms, each orbital containing a single electron. In looking at simple inorganic molecules such as molecular hydrogen H 2 or hydrogen fluoride HF , our present understanding of s and p atomic orbitals will suffice. In order to explain the bonding in organic molecules, however, we will need to introduce the concept of hybrid orbitals see section 2. The simplest case to consider is the hydrogen molecule, H 2. When we say that the two hydrogen nuclei share their electrons to form a covalent bond, what we mean in valence bond theory terms is that the two spherical 1 s orbitals the grey spheres in the figure below overlap, and contain two electrons with opposite spin. How far apart are the two nuclei?
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in. Already have an account? Log in here. Sigma and pi bonds are chemical covalent bonds. Sigma and pi bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are formed by end-to-end overlapping and Pi bonds are when the lobe of one atomic orbital overlaps another.
Discover the latest study tips, tech and tools to help you study smarter. The bonding attracting MO is full, and the antibonding repelling MO is empty. Privacy Policy Terms and Conditions.
Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But then we start putting in double bonds and triple bonds. So we need a more complex picture that works for all these electrons. The hybridization model helps explain molecules with double or triple bonds see figure below. The entire molecule is planar.
A description of the double bond is the sigma-pi model shown in Figure 1. In this case only two of the p orbitals on each C atom are involved in the formation of hybrids. Two of these hybrids from each C atom overlap with H 1 s orbitals, while the third overlaps with an sp 2 hybrid on the other C atom. This orbital has no nodes: electron density exists continuously from around one atom to the other atom. To view the sigma bonding orbital, select N6. This is actually sigma bonding between C-C and some sigma-like bonding around the Hs as well. Focus on the yellow portion. The sp2 hybrid orbitals on each carbon atom involve the 2 s and two of the 2 p orbitals, leaving a single 2 p orbital on each carbon atom. A second carbon-carbon bond is formed by the overlap of these two remaining p orbitals.
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
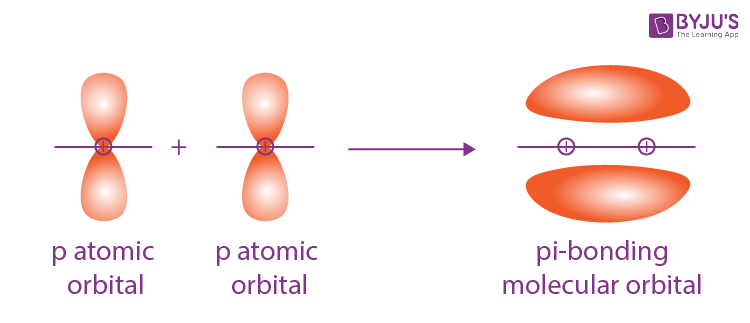
Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are a result of the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals whereas pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals. Various bond parameters such as bond length, bond angle, and bond enthalpy depend on the way the overlapping of atomic orbital takes place. This overlap occurs in two major ways, giving rise to two primary types of covalent bonds , i. This type of covalent bond is formed by head-on positive same phase overlap of atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis. Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds, owing to the direct overlapping of the participating orbitals. Generally, all single bonds are sigma bonds. They can be formed via the following combinations of atomic orbitals.
Taylors estate agents luton beds
Sign up Sign up to read all wikis and quizzes in math, science, and engineering topics. Note that sigma bond has been referred to as the strongest type of covalent bond because the extent of overlap is maximum in case of orbitals involved in the formation of the sigma bond. You can suggest the changes for now and it will be under the article's discussion tab. A triple bond is always made up of one sigma bond and two pi bonds. Metallic Solids. Electrochemical Series. Sign up Log in. Examples of sigma bonds with different types of overlap. Reactions of Halogens. Multiple bonds are also useful for deciphering spectra obtained via nuclear magnetic resonance NMR. Get Started! Reactions of Halides.
Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But then we start putting in double bonds and triple bonds.
Pi orbitals have two lobes above and below the bond axis. Last Updated : 07 Nov, Pi bonds usually form in addition to sigma bonds in double or triple bonds like in alkynes or alkynes and involve the overlap of unhybridized p orbitals. Electron Configuration. Previous Kinetic Theory of Matter. It's important to be able to draw Lewis structures accurately to count the number of bonds in a molecule. Bond order gives information about bond length and strength. As with ethene, these side-to-side overlaps are above and below the plane of the molecule. Share Share Share Call Us. Cite as: Sigma and Pi Bonds. In order to explain the bonding in organic molecules, however, we will need to introduce the concept of hybrid orbitals see section 2.

0 thoughts on “Sigma bond and pi bond examples”