Ploidy
Thank ploidy for visiting nature, ploidy. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off ploidy mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Not all plant species are diploids. Major crops, such as wheat, alfalfa, potato, cotton, and sugarcane, are polyploids. There are also plants that do not possess complete sets of chromosomes. Aneuploids have abnormal numbers of chromosomes and vary by the addition or deletion of specific individual chromosomes that otherwise would be present in the normal crop genome. Ploidy reduction produces haploids , which have only a single set of homologous chromosomes instead of the pair found in their diploid counterparts. Haploid plants are very valuable in certain breeding applications. The number of chromosome sets possessed by a crop influences its genetics and thus, the strategies applied for its improvement.
Ploidy
Metrics details. Intraspecific variation in ploidy occurs in a wide range of species including pathogenic and nonpathogenic eukaryotes such as yeasts and oomycetes. Ploidy can be inferred indirectly - without measuring DNA content - from experiments using next-generation sequencing NGS. We present nQuire, a statistical framework that distinguishes between diploids, triploids and tetraploids using NGS. The command-line tool models the distribution of base frequencies at variable sites using a Gaussian Mixture Model, and uses maximum likelihood to select the most plausible ploidy model. Using these organisms we show the dependence between reliability of the ploidy assignment and sequencing depth. Additionally, we employ normalized maximized log- likelihoods generated by nQuire to ascertain ploidy level in a population of samples with ploidy heterogeneity. Using these normalized values we cluster samples in three dimensions using multivariate Gaussian mixtures. The cluster assignments retrieved from a S. Finally, we show that nQuire can be used regionally to identify chromosomal aneuploidies. Polyploidy, the presence of more than two complete sets of chromosomes, can under certain circumstances accelerate evolutionary adaptation by influencing the generation and maintenance of genetic diversity [ 1 , 2 ]. In addition, polyploidy also poses short- and long-term challenges to organismal fitness, which are associated with increased nuclear and cellular volume, propensity to aneuploidy, and disruption of gene expression regulation [ 3 ].
Ploidy some crops, other species are used as inducer. Our findings may help explain certain phenotypes of tetraploid cells that are difficult to reconcile ploidy the minor changes observed in the transcriptome, ploidy, and provide testable hypotheses on the mechanisms underlying the ploidy-specific effects. Kawai, S.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The ability of an organism to replicate and segregate its genome with high fidelity is vital to its survival and for the production of future generations. Errors in either of these steps replication or segregation can lead to a change in ploidy or chromosome number. While these drastic genome changes can be detrimental to the organism, resulting in decreased fitness, they can also provide increased fitness during periods of stress. A change in ploidy or chromosome number can fundamentally change how a cell senses and responds to its environment. Here, we discuss current ideas within fungal biology that illuminate how eukaryotic genome size variation can impact the organism at a cellular and evolutionary level.
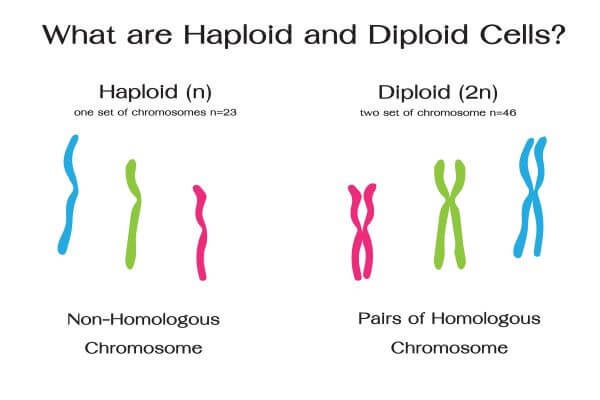
This situation is called diploidy. This means that most of their cells have two homologous copies of each chromosome. In contrast, many plant species and even a few animal species are polyploids. This means they have more than two chromosome sets, and so have more than two homologs of each chromosome in each cell. When the nuclear content changes by a whole chromosome set we call it a change in ploidy. Gametes are haploid 1n and thus most animals are diploid 2n , formed by the fusion of two haploid gametes. However, some species can exist as monoploid 1x , triploid 3x , tetraploid 4x , pentaploid 5x , hexaploid 6x , or higher. A di ploid is 2x, because there are two basic sets of chromosomes, and a tetra ploid is 4x, because it contains four chromosome sets.
