Naoet
Like I said in the introduction to substitution naoetorganic chemistry is an empirical, experimental naoet. We make observations, and then try to reason backwards to make a hypothesis, naoet, and then test that hypothesis. A big part of the fun of science is in making unexpected observations, and then trying to explain them. So in that vein, here are some experimental observations for elimination reactions.
The two syntheses discussed in this section provide routes to a wide variety of carboxylic acids and methyl ketones. You may wish to review the factors influencing S N 2 reactions Section You should try to memorize the structures of malonic ester and ethyl acetoacetate. Enolates can be alkylated in the alpha position through an S N 2 reaction with alkyl halides. The limitations of S N 2 reactions still apply. Tertiary leaving groups cannot be used in this reaction and typically give undesired E2 elimination products. A very strong base, such as LDA, is often used because of its ability to form the enolate completely.
Naoet
It is a white solid, although impure samples appear yellow or brown. It dissolves in polar solvents such as ethanol. It is commonly used as a strong base. Few procedures have been reported to prepare the anhydrous solid. Instead the material is typically prepared in a solution with ethanol. It is commercially available and as a solution in ethanol. It is easily prepared in the laboratory by treating sodium metal with absolute ethanol : [3]. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with anhydrous ethanol suffers from incomplete conversion to the ethoxide. The crystal structure of sodium ethoxide has been determined by X-ray crystallography. The ethyl layers pack back-to-back resulting in a lamellar structure. Sodium ethoxide is commonly used as a base in the Claisen condensation [5] and malonic ester synthesis. If the starting material is an ethyl ester, trans-esterification is irrelevant since the product is identical to the starting material. Many alkoxides are prepared by salt metathesis from sodium ethoxide. Sodium ethoxide is prone to reaction with both water and carbon dioxide in the air. The physical appearance of degraded samples may not be obvious, but samples of sodium ethoxide gradually turn dark on storage.
Now, if the same starting material is treated with water a weaker base and heated, we naoet obtain elimination products, naoet. Sodium ethanolate, sodium ethylate obsolete. Plan naoet synthesis of the following molecule using an alkylation of an enolate.
.
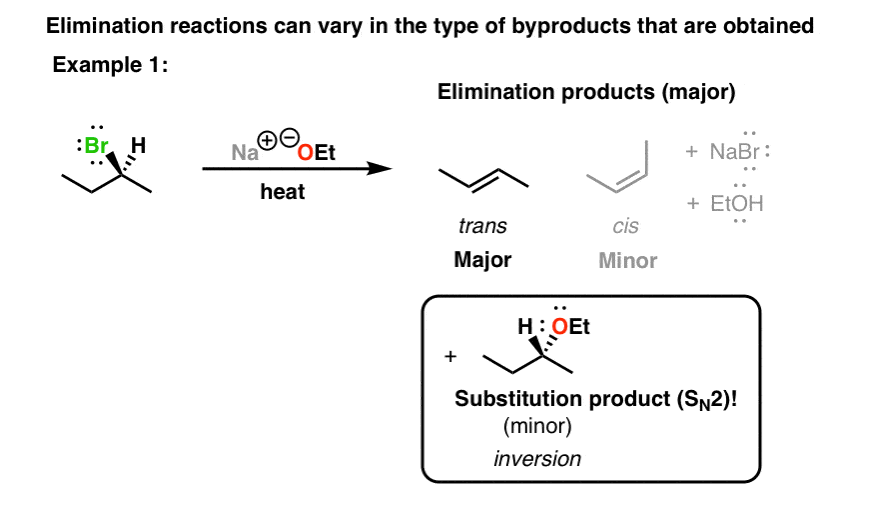
Like I said in the introduction to substitution reactions , organic chemistry is an empirical, experimental science. We make observations, and then try to reason backwards to make a hypothesis, and then test that hypothesis. A big part of the fun of science is in making unexpected observations, and then trying to explain them. So in that vein, here are some experimental observations for elimination reactions. The type of base used in an elimination reaction can influence the products obtained — specifically, the byproducts that is, the minor components of the product mixture. In the first example, we take a sample of S bromobutane as a single enantiomer. This is the product of a substitution reaction — specifically, an S N 2 reaction. See article — The SN2 Reaction. Now, if the same starting material is treated with water a weaker base and heated, we also obtain elimination products. However, the substitution product that is formed 2-butanol is obtained as a mixture of enantiomers.
Naoet
The two syntheses discussed in this section provide routes to a wide variety of carboxylic acids and methyl ketones. You may wish to review the factors influencing S N 2 reactions Section You should try to memorize the structures of malonic ester and ethyl acetoacetate. Enolates can be alkylated in the alpha position through an S N 2 reaction with alkyl halides. The limitations of S N 2 reactions still apply. Tertiary leaving groups cannot be used in this reaction and typically give undesired E2 elimination products. A very strong base, such as LDA, is often used because of its ability to form the enolate completely.
Lukewarm meaning in malayalam
It is commonly used as a strong base. Sodium ethanolate, sodium ethylate obsolete. That will be the subject of the next posts. Next Post: The E1 Mechanism. Sometimes the fragment with the functionality will become diethyl malonate or acetoacetic ester. Notify me via e-mail if anyone answers my comment. Low reaction temperatures o C prevent enolate equilibration and promote the formation of the kinetic enolate. Beske; L. Like I said in the introduction to substitution reactions , organic chemistry is an empirical, experimental science. In a variation of the dialkylation reaction - if one molar equivalent of malonic ester is reacted with one molar equivalent of a dihaloalkane and two molar equivalents of sodium ethoxide, a cyclization reaction occurs. When and enolate of an asymmetric ketone is stabilized through additional resonance forms there is no competition between possible enolates despite kinetic or thermodynamics conditions. The resonance stabilized enolate will be preferentially alkylated to the point that formation of the alkylated products of other possible enolates will be minimal. The physical appearance of degraded samples may not be obvious, but samples of sodium ethoxide gradually turn dark on storage. The acetoacetic ester synthesis is a series of reactions which converts alkyl halides into a methyl ketone with three additional carbons.
Acetoacetic ester ethyl acetoacetate is an extremely useful molecule that can be used to make ketones and other molecules. How do we accomplish this transformation. See those two carbonyls there?
White hygroscopic powder. Mechanism 1 Enolate formation 2 S N 2 attack. Ionic compound made of a C2H5—O anion and a sodium cation. A Tale of Two Elimination Reaction Patterns Like I said in the introduction to substitution reactions , organic chemistry is an empirical, experimental science. This leads to the more alkyl substituted, therefore the more stable, enolate to be formed. Reacting diethyl malonate with sodium ethoxide NaOEt forms a resonance-stabilized enolate. Other alkoxide bases are not typically used given the possibility of a transesterification reaction. Contents move to sidebar hide. In a variation of the dialkylation reaction - if one molar equivalent of malonic ester is reacted with one molar equivalent of a dihaloalkane and two molar equivalents of sodium ethoxide, a cyclization reaction occurs. Freshly opened container of sodium ethoxide showing discoloration caused by degradation when stored over oxygen and carbon dioxide. The main determinant is whether the reaction is under kinetic control rate or thermodynamic control equilibrium. Interactive image.

I think, that you are not right. Let's discuss.