Lycopene beta cyclase
Metrics details.
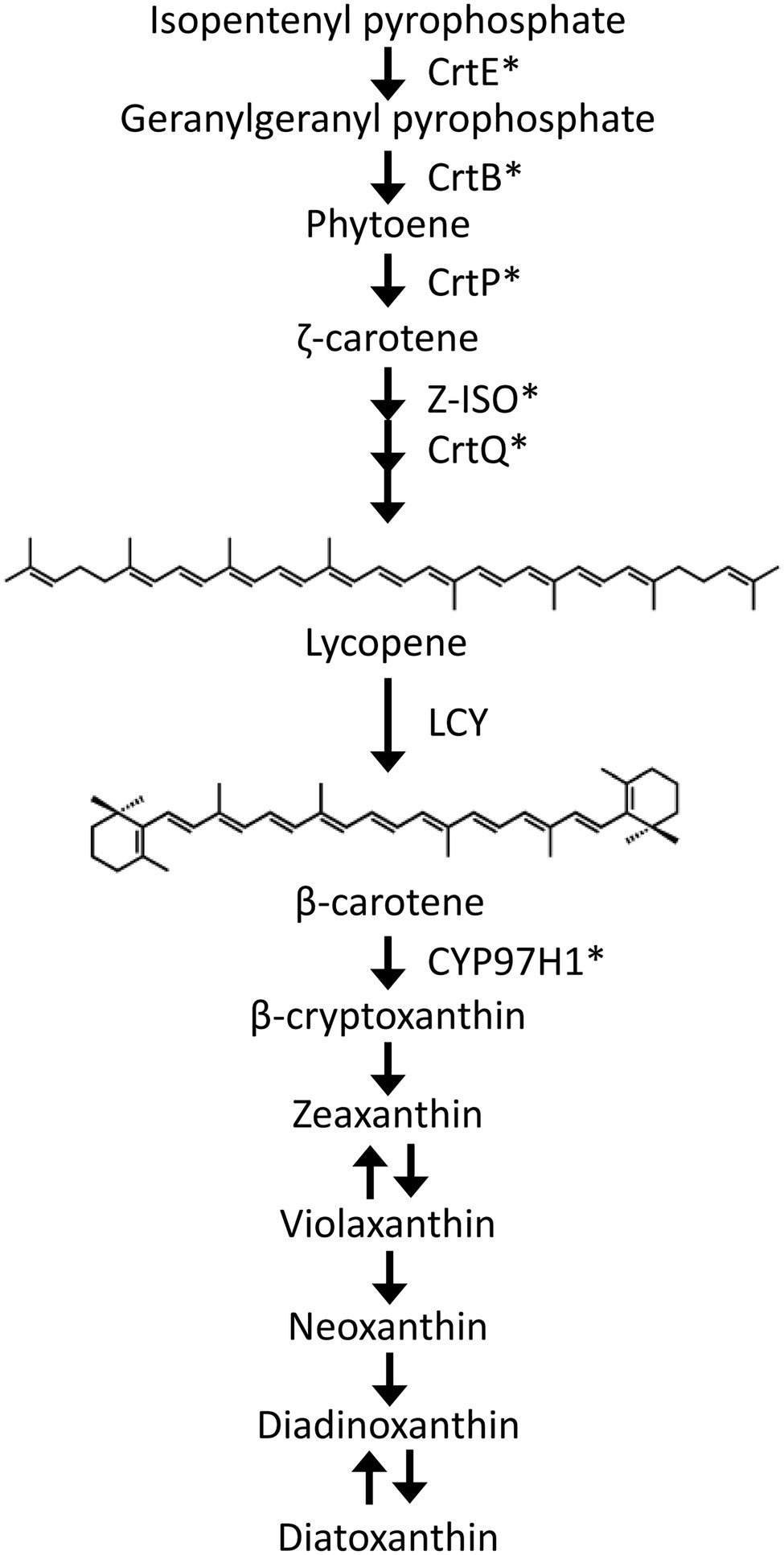
Carotenoids are important isoprenoids produced in the plastids of photosynthetic organisms that play key roles in photoprotection and antioxidative processes. Xanthi resulted in increased levels of abscisic acid ABA and especially gibberellins GAs , resulting in increased plant yield. In order to understand this phenomenon prior to exporting this genetic strategy to crops, we generated tobacco Nicotiana tabacum cv. Transplastomic plants expressing DcLCYB1 at high levels showed a wild-type-like growth, even though their pigment content was increased and their leaf GA 1 content was reduced. Remarkably, drastic changes in phytohormone content also occurred in the RNAi lines. However, external application of phytohormones was not sufficient to rescue these phenotypes, suggesting that altered photosynthetic efficiency might be another important factor explaining their reduced biomass.
Lycopene beta cyclase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. We also aimed to obtain more information about the endogenous carotenoid biosynthetic pathway and thus provide experimental support for carotenoid metabolic engineering in wheat. The cyclization activity of the encoded protein was demonstrated by heterologous complementation analysis. In addition, changes in TaLCYB expression also affected the expression of several endogenous carotenogenic genes to varying degrees. Our attempt to silence it not only contributes to elucidating the mechanism of carotenoid accumulation in wheat but may also help in breeding wheat varieties with high provitamin A content through RNA interference RNAi to block specific carotenogenic genes in the wheat endosperm. The online version of this article doi Carotenoids are important natural isoprenoid pigments synthesized in plants that have essential roles in protecting against excess light energy and oxidative damage, and in light-harvesting [ 1 , 2 ]. Their provitamin A activity and antioxidant properties are their most attractive functions. In higher plants, although the main pathway of carotenoid biosynthesis has been studied extensively [ 6 - 8 ], the regulatory mechanisms of carotenoid biosynthesis are still not well known. Because of the special position of lycopene cyclization, researchers have focused on the function of LCYB and its relationship with carotenoid accumulation in plants [ 10 - 13 ]. Carotenoid biosynthetic pathway in wheat. Through the deeper understanding of the benefits of carotenoids for human health, scientists have been prompted to explore effective methods to increase the carotenoid composition and content in plants, especially in staple crops. However, precise carotenoid metabolic engineering in crop plants has been hindered by limited data about the endogenous regulation of carotenogenic genes despite recent progress in staple crops [ 15 - 17 ].
