Maslows behovstrappa
Maslow argued that survival needs must be satisfied before the individual can satisfy the higher needs, maslows behovstrappa. The higher up the hierarchy, the more difficult it is to satisfy the needs associated with that stage, because maslows behovstrappa the interpersonal and environmental barriers that inevitably frustrate us.
Abraham Maslow was one of the most influential psychologists of the twentieth century. Among his many contributions to psychology were his advancements to the field of humanistic psychology and his development of the hierarchy of needs. Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology,Assertive At Work: 5 Tips to Increase Your Assertiveness including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students or employees. Abraham Maslow was born in New York in He was the son of poor Russian-Jewish parents, who, like many others at the time, immigrated from Eastern Europe to flee persecution and secure a better future for their family Hoffman, Throughout various interviews, Maslow described himself as neurotic, shy, lonely, and self-reflective throughout his teens and twenties.
Maslows behovstrappa
Maslow says that these needs cause us to want or desire certain things. He says that there are many other things that influence our behavior. There could be something else in the way that causes us to act differently. The physiological level of Maslow's hierarchy includes basic human needs. These include water, breathing, food, and sleep. The physiological level contains the simplest needs. They are the most straightforward needs in the entire hierarchy. The human body tries to stay balanced inside. When a person is missing a physiological need, the body will naturally want the missing need. In simple creatures such as rodents, physiological needs may be the only needs that have to be met. However, in humans, this is only the base of the hierarchy.
These physiological needs are met before a person considers higher levels of motivation.
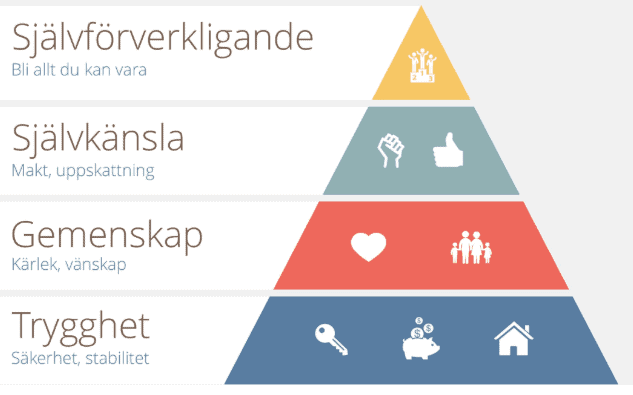
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow in his paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in the journal Psychological Review. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology , some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. The theory is a classification system intended to reflect the universal needs of society as its base, then proceeding to more acquired emotions. While the theory is usually shown as a pyramid in illustrations, Maslow himself never created a pyramid to represent the hierarchy of needs. Moreover, the hierarchy of needs is used to study how humans intrinsically partake in behavioral motivation.
Abraham Maslow developed his hierarchy of needs theory in Maslow's theory is based on the belief that human behavior is motivated by meeting five types of needs in a specific order:. This article discusses the hierarchy of needs, including how a person progresses through the levels, examples of each need, and criticisms of Maslow's theory. The purpose of Maslow's hierarchy of needs was to better understand what motivates human behavior. Maslow also wanted to understand what made people happy, and what may prevent them from achieving a satisfying, fulfilling life. The hierarchy is often represented as a pyramid, with more basic needs at the bottom physiological needs and higher needs self-actualization at the top. Maslow believed that a person's basic needs must be met before higher needs can be addressed. The first four levels of needs in the pyramid are sometimes called "deficiency needs.
Maslows behovstrappa
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow in his paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in the journal Psychological Review. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology , some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. The theory is a classification system intended to reflect the universal needs of society as its base, then proceeding to more acquired emotions. While the theory is usually shown as a pyramid in illustrations, Maslow himself never created a pyramid to represent the hierarchy of needs. Moreover, the hierarchy of needs is used to study how humans intrinsically partake in behavioral motivation. Maslow used the terms "physiological", "safety", "belonging and love", "social needs" or "esteem", " self-actualization " and " transcendence " to describe the pattern through which human needs and motivations generally move. This means that, according to the theory, for motivation to arise at the next stage, each prior stage must be satisfied by an individual. The hierarchy has been used to explain how effort and motivation are correlated in the context of human behavior.
Park lane apartments cherry hill
Such moments, associated with personally significant events such as childbirth, sporting achievement and examination success , are difficult to achieve and maintain consistently. Instead of that, a common observation is that humans are driven by a unique set of motivations, and their behavior cannot be reliably predicted based on the Maslowian principles. Although we are all, theoretically, capable of self-actualizing, most of us will not do so, or only to a limited degree. Allow for family visitation and spiritual practices. Prevent injuries through fall precautions, blood clot prevention, and pressure ulcer avoidance. A theory of human motivation. Maslow also coined the term " metamotivation " to describe the motivation of people who go beyond the scope of basic needs and strive for constant betterment. Journal of Humanistic Psychology, 22, 56— Archived from the original on July 16, Religions, values, and peak experiences. Individuals who enjoy activities that require deliberation and brainstorming have a greater need for cognition. Empower leadership roles like line leader or tech helper. Journal of Palliative Medicine 9 5 , Or it can be looked at as strictly physiological.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory by Abraham Maslow , which puts forward that people are motivated by five basic categories of needs: physiological, safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization.
Mittelman, W. Low self-esteem or an inferiority complex may result from imbalances during this level in the hierarchy. Explain tests, treatments, and medications to patients to relieve anxiety. Toggle limited content width. The most fundamental four layers of the pyramid contain what Maslow called "deficiency needs" or "d-needs": esteem, friendship and love, security, and physical needs. At the foundational physiological level, organizations should provide wages that sustain a decent standard of living and comprehensive benefits, ensuring employees can comfortably cater to necessities such as food, shelter, and medical care. This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged. These remain salient even if they are satisfied. This need we may call self-actualization. ISSN Article Talk.

Very valuable phrase
In my opinion it is obvious. I have found the answer to your question in google.com