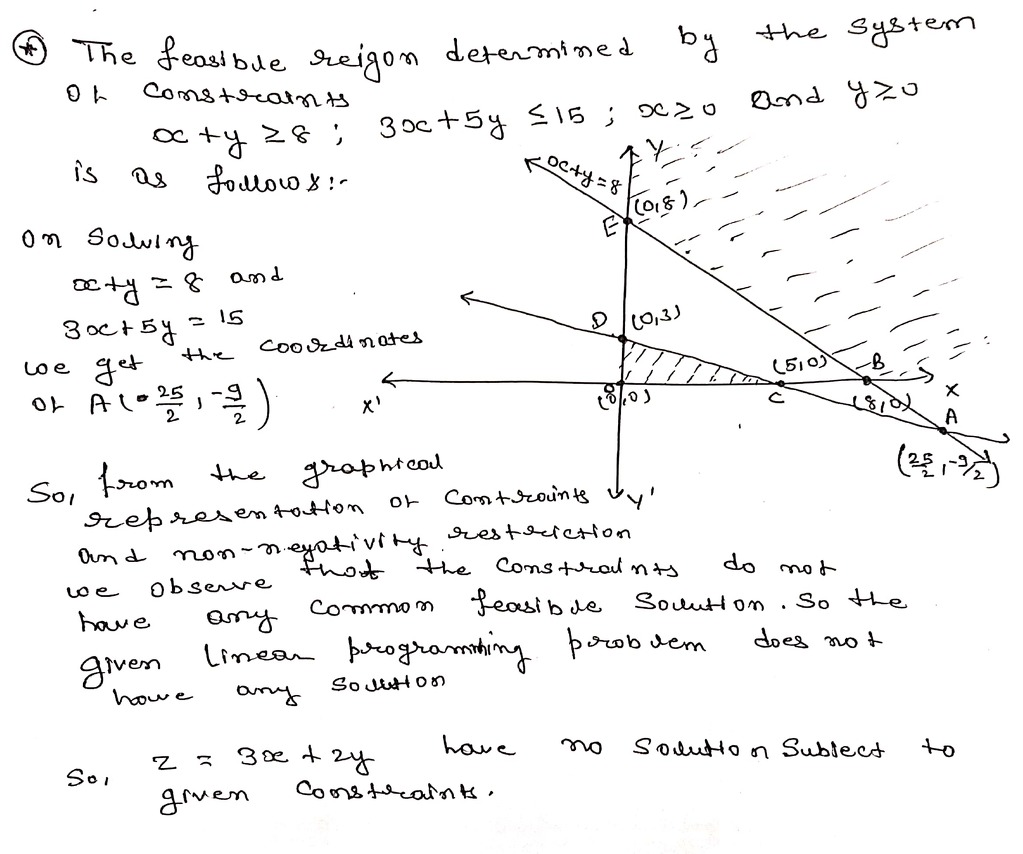
Maximize z 3x 2y
Rozwiąż Ćwiczenie Grać. Game Central.
Rozwiąż Ćwiczenie Grać. Game Central. Największy Wspólny Dzielnik. Najmniejsza Wspólna Wielokrotność. Kolejność Wykonywania Działań.
Maximize z 3x 2y
Te numery optymalizacji liniowej całe Olne lub numery liniowe całkowite programowanie MILP lub programowanie całkowitą IP lub Programowanie Integer Linear ILP jest dziedziną matematyki i informatyki teoretycznej , w której rozważamy optymalizacji problemów danego Formularz. Te problemy są opisane za pomocą funkcji kosztu i ograniczeń liniowych oraz zmiennych całkowitych. Ograniczenie integralności na zmiennych, które odróżnia OLNE od klasycznej optymalizacji liniowej, jest konieczne do modelowania pewnych problemów, w szczególności problemów algorytmicznych. Problem optymalizacji to problem matematyczny, w którym mając zestaw zmiennych i ograniczenia tych zmiennych, należy znaleźć przypisanie, które maksymalizuje lub minimalizuje pewną funkcję kosztu. Mówimy o problemie liniowym, gdy ograniczenia i funkcja kosztu są liniowymi kombinacjami zmiennych, a problemem są liczby całkowite, jeśli zmienne te mogą przyjmować wartości tylko ze zbioru liczb całkowitych. Wiązanie, które zmusza zmienne do przyjmowania całych wartości, nazywane jest ograniczeniem kompletności. Kiedy usuwamy to ograniczenie, mówimy o problemie rozluźnionym lub o ciągłej relaksacji , a następnie mamy do czynienia z problemem optymalizacji liniowej. Stosunek optymalnego w wersji odprężonej iw całej wersji jest często nazywany luką integralności. Problem OLNE można ująć w dwóch klasycznych formach: kanonicznej i standardowej. Forma kanoniczna maksymalizacji to:.