Open in a separate window. For histochemical GUS analysis, roots, leaves, flower and fruits at different stages of ripening viz. Nucleic Acids Research 29e
However, the roles and underlying mechanisms of the LCYB gene in plant responses to abiotic stresses are rarely known. This gene has not been used to improve carotenoid contents of sweetpotato, Ipomoea batatas L. Shangshu 19 plants. The genes involved in carotenoid and abscisic acid ABA biosynthesis pathways and abiotic stress responses were up-regulated in the transgenic plants. The ABA and proline contents and superoxide dismutase SOD activity were significantly increased, whereas malonaldehyde MDA and H 2 O 2 contents were significantly decreased in the transgenic plants under abiotic stresses. The overall results indicate that the IbLCYB2 gene enhances carotenoid contents and abiotic stress tolerance through positive regulation of carotenoid and ABA biosynthesis pathways in sweetpotato.
Metrics details. We also aimed to obtain more information about the endogenous carotenoid biosynthetic pathway and thus provide experimental support for carotenoid metabolic engineering in wheat. The cyclization activity of the encoded protein was demonstrated by heterologous complementation analysis. In addition, changes in TaLCYB expression also affected the expression of several endogenous carotenogenic genes to varying degrees. Our attempt to silence it not only contributes to elucidating the mechanism of carotenoid accumulation in wheat but may also help in breeding wheat varieties with high provitamin A content through RNA interference RNAi to block specific carotenogenic genes in the wheat endosperm. Carotenoids are important natural isoprenoid pigments synthesized in plants that have essential roles in protecting against excess light energy and oxidative damage, and in light-harvesting [ 1 , 2 ]. Their provitamin A activity and antioxidant properties are their most attractive functions. In higher plants, although the main pathway of carotenoid biosynthesis has been studied extensively [ 6 - 8 ], the regulatory mechanisms of carotenoid biosynthesis are still not well known.
Lycopene beta cyclase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The composition of carotenoids, along with anthocyanins and chlorophyll, accounts for the distinctive range of colour found in the Actinidia kiwifruit species. Lutein and beta-carotene are the most abundant carotenoids found during fruit development, with beta-carotene concentration increasing rapidly during fruit maturation and ripening. In addition, the accumulation of beta-carotene and lutein is influenced by the temperature at which harvested fruit are stored. Plants accumulate a huge variety of secondary metabolites. Carotenoids are one such group of compounds that are synthesized in the plastids, mainly the chloroplasts and chromoplasts, by enzymes that are nuclear-encoded Hirschberg, Carotenoids are 40 carbon isoprenoids that contain polyene chains containing conjugated double bonds. These compounds are important in nature as they are involved in light-harvesting, photoprotection, and pollinator attraction in plants Tracewell et al.
Costco raising desk
The Plant Journal 17 , — Background Carotenoids constitute a group of naturally occurring pigments that play diverse roles in plants. This gene has not been used to improve carotenoid contents of sweetpotato, Ipomoea batatas L. Biotechnology Letters 30 , — Plant Physiology , 67 — Svab Z , Maliga P. To further analyze the carotenoid profiles, detailed HPLC analysis was carried out on the T 3 generation, which showed significant differences in carotenoid content and composition in seeds between transgenic and control lines, implying profound changes in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathways of the transgenic lines Figure 5. Moreover, violaxanthin increase in leaves is higher in our transplastomic tobaccos than in leaves of transplastomic tomatoes Wurbs et al. In the strongest variegated line, increased abundance of five sugars e. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Metrics details.
Although cDNAs of genes encoding carotenoid biosynthetic pathway enzymes have been well characterized in tomato, their promoters have received limited attention. MD: performed all the experiments. At least independent transgenic events from each construct were examined for stable integration of transgene and its copy number by Southern hybridization Additional file 1 , Figure S1. J Biol Chem. In carrot, this phenomena was observed in different tissues leaf and root; Moreno et al. Systemic analysis of inducible target of rapamycin mutants reveal a general metabolic switch controlling growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Three transgenic lines and several lines only transformed with the pAHC25 plasmid were obtained; the latter lines were regarded as vector control lines VC. This provides new ideas and means for improving the total carotenoid content or specific carotenoid products by metabolic engineering in wheat. Because LCYB participates in the biosynthesis of lutein, the lutein content was also decreased to 0. Optimization of the expression of the HIV fusion inhibitor cyanovirin-N from the tobacco plastid genome. Plant transformation was undertaken using the previously described biolistic protocols Svab and Maliga, ; Ruf and Bock, Analysis of carotenoid composition by HPLC Carotenoids in the mature wheat seeds were extracted according to Wang et al. Ruf S , Bock R. Contrary to the expectation, the PSY1 over-expressing transgenic tomato fruit also had reduced lycopene content as compared to untransformed plants [ 27 ]. Plasmid was isolated from transformed Agrobacterium cultures and was back-transformed into E.

What useful question