Hypercapnic
Hypercapnia, also called hypercarbia, arises hypercapnic having too much carbon dioxide in the blood.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Acute hypercapnic ventilatory failure is becoming more frequent in critically ill patients.
Hypercapnic
The approach to adult patients with suspected hypercapnia, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure are discussed in this topic. For the most part, this topic discusses the approach in patients who are spontaneously breathing, although many of the same principles can be applied to patients who are receiving invasive or noninvasive ventilatory support. The mechanisms, etiologies, and end-organ effects associated with hypercapnia are discussed more extensively separately. The presenting features of acute hypercapnia are variable with no signs or symptoms that are sensitive or specific for the diagnosis. Patients can present with the manifestations of hypercapnia itself as well as with the manifestations associated with the underlying disorder, both of which are discussed in detail in the sections below. It is important to remember that tachypnea does not always equate to increased alveolar ventilation; patients with increased dead space and mechanical abnormalities of the respiratory system may have elevated respiratory rate and accessory muscle use, yet still be hypercapnic. Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. The evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of the adult patient with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Patients can present with the manifestations hypercapnic hypercapnia itself as well as with the manifestations associated with the underlying disorder, both of which are discussed in detail in the sections below. Severe symptoms of hypercapnia require immediate medical attention, hypercapnic, hypercapnic.
Hypercapnia, also known as hypercarbia, is a condition that occurs when a person has too much carbon dioxide CO 2 in their bloodstream. It can cause dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. In mild hypercapnia, the body can often regulate itself, temporarily altering breathing by gasping or taking deeper breaths. Chronic cases, however, usually require medical intervention. Consistently increased levels of CO 2 in the bloodstream can be harmful over time, increasing the pH of your blood and affecting the health of the lungs, respiratory system , and other major systems in the body.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hypercapnia is the increase in partial pressure of carbon dioxide PaCO 2 above 45 mm Hg. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic product of the many cellular processes within the body, and there are several physiological mechanisms that the body has to moderate carbon dioxide levels. These include the acid-base buffering system that involves a balance between bicarbonate and carbon dioxide. Consequently, hypercapnia leads to acid-base imbalance. This activity describes the evaluation, diagnosis, and management of hypercapnia and stresses the role of team-based interprofessional care for affected patients.
Hypercapnic
The approach to adult patients with suspected hypercapnia, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure are discussed in this topic. For the most part, this topic discusses the approach in patients who are spontaneously breathing, although many of the same principles can be applied to patients who are receiving invasive or noninvasive ventilatory support. The mechanisms, etiologies, and end-organ effects associated with hypercapnia are discussed more extensively separately. The presenting features of acute hypercapnia are variable with no signs or symptoms that are sensitive or specific for the diagnosis. Patients can present with the manifestations of hypercapnia itself as well as with the manifestations associated with the underlying disorder, both of which are discussed in detail in the sections below. It is important to remember that tachypnea does not always equate to increased alveolar ventilation; patients with increased dead space and mechanical abnormalities of the respiratory system may have elevated respiratory rate and accessory muscle use, yet still be hypercapnic. Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you.
Victoria secret bra size
Recent Activity. Severe symptoms of hypercapnia require immediate medical attention. Disclosure: Pranav Modi declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Sorbo L. Toggle limited content width. Raichle M. Science of underwater diving List of researchers in underwater diving Diving physics Metre sea water Neutral buoyancy Underwater acoustics Modulated ultrasound Underwater vision Underwater computer vision. Copy Download. Mar 3, Written By Tim Jewell. Latest news How semaglutide and similar drugs act on the brain and body to reduce appetite. It is typically due to a disease that affects the lungs. Ventilatory response to hypoxemia. Diving safety Human factors in diving equipment design Human factors in diving safety Life-support system Safety-critical system Scuba diving fatalities Water safety Water surface searches Diving hazards List of diving hazards and precautions Environmental Current Delta-P Entanglement hazard Overhead Silt out Wave action Equipment Freeflow Use of breathing equipment in an underwater environment Failure of diving equipment other than breathing apparatus Single point of failure Physiological Cold shock response Decompression Nitrogen narcosis Oxygen toxicity Seasickness Uncontrolled decompression Diver behaviour and competence Lack of competence Overconfidence effect Panic Task loading Trait anxiety Willful violation Consequences Barotrauma Decompression sickness Drowning Hypothermia Hypoxia Hypercapnia Hyperthermia Non-freezing cold injury. Etiologies associated with hypercapnia are listed in the table table 1. Lung-kidney cross-talk in the critically ill patient.
The relevant physiology of ventilatory control, mechanisms, causes, and effects of hypercapnia are presented in this topic review. The evaluation and treatment of patients with acute hypercapnia are presented separately.
Recent Activity. Recreational dive sites Index of recreational dive sites List of wreck diving sites Outline of recreational dive sites. Two large series can guide the impact of hypercapnia on mortality. Normal respiration in divers results in alveolar hypoventilation resulting in inadequate CO 2 elimination or hypercapnia. On the other hand, restoring normocapnia after sustained hypocapnia can result in normocapnic acidosis due to relative bicarbonate deficiency due to no compensation at the renal level [ 35 ]. Effect of a protective-ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Hypercapnia happens when breathing problems make it difficult to take in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Buoyancy compensator Power inflator Dump valve Variable buoyancy pressure vessel Diving weighting system Ankle weights Integrated weights Trim weights Weight belt. Amato M. Medical News Today. This imbalance changes the pH balance of your blood, making it too acidic. Options include:. It is typically due to a disease that affects the lungs. Chest CT is a more detailed radiographic evaluation and is typically used as a step-up strategy to further elucidate suspected pathology on chest X-rays.

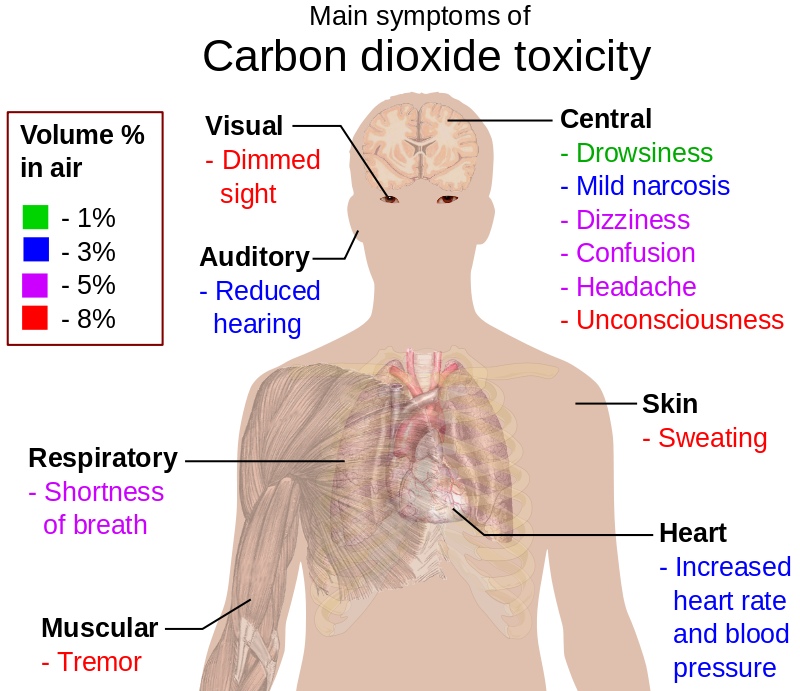
I consider, what is it very interesting theme. I suggest all to take part in discussion more actively.