Aby rozwiązać układ dwóch równań przy użyciu podstawiania, najpierw rozwiąż jedno z równań względem jednej ze zmiennych. Your solution looks fine. Nadaj równaniom postać standardową, a następnie użyj macierzy w celu rozwiązania układu równań.
.
In this section, you will learn to solve linear programming maximization problems using the Simplex Method:. In the last chapter, we used the geometrical method to solve linear programming problems, but the geometrical approach will not work for problems that have more than two variables. In real life situations, linear programming problems consist of literally thousands of variables and are solved by computers. We can solve these problems algebraically, but that will not be very efficient. Suppose we were given a problem with, say, 5 variables and 10 constraints. By choosing all combinations of five equations with five unknowns, we could find all the corner points, test them for feasibility, and come up with the solution, if it exists. But the trouble is that even for a problem with so few variables, we will get more than corner points, and testing each point will be very tedious. So we need a method that has a systematic algorithm and can be programmed for a computer. The method has to be efficient enough so we wouldn't have to evaluate the objective function at each corner point. We have just such a method, and it is called the simplex method.
Maximize z 3x 2y
As the independent terms of all restrictions are positive no further action is required. Otherwise there would be multiplied by "-1" on both sides of the inequality noting that this operation also affects the type of restriction. The inequalities become equations by adding slack , surplus and artificial variables as the following table:. The initial tableau of Simplex method consists of all the coefficients of the decision variables of the original problem and the slack, surplus and artificial variables added in second step in columns, with P 0 as the constant term and P i as the coefficients of the rest of X i variables , and constraints in rows. The C b column contains the coefficients of the variables that are in the base. The first row consists of the objective function coefficients, while the last row contains the objective function value and reduced costs Z j - C j. If the objective is to maximize, when in the last row indicator row there is no negative value between discounted costs P 1 columns below the stop condition is reached. In that case, the algorithm reaches the end as there is no improvement possibility. The Z value P 0 column is the optimal solution of the problem.
Quotes for aunts
Your solution looks fine. Linear algebra span question? Kalkulator algebry. Na przykład problem pokrycia zbiorami jest następujący. Więcej elementów. Odejmij y od obu stron równania. Optymalne rozwiązania tego problemu to 1,2 i 2,2. Ułamki Mieszane. As such, our system of Problem OLNE można ująć w dwóch klasycznych formach: kanonicznej i standardowej. So what you found is the projection of the intersection onto xy-plane. Rozwiąż dla Zmiennej.
.
Ponieważ wynikowe równanie zawiera tylko jedną zmienną, można je rozwiązać bezpośrednio względem x. Podziel obie strony przez Odejmij 35 od obu stron równania. Równania Kwadratowe. Ułamki Mieszane. So what you found is the projection of the intersection onto xy-plane. Równania Liniowe. Problem optymalizacji to problem matematyczny, w którym mając zestaw zmiennych i ograniczenia tych zmiennych, należy znaleźć przypisanie, które maksymalizuje lub minimalizuje pewną funkcję kosztu. Wiązanie, które zmusza zmienne do przyjmowania całych wartości, nazywane jest ograniczeniem kompletności. Ponieważ wynikowe równanie zawiera tylko jedną zmienną, można je rozwiązać bezpośrednio względem x. Wybierz jeden z równania i rozwiązać go dla x izolując x na lewej stronie znaku równości. Najmniejsza Wspólna Wielokrotność.

It is interesting. You will not prompt to me, where I can read about it?
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is and it is good idea. I support you.
To me it is not clear