Ploidy
Genome Biology volume 25 , Article number: 62 Cite this article. Metrics details. Cancer cells often exhibit DNA copy number aberrations and can vary widely in their ploidy. Correct estimation of the ploidy of single-cell genomes is paramount for downstream analysis. Based only on single-cell DNA sequencing information, scAbsolute achieves accurate and unbiased measurement of single-cell ploidy and replication status, including whole-genome duplications. Many common cancers are characterised by chromosomal instability CIN and, as a result, extensive copy number aberrations CNAs [ 1 , 2 ]. CNAs alter the number of copies of genomic regions in a cell, thus creating a background of genomic variation on which selection can act [ 3 ]. CNAs can act as drivers of cancer evolution [ 4 , 5 , 6 ] and be used to infer phylogenies [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Importantly, CNAs have been shown to play a crucial role in cancer treatment and prognosis [ 10 , 11 , 12 ], and they correlate with markers of immune evasion and increased activity in proliferation pathways [ 6 , 13 , 14 ]. As a consequence of CIN, tumour cells, unlike most normal cells, substantially vary in the amount of DNA they contain, the so-called ploidy.
Bts mots persona
An increase in ploidy can occur through mating, endoreduplication, or failure to undergo cytokinesis after replication described in detail below. The puromycin incorporation appeared to be constant when equal amount of proteins was loaded. Additionally, some cells continue to increase in ploidy during development, resulting in somatic tissues that have a mixture of diploid and polyploid cells, including human hepatocytes and megakaryocytes 5, 6, 7 F. Toggle limited content width. Alloploids occur more frequently in nature than other types of polyploids. Article Google Scholar. Plants can tolerate higher levels of aneuploidy, but aneuploidy female gametes are typically more viable than male gametes. This is an important evolutionary mechanism in both plants and animals and is known as a primary driver of speciation. Genome Res. We further demonstrate that the abundance of some proteins is differentially regulated with ploidy, and identify downregulation of the mTOR signaling to be responsible for the reduced protein biosynthesis in polyploid cells. Ploidy tug-of-war: Evolutionary and genetic environments influence the rate of ploidy drive in a human fungal pathogen. Exp Cell Res. Even in diploid organisms, many somatic cells are polyploid due to a process called endoreduplication , where duplication of the genome occurs without mitosis cell division.
Cell division cycle, figure from Wikipedia. Cells that stop dividing exit the G1 phase of the cell cycle into a so-called G0 state.
For example, in high salt medium, the rate of diploidization of haploids was faster than the rate of diploidization of isogenic tetraploids Here, n describes the numbers of data points and x i describes the value of each data point i. Similarly, polyploid cells have high rates of whole chromosome aneuploidy, which can provide fitness benefits during adaptation 20 , 86 , 88 , yet haploid cells rarely acquire aneuploidy during adaptation likely due to the increased fitness cost of these mutations in most environments Raw files were analyzed by MaxQuant software version 1. Lu, Y. Lamkey Eds. Mol Cell. Population studies in microorganisms. Thus, the changes in ribosomal protein abundance appear to be specific for cells that underwent whole-genome doubling. In vitro pollination and fertilization In self-incompatibility systems where pollen tubes fail to grow, in vitro pollination offers an alternative to overcome such incompatibility. Genetic linkages are extremely difficult to determine. Intratumor genomic heterogeneity in breast cancer with clonal divergence between primary carcinomas and lymph node metastases. It is possible on rare occasions for ploidy to increase in the germline , which can result in polyploid offspring and ultimately polyploid species. Albertin W, Marullo P.

True idea
You are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.