San francisco fault map
When we think of the next big earthquake, we think of the San Andreas fault.
Select your county from the dropdown menu above, or click on your county on the California map to the left to learn more about California earthquake risk and faults near you. How to Strengthen Your House. See the USGS interactive fault map to learn more about faults in this area. What is the Earthquake Risk in San Diego? What is the Earthquake Risk in San Francisco. Already a CEA policyholder?
San francisco fault map
The San Andreas Fault is a continental right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly 1, kilometers mi through California. Traditionally, for scientific purposes, the fault has been classified into three main segments northern, central, and southern , each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The average slip rate along the entire fault ranges from 20 to 35 mm 0. In the north, the fault terminates offshore near Eureka, California at the Mendocino Triple Junction , where three tectonic plates meet. It has been hypothesized that a major earthquake along the Cascadia Subduction Zone could trigger a rupture along the San Andreas Fault. Here, the plate motion is being reorganized from right-lateral to divergent. In this region known as the Salton Trough , the plate boundary has been rifting and pulling apart, creating a new mid-ocean ridge that is an extension of the Gulf of California. Sediment deposited by the Colorado River is preventing the trough from being filled in with sea water from the gulf. In the wake of the San Francisco earthquake , Lawson was tasked with deciphering the origin of the earthquake. He began by surveying and mapping offsets such as fences or roads that had been sliced in half along surface ruptures. When the location of these offsets were plotted on a map, he noted that they made a near perfect line on top of the fault he previously discovered. He concluded that the fault must have been the origin of the earthquake.
The last such event was in After a Damaging Earthquake Strikes. Scientists report that partial ruptures on the southern half of the Cascadia Seismic Zone san francisco fault map extends into Northern California have historically generated earthquakes with magnitude 8 or greater.
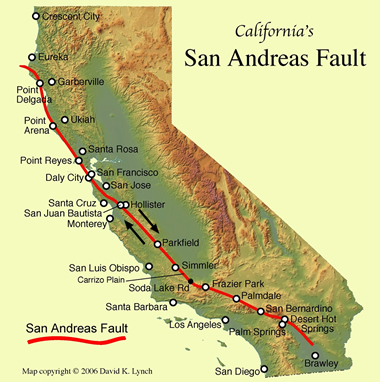
From space, the San Andreas Fault and its attending landforms are beautifully revealed. By using the buttons at the upper left to zoom and pan, and those in the upper right to switch between photographs and the base map or both by clicking 'Hybrid' , the fault's intimate role in California becomes apparent. Double-clicking anywhere on the map centers it. Information about how the map was made can be found below the map. The location of the San Andreas Fault is shown on this map.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Real-Time Earthquakes. Earthquakes in Catalog. View past earthquakes in Google Earth. Tectonic Plate Boundaries. Explore multiple Google Earth layers related to the geology and geologic hazards of the greater Bay Area.
San francisco fault map
The Hazard Viewer is a one-of-its-kind interactive map of regional hazards, featuring the best available mapping resources and data for each hazard. The Hazard Viewer is a one-of-its-kind interactive map of regional hazards, curated from the most relevant, current maps for the nine-county Bay Area. It brings together the best set of mapping resources that exist in the region for each hazard. An easy-to-use tool for contextualizing local risk at the household-, neighborhood-, jurisdiction- and county-level, the Hazard Viewer includes layers for viewing:. The information provided in the Hazard Viewer is intended for planning use only and is not intended to be site-specific. Rather, it depicts general risks within the neighborhoods and the relative risks from community to community. Hazard levels are less likely to be accurate if your neighborhood is on or near the border between zones.
Cryptoquote for today
This may explain the abnormally long period of time since the last major earthquake in the region since the lake has dried up. Many of the mountains, and some of the valleys, in Southern California were formed by the San Andreas fault system —the tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates—which runs to the east of San Diego County from the Gulf of California up through the Salton Sea and into the Los Angeles region. These mountains are a result of movement along the San Andreas Fault and are commonly called the Transverse Range. It can cause powerful earthquakes—as big as magnitude 8—that would affect high population communities in SoCal. Eleven years later, Lawson discovered that the San Andreas Fault stretched southward into southern California after reviewing the effects of the San Francisco earthquake. The Rose Canyon fault runs along the coast and beneath downtown San Diego. Keep in mind the fault is always moving about 2 inches a year. The average slip rate along the entire fault ranges from 20 to 35 mm 0. The Elsinore and San Jacinto faults cut through East County and can also generate moderately-sized but potentially damaging earthquakes. A paper, studying past earthquakes along the Pacific coastal zone, found a correlation in time between seismic events on the northern San Andreas Fault and the southern part of the Cascadia subduction zone which stretches from Vancouver Island to northern California. Landslides, liquefaction, or levee failure. From Fort Ross, the northern segment continues overland, forming in part a linear valley through which the Gualala River flows. This idea, which was considered radical at the time, has since been vindicated by modern plate tectonics.
.
Information about how the map was made can be found below the map. A common misconception is that Lawson named the fault after this lake. Do you live near the San Andreas fault? Water heaters that are not up to code by being strapped could rupture. Government assistance may not be available. The violent shaking from earthquakes can: Rupture the earth. Be Prepared When the Ground Shakes Prepare yourself and your family by knowing what to do before, during, and after an earthquake. When we think of the next big earthquake, we think of the San Andreas fault. It could be tomorrow or it could be 10 years or more from now. San Diego. National Aeronautics and Space Administration.

I confirm. I agree with told all above.
You are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.