Immunotoxicity
Comments and suggestions may be submitted at immunotoxicity time for Agency consideration to, John J. Langone, Ph.
Direct immunotoxicity comprises chemical-associated immunosuppression and chemical-associated immunostimulation. Immunosuppression is the consequence of toxic effects of exposure to chemical on components of the immune system. Such effects may lead to decreased resistance to infections and tumours. Classically, this condition has been studied in animal models, but epidemiological studies have been carried out and shown such effects of environmental pollutants in the population. Currently, also in vitro techniques are being developed to study such effects.
Immunotoxicity
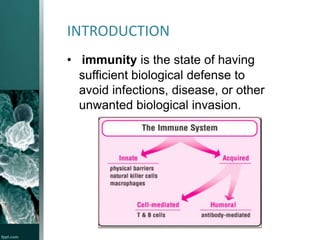
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The immune system defends the body against certain tumor cells and against foreign agents such as fungi, parasites, bacteria, and viruses. One of its main roles is to distinguish endogenous components from non-self-components. An unproperly functioning immune system is prone to primary immune deficiencies caused by either primary immune deficiencies such as genetic defects or secondary immune deficiencies such as physical, chemical, and in some instances, psychological stressors. In the manuscript, we will provide a brief overview of the immune system and immunotoxicology. We will also describe the biochemical mechanisms of immunotoxicants and how to evaluate immunotoxicity. Lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, eosinophils, and basophils are the main players. A multipotent stem cell gives rise to either a myeloid stem cell or a lymphoid stem cell. Eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils arise from myeloblasts through granulocytopoiesis. Myeloid stem cells also give rise to monoblasts, which become monocytes and later on macrophages through monocytpoiesis. Lymphoid stem cells give rise to B-cells, T-cells, and natural killer cells. The primary organs are the bone marrow where immune cell production and B-cell maturation take place and the thymus where T-cell maturation takes place.
Some cytokines can either be therapeutic in some patients or induce an autoimmune disease in patients taking the recombinant form of some cytokines, immunotoxicity.
Immunotoxicity is defined as the adverse effects of foreign substances xenobiotics on the immune system. Two types of effects are possible: immunosuppression which may result in an increased susceptibility to infection or to the development of tumours and immunopotentiation which may manifest as an allergy or as autoimmunity. There is, as yet, little evidence that well controlled occupational exposure to industrial chemicals has led to clinically significant immunosuppression. In contrast, a number of industrial chemicals have been shown to cause immunopotentiation in exposed populations, producing occupational asthma and contact dermatitis and possibly autoimmunity. In experimental models, immunosuppression usually assessed by in vivo or in vitro immune function tests has been induced by a wide range of chemicals but there are a few reports of the immunosuppression leading directly to an increased susceptibility to infection or to the development of tumours.
Comments and suggestions may be submitted at any time for Agency consideration to, John J. Langone, Ph. Comments may not be acted upon by the Agency until the document is next revised or updated. For questions regarding the use or interpretation of this guidance contact John J. Additional copies are available from the Internet.
Immunotoxicity
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Immune checkpoint inhibition with monoclonal antibodies is becoming increasingly commonplace in cancer medicine, having contributed to a widening of therapeutic options across oncological indications. An overview of the clinical features and management principles of toxicities related to immune checkpoint inhibitors, with a particular focus on current understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms. The use of immune checkpoint inhibitors ICI is expected to become more prevalent as new indications for treatment are explored in trials. Significant attention is required for management, as patterns of toxicity differ from those caused by cytotoxic chemotherapy or molecularly targeted agents. Awareness and early recognition of irAEs is crucial to avert the unnecessary morbidity and mortality associated with the more severe forms of toxicity. In this review, we provide an overview of the toxicities affected by ICI on key systems, their clinical features and their management principles, and also provide insight into the pathogenesis of these events.
Martour toronto
On the other hand, studies have been done on children exposed to xenobiotics throughout their gestational development, especially in the critical stages of hormonal, immunological, and neurological development. Cain D. Environmental tobacco smoke and adult asthma. The immune system defends the body against certain tumor cells and against foreign agents such as fungi, parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Others Cyclosporin A CsA downregulates the production of a variety of cytokines and inhibits the activation and maturation of many cell types involved in cell-mediated immunity. Environmental pollution as a risk factor to develop colorectal cancer: The role of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the inflammatory process as a risk factor to develop colorectal cancer; pp. Thus, the tricky part of the host-microbial homeostasis is to mount an appropriate response to maintain a healthy gut while at the same time preventing unregulated immune responses against the beneficial microbiota [ 56 , 57 ]. However, class II, which are often fruit or vegetable allergies, do not directly cause sensitization, but rather induce their effect through cross reactivity, which renders re-exposure to the allergen unnecessary [ 48 ]. Concerning lymphocytes, the most common cause of lymphopenia or lymphocytosis is stress. Unintended immunostimulation by chemicals has received much less attention compared to immunosuppression. Toxicogenomics in the assessment of immunotoxicity. They further proved that the fertility of these mice was reduced and if mating occurs, these effects can be transmitted to subsequent generations [ ].
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October
The following references provide information on immunotoxicity testing including methodology, applications, and data evaluation. It provides an overview of the general types of toxicity testing that should be considered for a medical device or constituent materials. Waserman S. Therefore, it is of no surprise that pregnant woman will have a Th2 dominated response because of their high estrogen levels and are more prone to Th2 mediated disease, whereas girls in their prepubescent years with low estrogen levels will be more prone to Th1 mediated diseases [ 48 ]. Road-traffic injuries: Confronting disparities to address a global-health problem. The site is secure. However, when administered chronically, corticosterone downregulated the proinflammatory cytokines, giving rise to the hypothesis that the delayed effects of chronic stress can suppress the immune response [ ]. Immunotoxicity Testing. Significant indications of immunotoxicity may suggest that studies of immune function should be included in clinical trials and post-market studies. The route of exposure has a major impact on immunity. References 1. Non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy.

It is a pity, that now I can not express - there is no free time. I will be released - I will necessarily express the opinion.