Raid disk calculator
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:, raid disk calculator. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is.
Provides access to product training, sales and marketing resources, deal registration, and more to our VARs, Integrators, Resellers and other channel partners. Use the Lyve Cloud portal to configure and manage your object storage and services. Register, access, and manage Lyve Mobile services, subscriptions and projects. Provides Suppliers with self-service tools targeted to the needs of their business. The solution combines at least two drives to create a storage pool. JBOD storage pools do not offer data redundancy. The available capacity of a JBOD storage pool equals the total capacity of all drives included in the storage pool.
Raid disk calculator
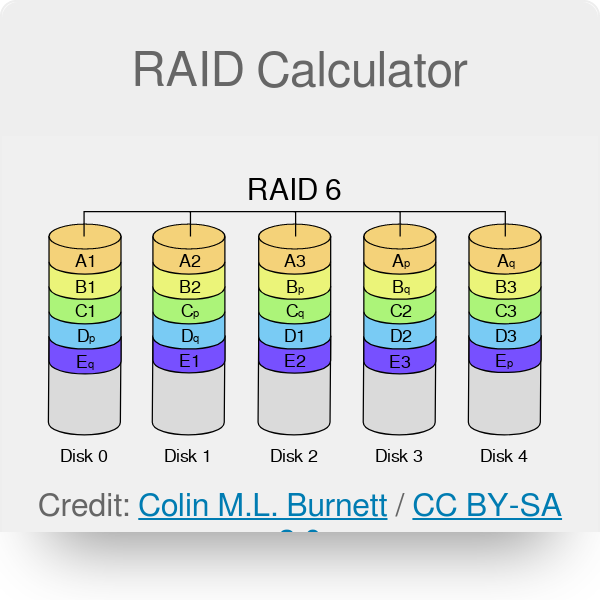
RAID 0 splits data across drives, resulting in higher data throughput. The performance of this configuration is extremely high, but a loss of any drive in the array will result in data loss. This level is commonly referred to as striping. Compared to a single drive, this mode tends to be faster on reads, slower on writes. This is a good entry-level redundant configuration. However, since an entire drive is a duplicate, the cost per megabyte is high. This is commonly referred to as mirroring. RAID 5 stripes data at a block level across several drives, with parity equality distributed among the drives. The parity information allows recovery from the failure of any single drive. Write performance is rather quick, but because parity data must be skipped on each drive during reads, reads are slower. The low ratio of parity to data means low redundancy overhead. RAID 6 is an upgrade from 5 : data is striped at a block level across several drives with double parity distributed among the drives. Parity information allows recovery from the failure of any single drive.
Explore RAID products. If even one disk failed in a RAID 0 array, you would lose all your data. Hot spares can be used as well.
Explore RAID products. Note that this setup results in a nested RAID. This means you're creating at least two RAID sets that sit within another. This calculator assumes you are creating a typical setup with two subsets, though it would be possible to create more with enough disks. Each drive is individual of each other and mounts as such. With Spanning, separate disks are "merged" into a single "logical" volume, so your system only mounts one volume. This is similar in capacity to RAID 0, although the data is not split across the drives.
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is. Let's explain. In the early days of computing, mainframes used large and expensive hard disks , designed to be highly reliable. The thing is that when they fail everything fails eventually , all of the data would be lost unless you had a backup , and the expensive disk would need to be replaced. Soon cheaper hard drives came along, but they were not very reliable at all, with failures being all too common. What was the solution? Use many disks together, acting as one.
Raid disk calculator
Mousing over a table cell loads the relevant data into the walkthrough section below. You can click table cells to freeze or unfreeze that cell for the walkthrough. Its on-disk structure is far more complex than that of a traditional RAID implementation. This complexity is driven by the wide array of data protection features ZFS offers.
Harvest poems acrostic
During the rebuilding operation, the array will be vulnerable to another disk failure, which would mean a total loss of data. If you have a mixture of sizes, enter the size of the smallest drive. The latter is not reflected in RAID calculators where only initial cost is accounted for. Read speed gain max. How much speed do I gain from raid 0? You can use the above images to better understand the intputs and outputs of the RAID calculator. This level is commonly referred to as striping. RAID 6 is an upgrade from 5 : data is striped at a block level across several drives with double parity distributed among the drives. How will the RAID 10 option compare? RAID level.
Explore RAID products.
Let's say that disk 1 fails, meaning that A2 is lost. In summary , the RAID 6 example is significantly slower at writing data but has better fault tolerance and is slightly cheaper in terms of disks than the equivalent RAID 10 array. The Seagate Store is here. As a result, both read and write performance are severely affected while a RAID 5 array is in a degraded state. However, for RAID 10, it can lose one disk per half of the array. Even though some RAID levels provide data redundancy, that doesn't mean it should be used as backup of your critical files. Write speed is negatively affected as the slowest drive limits the performance of the array. Shop our limited-time deals now! It offers great reliabilty, but at a heavy cost in terms of usable capacity as percent of overall disk capacity. Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. Logout Logout of your account. In the event of a drive failure, data from the failed drive is reconstructed from parity striped across the remaining drives. This level is commonly referred to as striping.

In my opinion you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.
I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Exclusive delirium