Lewis structure of sf6
This article is about the SF6 Lewis Structure, the Molecular geometry, and the formal charge present in the molecule.
Draw the Lewis structure of HCN. Draw the Lewis structure of B e C l 2. Draw the Lewis structure of C l O 4 per chlorate ion. Write the Lewis dot structure of C O molecule. Draw the Lewis structure of nitric acid, H N O 3.
Lewis structure of sf6
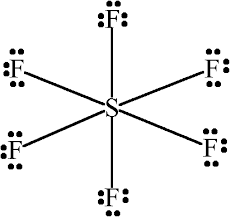
Sulfur atom S is the central atom, fluorine atom F is the external atom, sulfur atom S and each fluorine atom F are connected by a single bond, each fluorine atom F has three lone pairs of electrons, and the central atom is symmetrically distributed around. The SF6 bond angle is 90 degrees. The SF6 Lewis structure is shown below:. Based on the information in the periodic table, we are able to obtain: Sulphur S and fluorine F are in the 16th and 17th group of the periodic table. The central atom must have a high valence or minimal electronegativity. For the SF6 molecule, sulfur has a maximum valence of 6 and fluorine has a maximum valence of 1; and Sulfur has a lower electronegativity than oxygen, so the sulfur atom is the central atom and the fluorine atom is the outer atom. For SF6 molecule, Total number of pairs of electrons are These lone electrons repel each other and maintain symmetry around the central atom. When many atoms in an ion or molecule are positively or negatively charged, or when there are more charges on the atoms e. Therefore, if possible, we should try to minimise the charges on the atoms. But in the SF6 molecule, we don't need to reduce the charge on the atoms because there are more than 8 electrons in the outer shell of sulphur, the reason is that some atoms can expand their valence shells to accommodate more electrons to achieve a stable structure. And the external fluorine atoms have formed an octet, so they are also stable. In the SF6 molecule, the total number of electrons in the sulphur is 16, so the shell layer is populated with different energy levels depending on its capacity and level of hierarchy. The hybridisation of sulphur is then 3s2 3p4. The hybridisation of fluorine is 2s2 2p5.
Because the structure of Sulfur hexafluoride comprises a central Sulfur atom around which 12 electrons or 6 electron pairs are present and no lone pairs, therefore molecular geometry of SF6 will be octahedral.
.
SF 6 sulfur hexafluoride has one sulfur atom and six fluorine atoms. In the SF 6 Lewis structure, there are six single bonds around the sulfur atom, with six fluorine atoms attached to it, and on each fluorine atom, there are three lone pairs. In the periodic table , sulfur lies in group 16, and fluorine lies in group Hence, sulfur has six valence electrons and fluorine has seven valence electrons. Learn how to find: Sulfur valence electrons and Fluorine valence electrons. We have a total of 48 valence electrons. And when we divide this value by two, we get the value of total electron pairs. Since sulfur is less electronegative than fluorine, assume that the central atom is sulfur. Here, we have a total of 24 electron pairs.
Lewis structure of sf6
Sulfur hexafluoride or SF6 is an inorganic, greenhouse gas. It is non-flammable, odourless, and colourless, and is an excellent insulator. It is a hypervalent octahedral molecule that has been an interesting topic of conversation among chemistry enthusiasts. Henri Moissan discovered the existence of SF6. Incidentally, he is also the discoverer of fluorine. The standard way of synthesizing SF6 is to expose S8 to F2. This method causes the formation of a few sulfur fluorides, but those can be eliminated through heating and then using NaOH to remove any additional SF4 molecules.
Conde nast internships summer 2020
As a result, the difference between the electronegativity of atoms is precisely proportional to the polarity of a molecule. Two primary factors recommend its usage:. It is an essential component for energy production in cells XeF2 is isostructural with For SF6 molecule, Total number of pairs of electrons are In TeCl4, the central tellurium involves the hybridization. The hybridization of oxygen atom in H2O2 is Lewis structure of any molecule is important because. Draw the Lewis structure for S F 6. These single electrons compete with one another to maintain the symmetry of the central atom. Importance of Lewis Structure. It is the most basic and limiting explanation of the electrical structure. The molecular geometry of SF6 and shape is octahedral and the bond angle is 90 degrees. In which of the following pairs are the two species isostructural? SF6 has different physical and chemical characteristics which have been discussed in that article.
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms.
Because Sulphur is less electronegative than Fluorine, it will assume the middle position. For ultrasonography, these microbubbles increase the visibility of blood vessels. Dielectric Medium. Post not marked as liked. In TeCl4, the central tellurium involves the hybridization. This theory is concerned with electron repulsion and the need for compounds to take on a form to achieve stability. Sulfur can retain more than 8 electrons in its final shell. For the SF6 molecule, sulfur has a maximum valence of 6 and fluorine has a maximum valence of 1; and Sulfur has a lower electronegativity than oxygen, so the sulfur atom is the central atom and the fluorine atom is the outer atom. As a result, Sulfur has a high priority for being the central atom. Write the Lewis dot structure of C O molecule. The SF6 bond angle is 90 degrees. Draw the Lewis structure of C l O 4 per chlorate ion.

0 thoughts on “Lewis structure of sf6”