Met office northern lights map
Find out about how and why the northern lights form, and where to see them in the UK. The northern lights also known as aurora borealis appear as large areas of colour including pale green, pink, shades of red, yellow, blue and violet in the direction due north. During a weak aurora, the colours are very faint and spread out whereas an intense aurora features greater numbers of and brighter colours which can be seen higher in the sky with a distinct arc, met office northern lights map.
Plenty of people have seen great photos of the auroras, but how do you take a great photo of them? Auroras — best known in the northern hemisphere as the aurora borealis — are amongst the most dramatic and engaging sights of the natural world. For millennia they have been considered a sign from the gods or a precursor of key events of human significance. Today we can explain the origins or auroras, and even predict them, through science and careful observation. The long exposures and technical difficulties of early photography meant that it was not until that the first successful photograph of the aurora borealis from Norway was made — in black and white, of course.
Met office northern lights map
Photo courtesy of Jim Henderson Photography click to enlarge What is the cause of aurora? It is easier to see the northern lights aurora borealis in the UK than you might think. All you need is a dark place, a clear sky and very good timing! The good timing is important as the northern lights are a result of a geomagnetic storm. These storms are short-lived periods of high geomagnetic activity where the Earth's magnetic field changes very quickly and strong electric currents flow high in the atmosphere. The aurora is a consequence of activity on the surface of the Sun. Occasionally there are large explosions on the Sun, and huge amounts of charged particles are thrown out into space. These particles sometimes travel towards Earth where they are captured by the Earth's magnetic field and guided towards the geomagnetic polar regions. On their way down these particles are slowed down by Earth's atmosphere, which acts as a shield. These charged particles collide with gas molecules in the atmosphere.
This continues to be by far the largest and most complex of the seven sunspot regions on the visible disc, despite some apparent reduction in complexity prakash theatre yelahanka the past 12 hours or so. Usually, when we talk about the first met office northern lights map of summer, we are referring to the astronomical summer which is defined by the Earth's axis and orbit around the Sun. This gives a slight chance of seeing the aurora in the far north of Scotland and similar geomagnetic latitudes under favorable viewing conditions.
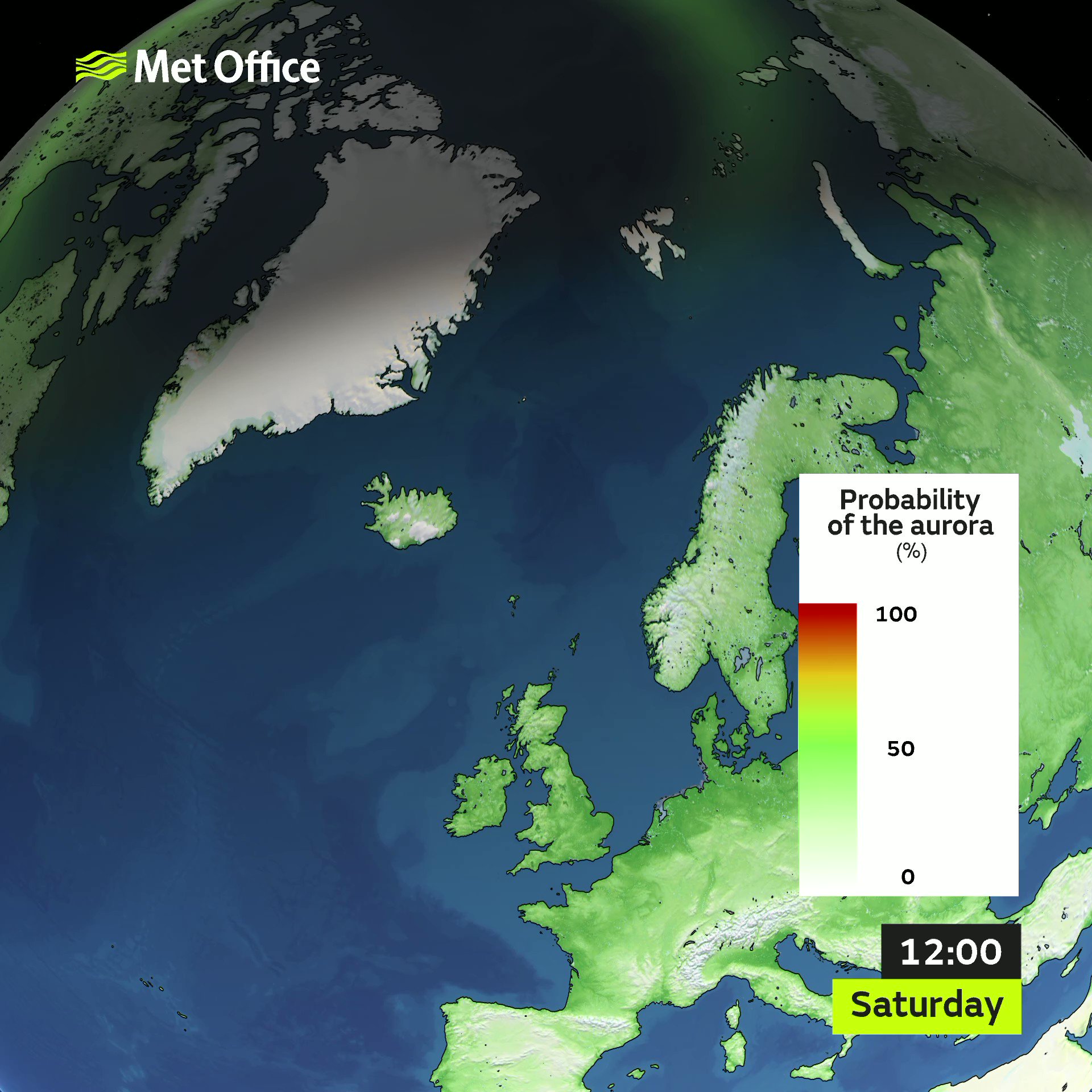
Space weather describes changing environmental conditions in near-Earth space. Learn more about Space Weather. The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb. This gives a slight chance of seeing the aurora in the far north of Scotland and similar geomagnetic latitudes under favorable viewing conditions. Otherwise no significant enhancements are forecast, with visible aurora unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes.
Learning how to read the Northern Lights forecast and be patient is crucial if you want to increase your chances of seeing this elusive phenomenon. No matter how good you are at predicting the Northern Lights, forecasts can change in minutes! Before discussing how to predict the Northern Lights, I recommend that you take a look at our articles on the best time to see Northern Lights and the best places to see Northern Lights. In the Northern Lights forecast, there are three main indicators for tracking the Aurora:. The KP index is the most common way to forecast the Northern Lights, and you can use it both for short-term and long-term Aurora prediction. Here, you can learn a little more about what causes the Northern Lights. The KP-index ranges from and, generally speaking, has the following implications for the Northern Lights forecast :.
