Lhs in maths means
Mathematics is a field that necessitates exactitude and deliberation at each and every stage of the problem-solving process, lhs in maths means. The left-hand side, also known as the LHS of an equationis considered to be one of the most fundamental mathematical ideas.
A linear equation is present in the forms of one-variable, two, or three-variable. In this method, the variable part and the constant part of the equation are separated from each other so that the value of the variable part can be found. The value is then put into the initial equation to check whether the correct value was found. To solve the linear equation with two variables, methods like. Substitution method. Elimination method. Cross multiplication method, and.
Lhs in maths means
In mathematics , LHS is informal shorthand for the left-hand side of an equation. Similarly, RHS is the right-hand side. The two sides have the same value, expressed differently, since equality is symmetric. More generally, these terms may apply to an inequation or inequality ; the right-hand side is everything on the right side of a test operator in an expression , with LHS defined similarly. In solving mathematical equations, particularly linear simultaneous equations , differential equations and integral equations , the terminology homogeneous is often used for equations with some linear operator L on the LHS and 0 on the RHS. In contrast, an equation with a non-zero RHS is called inhomogeneous or non-homogeneous , as exemplified by. Then any solution of the inhomogeneous equation may have a solution of the homogeneous equation added to it, and still remain a solution. For example in mathematical physics , the homogeneous equation may correspond to a physical theory formulated in empty space , while the inhomogeneous equation asks for more 'realistic' solutions with some matter, or charged particles. More abstractly, when using infix notation. This usage is less common, though. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history.
Determine the value of the variable in an equation with one variable as the first step in the process of solving the equation. Tools Tools.
.
Intro Trying Stuff A Trick. Proving an identity is very different in concept from solving an equation. Though you'll use many of the same techniques, they are not the same, and the differences are what can cause you problems. An identity is a tautology; that is, an identity is an equation or statement that is always true, no matter what you plug in for the variable. To prove an identity, you have to use logical steps to show that one side of the equation can be transformed into the other side of the equation. You do not plug values into the identity to prove anything. There are infinitely-many values you can plug in. Are you really going to prove anything by listing three or four values where the two sides of the equation are equal? Of course not.
Lhs in maths means
Medical » Physiology -- and more Miscellaneous » Unclassified. Community » Schools. Computing » File Extensions. Computing » General Computing. Regional » Airport Codes. Governmental » US Government. We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe. If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Hanging monkey toy
Cross multiplication method, and. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. The LHS is also significant in defining the type of mathematical operation that must be performed in order to solve a problem. Search for:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Algebraic inequality. Equations in mathematics are utilized to both solve difficult issues and generate accurate forecasts in a variety of professions, including engineering, finance, and design. The left-hand side, or LHS , of an equation, is an important notion in mathematics since it assists in determining the value of the unknown quantity and lays the groundwork for finding a solution to the problem. If LHS is not equal to RHS, then the value of the variable you found is incorrect, or the equation does not have a value that would equate them. A linear equation is present in the forms of one-variable, two, or three-variable. Contents move to sidebar hide.
In mathematics, inequality occurs when a non-equal comparison is made between two mathematical expressions or two numbers.
Plotting the graph method. A linear equation is present in the forms of one-variable, two, or three-variable. The order in which these terms are written is important. The left-hand side, or LHS , of an equation, is an important notion in mathematics since it assists in determining the value of the unknown quantity and lays the groundwork for finding a solution to the problem. Less Hour Side. An equation is said to be rational if it contains fractions with a variable, and either the numerator, the denominator, or both have fractions containing a variable. Ans: Left Hand Side. Download as PDF Printable version. Search for:. For example in mathematical physics , the homogeneous equation may correspond to a physical theory formulated in empty space , while the inhomogeneous equation asks for more 'realistic' solutions with some matter, or charged particles. More generally, these terms may apply to an inequation or inequality ; the right-hand side is everything on the right side of a test operator in an expression , with LHS defined similarly. This article needs additional citations for verification. Algebraic equality. To discover the answer to a mathematical issue, you must first determine the value of the variable that represents the unknown quantity and write it down on the left-hand side of the equation.

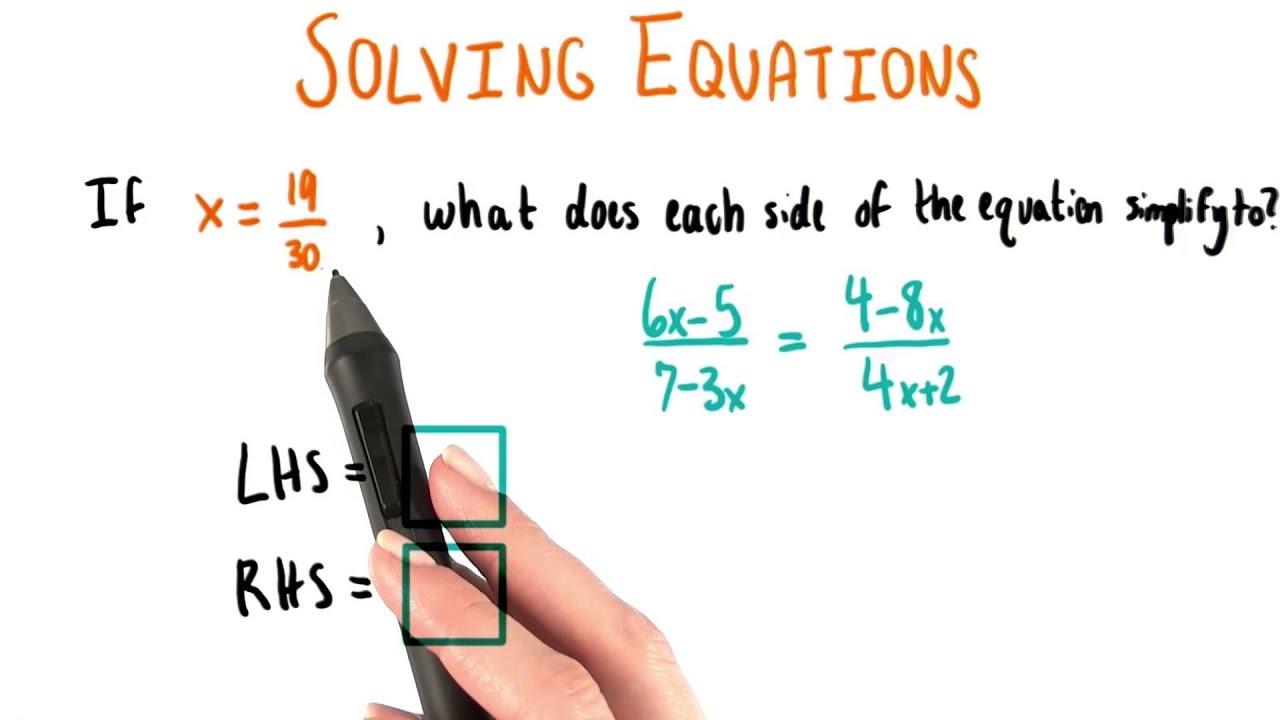
I do not understand