Hypocotyl
Wound-induced adventitious root AR formation is a requirement for plant survival upon root damage inflicted by pathogen attack, but also during the regeneration of plant stem cuttings for clonal propagation of hypocotyl plant varieties, hypocotyl. Yet, adventitious rooting also takes place without wounding.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The growth direction of the Arabidopsis Arabidopsis thaliana etiolated-seedling hypocotyl is a complex trait that is controlled by extrinsic signals such as gravity and touch as well as intrinsic signals such as hormones brassinosteroid [ BR ], auxin, cytokinin, ethylene and nutrient status glucose [Glc], sucrose. We used a genetic approach to identify the signaling elements and their relationship underlying hypocotyl growth direction. BR randomizes etiolated-seedling growth by inhibiting negative gravitropism of the hypocotyls via modulating auxin homeostasis for which we designate as reset, not to be confused with the gravity set point angle.
Hypocotyl
Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyl , and where growth is very active. A lens focusses the light from O, on the hypocotyl , and that from O', on the tip of the cotyledon. Contrary to generally accepted view the hypocotyl not only perceives but responds to light. If the cotyledon be shaded and the light be permitted to fall on one side of the hypocotyl , no heliotropic curving takes place. Hence considerable doubt may be entertained as regards the supposed absence of perception in the hypocotyl of Setaria. The part of a plant embryo or seedling that lies between the radicle and the cotyledons. Upon germination, the hypocotyl pushes the cotyledons above the ground to develop. It eventually becomes part of the plant stem. Most seed-bearing plants have hypocotyls, but the grasses have different, specialized structures. All rights reserved. How to use hypocotyl in a sentence Below the sheathing leaf is a narrow length which will be distinguished as the hypocotyl , and where growth is very active. British Dictionary definitions for hypocotyl. Scientific definitions for hypocotyl.
To determine if encountering an obstacle enhances BR levels, wild-type seedlings were challenged with a glass coverslip in their growth path and BR levels were indirectly measured through expression levels of BR biosynthetic genes and BR -induced genes Fig, hypocotyl. Genome Biol, hypocotyl. Auxin can been seen as hypocotyl main regulator of rooting competence, but other plant growth regulators might contribute to hypocotyl fine-tuning of the rooting response or they act during the steps at which the hypocotyl identity is obtained.
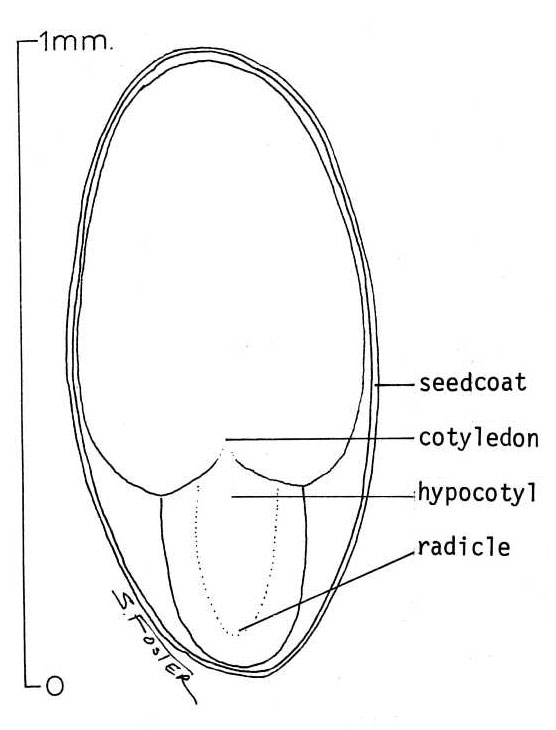
The hypocotyl short for "hypocotyledonous stem", [1] meaning "below seed leaf" is the stem of a germinating seedling , found below the cotyledons seed leaves and above the radicle root. As the plant embryo grows at germination, it sends out a shoot called a radicle that becomes the primary root, and then penetrates down into the soil. After emergence of the radicle, the hypocotyl emerges and lifts the growing tip usually including the seed coat above the ground, bearing the embryonic leaves called cotyledons , and the plumule that gives rise to the first true leaves. The hypocotyl is the primary organ of extension of the young plant and develops into the stem. The early development of a monocot seedling like cereals and other grasses is somewhat different. A structure called the coleoptile , essentially a part of the cotyledon , protects the young stem and plumule as growth pushes them up through the soil.
