Nursing diagnosis for uti
A simple validated scale to measure urgency. J Urol. Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections.
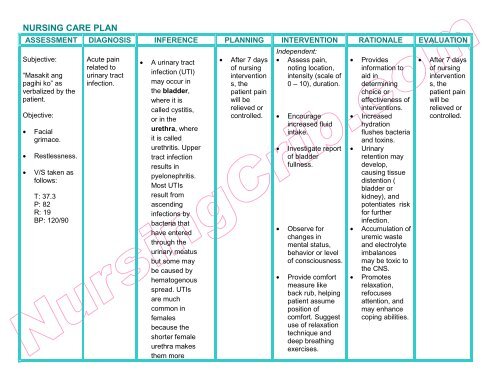
Use this nursing care plan and management guide to help care for patients with urinary tract infection. Enhance your understanding of nursing assessment , interventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis , all specifically tailored to address the unique needs of individuals facing urinary tract infections. Urinary tract infections UTIs are caused by pathogenic microorganisms in the urinary tract kidney, bladder , urethra. UTI is defined as significant bacteriuria in the setting of symptoms of cystitis or pyelonephritis. Among the pathogens responsible for the remainder are Staphylococcus saprophyticus , Proteus mirabilis , Klebsiella pneumoniae , or Enterococcus faecalis.
Nursing diagnosis for uti
Urinary Tract Infections UTIs stand as one of the most prevalent and burdensome healthcare challenges affecting millions of individuals worldwide. As nurses, our frontline role in patient care places us at the forefront of detecting, managing, and preventing UTIs. It is imperative that we possess a thorough understanding of this common condition to deliver efficient, evidence-based care and contribute to improved patient outcomes. This study guide aims to provide nurses with a comprehensive guide to UTI management, encompassing the pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, and evidence-based interventions to combat this significant healthcare concern. The urinary system is responsible for providing the route for drainage of urine formed by the kidneys, and these should be fully functional because the damage could easily affect other body systems. UTIs are classified by location and are further classified according to other factors and conditions. For infection to occur, bacteria must gain access to the system. Urinary tract infection cases are widespread around the world and affect both the young and the old. UTI is a preventable disease mainly focusing on the hygienic practices of the individual. Early recognition of UTI and prompt treatment are essential to prevent recurrent infection and the possibility of complications.
A short urethra makes nursing diagnosis for uti easier for the uropathogen to invade the urinary tract, especially when a client takes frequent baths and long periods of soaking in the bath water Ackerman, Disclosure: Michael Bono declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Avoid bath tubs.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Michael J. Bono ; Stephen W. Leslie ; Wanda C.
A urinary tract infection UTI is a common infection that occurs when bacteria, typically from the rectum, enter the urethra and infect the urinary tract. Infections can affect several parts of the urinary tract, but the most common type is a bladder infection cystitis. Kidney infections pyelonephritis are more serious than a bladder infection because they can have long-lasting effects on the kidneys. Some people are at higher risk of getting a UTI. UTIs are more common in females because their urethras are shorter and closer to the rectum, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract. Other factors that can increase the risk of UTIs include the following:. Symptoms of a UTI include the following: [3]. Symptoms of a more serious kidney infection pyelonephritis include fever above degrees F
Nursing diagnosis for uti
It includes three nursing diagnoses and nursing interventions with the rationales. An year old female presents to the ED with fever, chills, frequent urination, urgency, and dysuria. The patient has a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes. She was recently admitted 1 week ago for a fall and was discharged after 1 night in observation. Patient reports waking up times overnight to urinate and feels that she is unable to fully empty her bladder. She experiences burning and pain when she attempts to urinate, and also notes an abnormal urine odor.
Boyfriend fnf
The probiotic administration in hygiene products, such as tampons, has emerged as a new possibility to carry beneficial strains and exert the claimed effect. Healthcare providers should prescribe appropriate antibiotics based on the specific bacteria causing the infection and any relevant resistance patterns. Due identification of this condition enables choosing more appropriate interventions, as well as achieving more efficient results, supporting measures for its prevention and public policy implementation. Assess for factors related to the cause of urinary tract infection UTI :. Frequently this nursing diagnosis can only be identified retrospectively; on the other hand, when signs and symptoms persist for more than six months, this nursing diagnosis must be reconsidered. Trimethoprim TMP or cephalexin are usually the first choices of antibiotics. Collaboration of antipyretic drugs. In the USA, for example, a UTI is a common medical condition that accounts for 7 to 8 million clinic visits by women per year Robinson et al, Mechanisms of urinary tract sterility maintenance article in Polish. A study of women with recurrent UTIs showed that increased fluid intake reduces the risk of repeat infections. Learning Outcome List the causes of urinary tract infections. Use of non-pharmacological techniques for pain management as appropriate. What is Scribd? Alternative measures such as regular toileting can prevent infection.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Pathophysiology of urinary incontinence, faecal incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse. Promote optimal rest and minimal physical activities. The client should squeeze their pelvic floor muscles for three seconds, then relax them for a count of three and repeat the procedure several times Mayo Clinic, Increasing fluid intake to 2 to 3 liters per day helps facilitate urine production, dilutes urine, reduces irritation of the inflamed bladder, promotes renal blood flow, and flushes bacteria from the urinary tract. Rationale: To identify the indications of progress or deviations from expected results 2. Review Management of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in adults. As the defense mechanisms react to the bacteria, inflammation starts to set in as well as other signs of infection. Urinalysis This assesses for pyuria, bacteria, and blood cells in urine that is associated with the inflammation process during infection. Acute and chronic UTIs are often managed by prescribing antibiotics. Encourage the use of a hypothermia blanket and wrap extremities with bath towels. Managing fever and hyperthermia in patients with urinary tract infection UTI is essential to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. Voiding habit. Search for:. Dukes C.

It do not agree
In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it.