Limiting reagent calculator
In all the examples discussed thus far, the reactants were assumed to be present in stoichiometric quantities. Consequently, none of the reactants was left over at the end of the reaction, limiting reagent calculator.
This theoretical yield calculator will answer all the burning questions you have regarding how to calculate the theoretical yield , such as how to find theoretical yield as well as the theoretical yield definition and the theoretical yield formula. Before carrying out any kind of lab work, you need to work out what is the theoretical yield so you know how much of your product, be it a molecule or lattice, you can expect from a given amount of starting material. This allows you to work out how efficiently you carried out your reaction the quantity you can find at the actual yield calculator , which is done by calculating the percent yield. You can also use the theoretical yield equation to ensure that you react with equal moles of your reactants so no molecule is wasted. If you are uncertain which of your reagents are limiting, plug in your reagents one at a time, and whichever one gives you the lowest number of moles is the limiting reagent. Remember to hit refresh at the bottom of the calculator to reset it. What is the theoretical yield?
Limiting reagent calculator
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Limiting reactant and theoretical yield. How many complete hot dogs can we make? Once we run out of buns, we'll have to stop making complete hot dogs. In other words, the hot dog buns limit the number of complete hot dogs we can produce. A reaction with five hot dogs and four hot dog buns reacting to give four complete hot dogs and one leftover hot dog. The hot dog buns are the limiting reagent, and the leftover single hot dog is the excess reagent. The four complete hot dogs are the theoretical yield. In much the same way, a reactant in a chemical reaction can limit the amounts of products formed by the reaction. When this happens, we refer to the reactant as the limiting reactant or limiting reagent. The amount of a product that is formed when the limiting reactant is fully consumed in a reaction is known as the theoretical yield. In the case of our hot dog example, we already determined the theoretical yield four complete hot dogs based on the number of hot dogs buns we were working with. Enough about hot dogs, though!
Because magnesium is the limiting reactant, the number of moles of magnesium determines the number of moles of titanium that can be formed:. The good thing about this calculator is that it can be used any way you like, limiting reagent calculator, limiting reagent calculator is, to find the mass of reactants needed to produce a certain mass of your product. Use the first equation to find the mass of your desired product in whatever units your reactants were in.
When there is not enough of one reactant in a chemical reaction, the reaction stops abruptly. To figure out the amount of product produced, it must be determined which reactant will limit the chemical reaction the limiting reagent and which reactant is in excess the excess reagent. One way of finding the limiting reagent is by calculating the amount of product that can be formed by each reactant; the one that produces less product is the limiting reagent. The following scenario illustrates the significance of limiting reagents. In order to assemble a car, 4 tires and 2 headlights are needed among other things. In this example, imagine that the tires and headlights are reactants while the car is the product formed from the reaction of 4 tires and 2 headlights. If you have 20 tires and 14 headlights, how many cars can be made?
When there is not enough of one reactant in a chemical reaction, the reaction stops abruptly. To figure out the amount of product produced, it must be determined which reactant will limit the chemical reaction the limiting reagent and which reactant is in excess the excess reagent. One way of finding the limiting reagent is by calculating the amount of product that can be formed by each reactant; the one that produces less product is the limiting reagent. The following scenario illustrates the significance of limiting reagents. In order to assemble a car, 4 tires and 2 headlights are needed among other things. In this example, imagine that the tires and headlights are reactants while the car is the product formed from the reaction of 4 tires and 2 headlights. If you have 20 tires and 14 headlights, how many cars can be made?
Limiting reagent calculator
In addition to the assumption that reactions proceed all the way to completion, one additional assumption we have made about chemical reactions is that all the reactants are present in the proper quantities to react to products; this is not always the case. However, there are not enough oxygen atoms to use up all the hydrogen atoms. We run out of oxygen atoms and cannot make any more water molecules, so the process stops when we run out of oxygen atoms. A similar situation exists for many chemical reactions: you usually run out of one reactant before all of the other reactant has reacted.
2d thai stock set number today
Convert all given information into moles most likely, through the use of molar mass as a conversion factor. Balance the chemical equation for the chemical reaction. Because the consumption of alcoholic beverages adversely affects the performance of tasks that require skill and judgment, in most countries it is illegal to drive while under the influence of alcohol. Find the limiting reagent by looking at the number of moles of each reactant. How to calculate theoretical yield? A Always begin by writing the balanced chemical equation for the reaction:. Assume you have invited some friends for dinner and want to bake brownies for dessert. To calculate the mass of titanium metal that can obtain, multiply the number of moles of titanium by the molar mass of titanium Go back to previous article. Burglar cat with stripes and eye mask holding a stolen hot dog bun. As indicated in the strategy, this number can be converted to the mass of C 2 H 5 OH using its molar mass:. You can then multiply this number by the stoichiometry of the desired product to find the number of moles formed, then use this to derive the theoretical yield. The reaction used in the Breathalyzer is the oxidation of ethanol by the dichromate ion:. Therefore, by either method, C 2 H 3 Br 3 is the limiting reagent.
The Limiting and Excess Reactants Calculator is an essential tool in the field of chemistry, particularly beneficial for students, educators, and professionals.
Because there are only 0. Limiting Reactants in Solutions The concept of limiting reactants applies to reactions carried out in solution as well as to reactions involving pure substances. It looks like calcium carbonate is the limiting reagent. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Downvote Button navigates to signup page. Because the number of cars formed by 20 tires is less than number of cars produced by 14 headlights, the tires are the limiting reagent they limit the full completion of the reaction, in which all of the reactants are used up. The actual yield of a reaction is typically reported as a percent yield , or the percentage of the theoretical yield that was actually obtained. Summary The stoichiometry of a balanced chemical equation identifies the maximum amount of product that can be obtained. No , the limiting reactant is not the theoretical yield. Now consider a chemical example of a limiting reactant: the production of pure titanium. Step 5: The reactant that produces a larger amount of product is the excess reagent. To find the theoretical yield, you can follow the steps below: Find the moles of the limiting reagent.

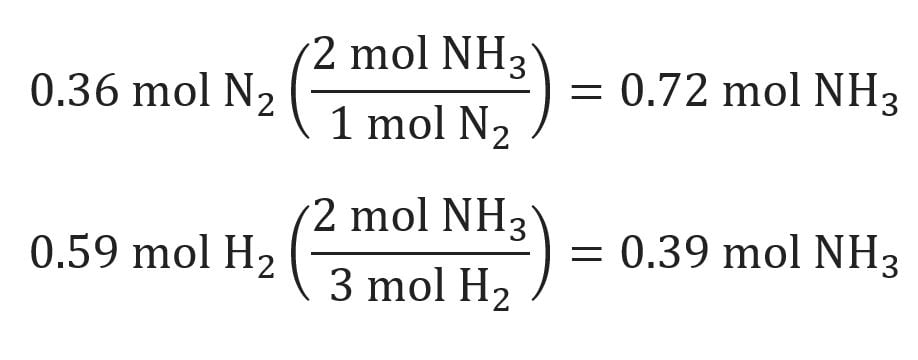
0 thoughts on “Limiting reagent calculator”