Met office northern lights map
Finland is one of the best inhabited regions in the world for viewing northern lights, i. Finland is on the southern rim of the auroral oval. The probability for seeing auroras is best in the northernmost part of the country, i.
Synonyms for frolicking
This is simply the result of how the photos are taken. The current progress of the solar cycle is tracked by counting the number of sunspots seen on the Sun. Check the Met Office Space Weather forecast that will tell you where and when you are likely to observe an aurora. To receive automated space weather alerts and warnings, follow us on Twitter or users with a sector specific interest in space weather services can request a specialist space weather account. AuroraWatch UK magnetometer. Occasionally there are large explosions on the Sun, and huge amounts of charged particles are thrown out into space. The excited molecule is unstable and will give up its extra energy by emitting light. The more opaque darker the green, the more likely it is that an aurora will be visible overhead. It is under these circumstances that the lights can be seen in the UK. Auroras — best known in the northern hemisphere as the aurora borealis — are amongst the most dramatic and engaging sights of the natural world. BGSauroraAlerts for occasional aurora alerts. This gives a slight chance of seeing the aurora in the far north of Scotland and similar geomagnetic latitudes under favorable viewing conditions. Nitrogen causes the sky to glow blue yet when higher in the atmosphere the glow has a purple hue.
Information about the auroras - what are they and when are you likely to be able to see them
Hot active regions, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections will appear bright here. The long exposures and technical difficulties of early photography meant that it was not until that the first successful photograph of the aurora borealis from Norway was made — in black and white, of course. The lights generally extend from 50 miles to as high as miles above the Earth's surface. During this phase the position of coronal holes on the Sun's equator give rise to high speed solar wind streams that buffet the Earth, disturbing the Earth's magnetic field and increasing the likelihood of auroras. All you need is a dark place, a clear sky and very good timing! Navigation: Low-frequency navigation signals degraded for brief intervals. Occasionally there are large explosions on the Sun, and huge amounts of charged particles are thrown out into space. Four-Day Space Weather Forecast Summary Solar Activity: Activity is forecast to remain Moderate to High, with occasional Moderate flares expected and a chance of further isolated Strong flares, particularly in the near term, from the large region in the northeast. Help us improve our website Take our short survey. In time, you can experiment with adding light from a strobe or LED lamp to bring out detail into the foreground. Get creative and experiment. Usage Impacts Details History Data This is a short-term forecast of the location and intensity of the aurora. All-sky camera or webcam. The more opaque darker the green, the more likely it is that an aurora will be visible overhead.

You are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position.
I think, that you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I will know, I thank for the information.