Sap rfc connection
From enabling real-time data exchange to fortifying security, SAP RFC connections are the unsung champions of affordable synonym and glucokinase, facilitating efficient communication between systems, managing called function module runs, and ensuring proper function modules are available for users. Remote Function Call RFC is the standard SAP interface designed to facilitate efficient communication between SAP sap rfc connection, allowing different components of an SAP system to communicate and interact with each other, regardless of whether they are running on the same server or distributed across different servers. The RFC interface system enables the execution of functions or methods in remote systems and the exchange of data between these systems. RFC connection in SAP involves the use of intelligent sap rfc connection to facilitate connection, sap rfc connection, communication, and exchange of data in predefined formats between SAP business applications and other systems.
RFC calls a function to be executed in a remote system. There is now a whole series of different RFC variants, each of which has different properties and is used for a specific purpose. This type of RFC executes the function call based on synchronous communication , meaning that the systems involved must both be available at the time the call is made. Despite its name, aRFC is not really an asynchronous type of communication, as it does not meet the conditions for this. With sRFC, for example, the called system must be available during the call.
Sap rfc connection
This connection is used for all read accesses that do not affect sensitive data. This user has only the following authorizations:. If the authorization for user TMSADM are not sufficient for certain actions, this internal connection always triggers a logon screen in the target system where you must identify yourself with a user name and a password. You can also change the target client on this logon screen. This user must be authorized to make changes. This ensures that the user must log on in the target system with a user name and password as soon as a function is executed that causes a change in the target system viewable on the Alert Viewer. Since changes to the import queue and to imports are considered to be critical to security, an explicit logon is needed to perform these changes. If you have a large number of SAP systems to manage, this logon procedure can be time-consuming. This user has the following authorizations:. A connection for accesses that cause changes in the target system. Since you can only change transport proposals in the transport proposal inbox or TMS worklist , you must log on to them explicitly.
Table of Content:. Implementation of tRFC is recommended if you want to maintain the transactional sequence of the calls, sap rfc connection. After the RFCs are created or sometimes in the case of already existing RFCs we need to test, whether the connection is established successfully or not.
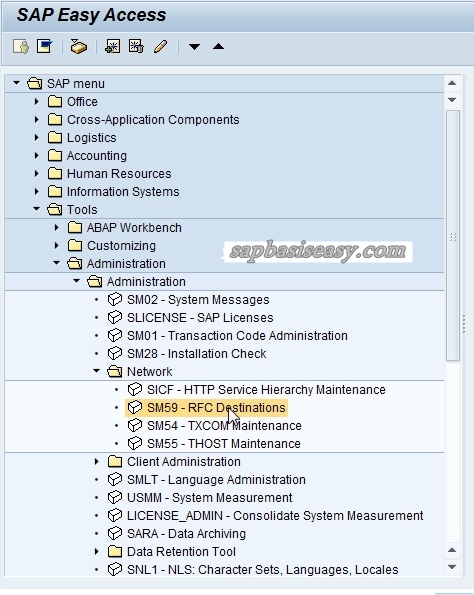
In the SM59 screen, you can navigate through already created RFCs connection with the help of option tree, which is a menu-based method to organize all the connections by categories. Note : By default, a connection is defined as aRFC. To define qRFC, use the special options tab. After the RFCs are created or sometimes in the case of already existing RFCs we need to test, whether the connection is established successfully or not. We have three options:. If both systems are not able to connect, it throws an error. On success, it displays the table with response times.
I also noticed on the SCN forums that there are often questions regarding the setup. After you have set up a trust connection from AA1 to BB1 for example, you can access BB1 through AA1 without having to login again, given your username exists on both sides and you have sufficient authorizations. In transaction SM59 you need to define a RFC connection towards the target system you want to enable as trusted in your source system. When it is done it would mean that when you are logged onto AA1 and your user has enough authorization in BB1, you can use the RFC connection and logon to BB1 without having to re-enter user and password. Now you can first test this RFC connection to see if it works, if you run into problems you need to fix them before continuing.
Sap rfc connection
RFC is a mechanism that allows business applications to communicate and exchange information in pre-defined formats with other systems. It is the process of calling a function module which is residing on a different machine from the caller program. RFC helps to reduce the efforts of programmers, by letting them avoid the re-development of modules and methods at remote systems. It is capable enough to:. Requires both the systems client and server to be available at the time of communication or data transfer. It is the most common type and is required when the result is required immediately after the execution of sRFC. The Data is consistent and reliable for communication.
What happened to vagrant holiday
You can also change the target client on this logon screen. Previous Prev. The only thing that can be guaranteed is that all LUWs are transferred sooner or later. It is therefore impossible to guarantee that the transactions will be executed in the sequence dictated by the application. There is now a whole series of different RFC variants, each of which has different properties and is used for a specific purpose. On success, it displays the table with response times. Live Project Toggle child menu Expand. The calling program can receive results from the asynchronous RFC. SAP RFC connections come with robust security features, like authorization control, to ensure only authorized users can access and execute functions remotely, safeguarding sensitive data and preventing unauthorized actions. SAP RFC function modules allow business users to convert data from the called system to the representation needed in the remote system, call specific communication routes needed to initiate communication between systems, and handle any communication errors within the external or remote system. Asynchronous RFC is utilized when real-time communication is established with the remote system, where processing functions in the calling program cannot be interrupted until the results of the called function module are obtained.
You can use:. A server started by the application server or by an Gateway.
Next Continue. Get Started. This way, users can make informed business decisions, optimize processes, and ensure data consistency across the organization. To guarantee that multiple LUWs are processed in the order specified by the application, tRFC can be serialized using queues inbound and outbound queues. End of the caution. Asynchronous RFCs allow the user to carry on an interactive dialog with the remote system. We have a high-priority project Our team needs an expert boost Our team is a man down We're ready to team up with a new consulting firm Our project is behind schedule We need an unbiased audit Something Else. The main characteristics of aRFC are as follows: Function control returns to the calling program directly after the call. This user has only the following authorizations:. When the caller starts an aRFC, the called server must be available to accept the request. See All.

It is remarkable, very useful idea
So simply does not happen
Yes, really. It was and with me. Let's discuss this question.