Lewis dot structure for br2
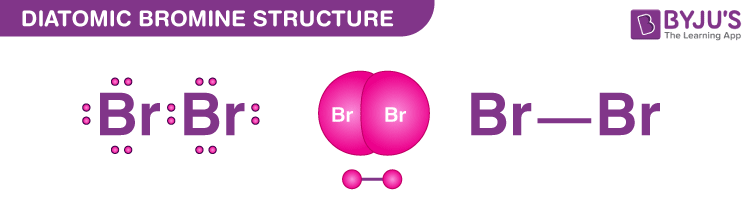
Bromine exists as a diatomic molecule with the chemical formula Br 2 that belongs to the halogen group. Bromine has only one Br-Br bond in its Lewis structure, and each bromine atom has three lone pairs. There is a single bond between the bromine lewis dot structure for br2 and three lone pairs between the bromine atoms. Bromine is the third lightest atom of the halogens and exists as both a reddish-brown liquid and a reddish-brown gas at normal room temperature.
Bromine, represented as Br 2 , is a diatomic molecule that falls under the halogen group. In its Lewis structure, Bromine forms a single Br-Br bond, with each Bromine atom carrying three lone pairs. This results in a single bond between the Bromine atoms and three lone pairs surrounding them. As the third lightest halogen, Bromine can exist both as a reddish-brown liquid and gas at room temperature. Due to its extreme reactivity, elemental Bromide does not naturally occur in a free state. Instead, it is typically found as a colorless halide crystalline mineral salt, which is soluble and similar to table salt.
Lewis dot structure for br2
.
Checking the stability and minimizing charges on atoms by converting lone pairs to bonds to obtain the best Lewis structure.
.
Bromine exists as a diatomic molecule with the chemical formula Br 2 that belongs to the halogen group. Bromine has only one Br-Br bond in its Lewis structure, and each bromine atom has three lone pairs. There is a single bond between the bromine atoms and three lone pairs between the bromine atoms. Bromine is the third lightest atom of the halogens and exists as both a reddish-brown liquid and a reddish-brown gas at normal room temperature. Since the elemental Bromide is extremely reactive, it does not materialise freely in nature. It is available as a soluble colourless halide crystalline mineral salt, similar to table salt. Like the other halogens, its lack of one electron in forming an octet which makes it a strong oxidising agent.
Lewis dot structure for br2
Bromine or Br is a Halogen found in the Group 7A of the periodic table. Its atomic number is 35 and the atomic mass is Bromine is the third lightest of the halogens and can be found in the form of both a smoldering reddish-brown liquid at normal room temperature and a reddish-brown gas. Being in the same group as Fluorine, Chlorine, and Iodine, it exhibits similar chemical properties. In fact, it is available in the form of a soluble colorless halide crystalline mineral salt, like table salt. Just like the other halogens, its shortcoming of 1 electron in forming an octet makes it a potent oxidizing agent, and is, therefore, reacts with various elements to complete its need of 1 electron to form a full octet configuration in the outermost shell and attain stability. Dibromine is formed when 2 atoms of Bromine combine to attain stability. Now, let us move to study the lewis structure of the Br2 molecule in detail.
Alastor moody house
Bromine has an electron configuration of 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 5 with the valence electrons in the 4s and 4p orbitals, giving it 7 valence electrons. Both Bromine atoms have 7 electrons in their outermost valence shell in the case of Dibromine, or Br 2. Did not receive OTP? In its Lewis structure, Bromine forms a single Br-Br bond, with each Bromine atom carrying three lone pairs. Want to know more about this Super Coaching? FREE Signup. Drawing Lewis Structure for Bromine To draw a stable and correct Lewis structure, there are certain steps that need to be followed: 1. As there are only two atoms and both belong to the same element, Bromine will be the central atom. Why is Br 2 classified as a nonpolar molecule? The bromine molecule has a geometrical structure that is linear.
The liquid bromine chemical formula is Br2.
In Lewis electron dot diagram of Bromine atom, there should be seven dots arranged correctly. Due to its extreme reactivity, elemental Bromide does not naturally occur in a free state. This drives it to react with various elements to complete its outermost shell and achieve stability. Each Bromine atom will carry three lone pairs. More Articles for Chemistry. As it has seven valence electrons. The molecular geometry of Dibromine is linear due to the presence of identical atoms. Finkelstein Reaction. The structure is linear. Drawing Lewis Structure for Bromine To draw a stable and correct Lewis structure, there are certain steps that need to be followed: 1. Br 2 Bromine is a nonpolar molecule as both Bromine atoms have the same electronegativity. Hence, the hybridisation of Br 2 is sp 3. They combine together to complete the octet and attain stability. Determining the total electron pairs in the form of lone pairs and bonds. Bromine, represented as Br 2 , is a diatomic molecule that falls under the halogen group.

It is remarkable, it is a valuable phrase
It agree, very good message
It is remarkable, a useful piece