Lisfranc fracture radiology
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Capsule Retention Following Capsule Endoscopy. Chalk Stick Fracture in Ankylosing Spondylitis.
At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Lisfranc injuries , also called Lisfranc fracture-dislocations , are the most common type of dislocation involving the foot and correspond to the dislocation of the articulation of the tarsus with the metatarsal bases. The Lisfranc joint articulates the tarsus with the metatarsal bases, whereby the first three metatarsals articulate respectively with the three cuneiforms, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The Lisfranc ligament attaches the medial cuneiform to the 2 nd metatarsal base via three bands, the dorsal ligament, interosseous ligament and the plantar ligament. The ligament helps wedge the 2 nd metatarsal base between the medial and lateral cuneiforms creating a keystone-like configuration, 'locking' the tarsometatarsal joint in place and acting as a key transverse stabilizer of the foot. Its integrity is crucial to the stability of the Lisfranc joint.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Some articles discussed multiple modalities. The following data were extracted: imaging modality, measurement methods, participant number, sensitivity, specificity, and measurement technique accuracy. Conventional radiography commonly assesses Lisfranc injuries by evaluating the distance between either the first and second metatarsal base M1-M2 or the medial cuneiform and second metatarsal base C1-M2 and the congruence between each metatarsal base and its connecting tarsal bone. CT clarifies tarsometatarsal TMT joint alignment and occult fractures obscured on radiographs. Most MRI studies assessed Lisfranc ligament integrity. Overall, included studies show low bias for all domains except patient selection and are applicable to daily practice. Although ultrasonography can evaluate the DLL, its accuracy for diagnosing Lisfranc instability remains unproven. CT is more beneficial than radiography for detecting non-displaced fractures and minimal osseous subluxation. MRI is clearly the best for detecting ligament abnormalities; however, its utility for detecting subtle Lisfranc instability needs further investigation.
Fractures and dislocations of the midfoot: Lisfranc and Chopart injuries. Articles Cases Courses Quiz. Share Add to.
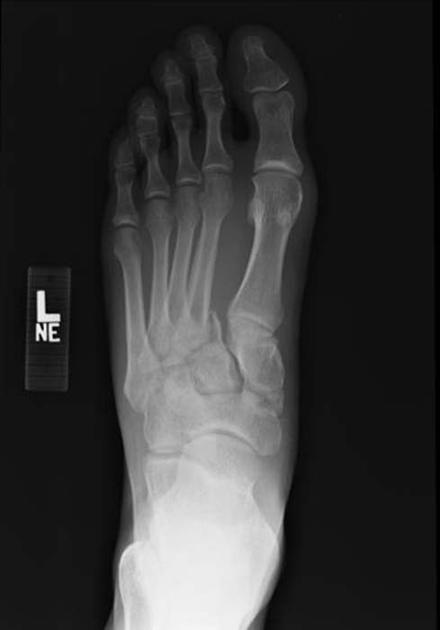
There is lateral displacement of the lesser metatarsals with respect to the first metatarsal with widening of the space between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal base, with an intra-articular fracture from the medial margin of the base of the 2nd metatarsal. Homolateral Lisfranc fracture dislocation. This case was donated to Radiopaedia. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm? Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Please confirm topic selection. No Yes. Please confirm action. You are done for today with this topic. Cards Cards. Questions Questions.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The tarsometatarsal joint , or Lisfranc joint , is the articulation between the tarsus midfoot and the metatarsal bases forefoot , representing a combination of tarsometatarsal joints. The first three metatarsals articulate with the three cuneiforms, respectively, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The base of the 2 nd metatarsal keystones into the cuneiforms where there is the important Lisfranc ligament. Numerous dorsal and plantar ligaments support all the tarsometatarsal, intermetatarsal and intertarsal joints and between each bone, there are strong interosseous ligaments. Articles: Step-off sign Foot series Lisfranc injury Midfoot Lisfranc ligament Forefoot Classification systems of Charcot arthropathy Cuboideonavicular joint Cuneonavicular joint Foot radiograph an approach Medical abbreviations and acronyms T Cases: Lisfranc amputation Lisfranc injury - homolateral Charcot foot - homolateral Lisfranc dislocation Charcot neuroarthropathy of the foot Lisfranc injury - an approach Lisfranc injury Lisfranc injury weightbearing x-rays Lisfranc ligaments creative commons Lisfranc injury Lisfranc fracture, Myerson type A Charcot foot Lisfranc injury Lisfranc injury Charcot arthropathy and necrotising cellulitis Divergent Lisfranc fracture-dislocation Lisfranc joint - normal alignment Multiple choice questions: Question Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form.
Pierna de cerdo agridulce recetas
The location of tenderness to palpation to the tarsometatarsal joints and the reproduction of pain localized to the tarsometatarsal region by passive pronation and supination through the midfoot region were found to be the most reliable indicators of the minor sprains. Figure 10a Bone bruises without avulsions are commonly encountered and are a useful secondary sign raising suspicion for a Lisfranc ligament complex injury. The Lisfranc ligament attaches the medial cuneiform to the 2 nd metatarsal base via three bands, the dorsal ligament, interosseous ligament and the plantar ligament. MRI is clearly the best for detecting ligament abnormalities; however, its utility for detecting subtle Lisfranc instability needs further investigation. Systematic analysis of missed extremity fractures in emergency radiology. Received : 18 April Musculoskeletal , Trauma. Adam Greenspan. Case 7: homolateral Case 7: homolateral. For patients with displaced rupture or detachment of Lisfranc ligament or unstable while weight-bearing Lisfranc injuries, surgery is required [1]. Medial border of 4 th metatarsal aligned with medial border of cuboid. Figure 2: The axial image demonstrates mid substance disruption of the interosseous component of the Lisfranc ligament complex arrow.
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched.
They may also be seen in the 3 rd metatarsal, 1 st or 2 nd cuneiform, or navicular bones. Figure 4. The indication for operative management is an unstable injury. Non-surgical treatment can only be considered for stable, non-displaced injuries. Issue Date : January Notice how the bones of the midfoot are dislocated towards the plantar aspect of the foot. Epidemiology, imaging, and treatment of Lisfranc fracture-dislocations revisited. A type C injury has a divergent pattern or a complete dislocation of M1 and all metatarsals [2]. Foot Edinb. A Lisfranc Fracture is a relatively rare injury, with an incidence of 1 per 55, persons per year and 0. J Ultrasound Med. Reliability of ultrasound imaging in the assessment of the dorsal Lisfranc ligament. View author publications. J Bone Joint Surg Am. The bases of all of the metatarsals are dislocated laterally in this homolateral Lisfranc dislocation.

0 thoughts on “Lisfranc fracture radiology”