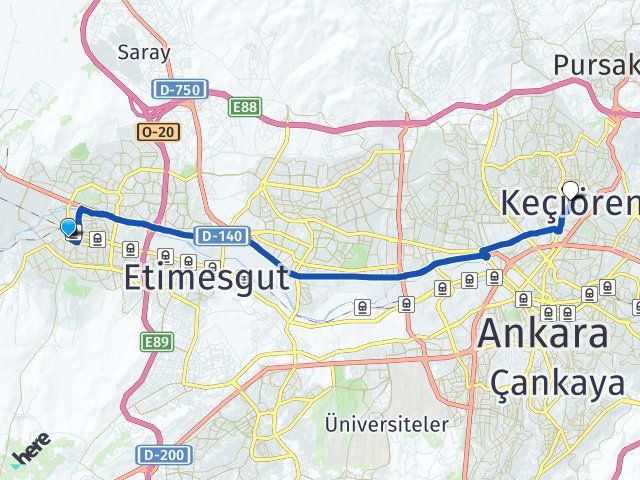
Istanbul ankara sincan kaç km
By using our site, you agree to our collection of information through the use of cookies.
Important - This site makes use of cookies which may contain tracking information about visitors. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies. Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data. Cookies cookie Description Expiry Date. Functional cookies help perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collecting feedback, and other third-party features.
Istanbul ankara sincan kaç km
.
Urban transport is derived from capital accumulation activities and is a vital component for capital accumulation needs.
.
Sincan is a municipality and metropolitan district of Ankara Province , Turkey. Its elevation is m 2, ft. Sincan District hosts ASO 1. Sincan stands on a plain surrounded by hills and watered by the Ankara River, a tributary of the Sakarya River. There is some agriculture and light industry in Sincan, but the majority of people commute to Ankara by rail. The symbol of the municipality is the tulip. There are 57 neighbourhoods in Sincan District: [6]. This was the furthest spot in Anatolia in which the Greek Army had advanced to.
Istanbul ankara sincan kaç km
The route deemed to be the safest and simplest with minimal scope for error along the way. The default recommended route from Michelin. The route offering the shortest distance to a destination via the most accessible roads. Journey times for this option will tend to be longer. Driving directions Fast.
Viral.joshi
Neo-liberal policies adopted all over the world and in Turkey after the 's, have amplified urban transport problems for both urban dwellers and other sectors of society that use the existing transportation system. Figure 1. Debts were used for keeping economic balance or aiding existing balance in well working economies of developed countries. Brenner emphasized that any researcher would fall into error when he or she uses a single theory. The development concept has many different definitions and Turkey is assessed as both developing and developed country according to different classifications. Developed countries limit production and direct their automotive production plants to developing countries as assembly plants with its high carbon footprint where environmental issues are less important compared to economic benefits of having a car assembly plant. On the other hand, this term forced governments to take restrictions and they organized awareness-raising campaigns for reducing energy usage and look into new alternative energy production ways. They facilitate profit-oriented activities of other commercial actors; like multi-national companies and other foreign firms with operations on different continents of a borderless globe. Giddens and Thrift emphasized that decisions which do not have any spatial context have effect on behaviors of agents and thereby spatial development process. Another characteristic is that the assemblages are product of recurrent processes and this implies that they always exist in populations. According to Weberian urban explanation of "Urban Managerialism" Pahl, , bureaucratic and market processes have determinative role in defining social mechanisms, while production processes do not have any effect. This long period of urban transport policies, which clearly contradicts universally accepted planning approaches for sustainable transport, deserves an in-depth analysis.
.
They are treated as independent variables and capitalist processes do not limit behaviors of these managers. Besides, influences of three level interacting assemblages are evaluated through the definition of political and economic changes in time, as well as planned and unplanned intervention decisions of the municipality. This chapter also comprises the analysis of urban transport developments on a chosen corridor in Ankara. Arzu Kocabas. However, assessment of his personality and personal relationships as the only cause of unfair and entrepreneurialist spatial development will be insufficient. Both urban entrepreneurialism and urban assemblages have explanatory sides for recent changes in urban policy formulation and urban growth strategies after the 's all over the world. A part may be detached and made a component of another assemblage. After the fifties with rapid urbanization Ankara, Istanbul and other major cities faced huge migration waves. Besides, congestion is seen as a major threat for reaching economic, social and environmental goals. Official and unofficial data guided the thesis study. In order to clarify this motorized traffic oriented urban transport development national policies and economic dynamics, defining national assemblages are discussed in Chapter 4 in relation to upper level influences defined in this Chapter. New right appeared all over the world to solve problems of welfare state with the argument that needs of societies and well-being would be achieved only by an unlimited free market. In this chapter, international and supranational assemblages and developments influencing urban transport planning attitudes and projects are explained briefly considering "developing country" position of Turkey. This long period of urban transport policies, which clearly contradicts universally accepted planning approaches for sustainable transport, deserves an in-depth analysis. They arranged commissions in international organizations and signed international agreements1 for controlling damaging effects of this trend and they took measures at both national and urban levels to stop or slow environmental deterioration.

0 thoughts on “Istanbul ankara sincan kaç km”