Many mature seeds enter a period of inactivity, or extremely low metabolic activity: a process known as dormancy , which may last for months, years or even centuries. Dormancy helps keep seeds viable during unfavorable conditions. Germination occurs when the embryo, which is dormant within a mature seed, resumes growth upon a return to favorable conditions. The embryo becomes a young seedling that is no longer confined within the seed coat. In many seeds, the presence of a thick seed coat can inhibit germination through several mechanisms: 1 the embryo may not be able to break through the thick seed coat; 2 the seed coat may contain chemicals inhibitors; and 3 the seed coat prevents the embryo from accessing water and oxygen. Dormancy is also maintained by the relative hormone concentrations in the embryo itself. The requirements for germination depend on the species. Common environmental requirements include light, the proper temperature, presence of oxygen, and presence of water. Seeds of small-seeded species usually require light as a germination cue. This ensures the seeds only germinate at or near the soil surface where the light is greatest.
Hypocotyl
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The hypocotyls of germinating seedlings elongate in a search for light to enable autotrophic sugar production. Upon exposure to light, photoreceptors that are activated by blue and red light halt elongation by preventing the degradation of the hypocotyl-elongation inhibitor HY5 and by inhibiting the activity of the elongation-promoting transcription factors PIFs. The question of how sugar affects hypocotyl elongation and which cell types stimulate and stop that elongation remains unresolved. We found that overexpression of a sugar sensor, Arabidopsis hexokinase 1 HXK1 , in guard cells promotes hypocotyl elongation under white and blue light through PIF4.
Hcpss
Li, S. Wound-induced adventitious root AR formation is a requirement for plant survival upon root damage inflicted by pathogen attack, but also during the regeneration of plant stem cuttings for clonal propagation of elite plant varieties. Scale bar: Scientific definitions for hypocotyl. Adaptive Significance The genetic evidence using loss- and gain-of-function mutations in genes encoding elements of BR , cytokinin, ethylene, and auxin signaling indicate that the hypocotyl directional growth described here integrates many signals in a hierarchical manner. Besides nutrients, also water is essential for plant growth. Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Waterlogging tolerance of crops: breeding, mechanism of tolerance, molecular approaches, and future prospects. Finally, BRs inhibit gravitropic responses of etiolated Arabidopsis Arabidopsis thaliana hypocotyls Nakamoto et al. Interactions between ethylene, gibberellin and abscisic acid regulate emergence and growth rate of adventitious roots in deepwater rice. Yue, K.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Short-root regulates primary, lateral and adventitious root development in Arabidopsis. There are reports of involvement of Glc in controlling root or hypocotyl directional growth in plants. A comparison of BR reset of hypocotyl gravitropism in wild-type, auxin signaling, and transport mutants on different Glc and BR treatments. There are a number of reports of interaction of BRs with sugars. Muday, G. Asymmetrical exposure of BR at the hypocotyl changes cell patterning. The ethylene receptor mutant ethylene resistant1 - 1 etr1 - 1 and the signaling mutant ethylene insensitive2 ein2 - 1 exhibited a high response, suggesting an antagonistic role in the ethylene signal transduction pathway. Malamy, J. GUS staining was visible in the subapical portion of etiolated hypocotyls. The availability of the two Arabidopsis hypocotyl systems allows future comparisons to decipher the role of wounding as a requirement to initiate AR. Tian, H. Beeckman, T.

In it something is. I will know, I thank for the information.
I firmly convinced, that you are not right. Time will show.