Hybridization of carbon in co2
We will learn about the hybridization of CO 2 on this page.
To determine the hybridization of carbon dioxide, let us take the carbon atom first. The carbon atom has two double bonds, or two effective pairs exist in it. However, this is not enough to produce bonds with oxygen. So, then, one electron from 2s orbital moves from the 2s level to the 2p level that results in the formation of two hybrid orbitals. Now, these hybridized sp orbitals of carbon atoms overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to produce 2 sigma bonds. They are used to form a pi bond as for the two remaining p electrons.
Hybridization of carbon in co2
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of chemistry to explore the hybridization of CO 2. Carbon dioxide is an interesting molecule, with carbon at its core exhibiting sp hybridization. This hybridization arises due to the carbon atom being bonded to two other atoms, which can be either two double bonds or a combination of one single and one triple bond. We can understand this better by scrutinizing each atom of CO 2 more closely. When we discuss the hybridization of carbon dioxide, we start with the central carbon atom. This atom has two effective pairs, or two double bonds. However, to form bonds with oxygen, this is not sufficient. This is where the magic of hybridization comes into play. One electron from the 2s orbital hops to the 2p level, leading to the creation of two hybrid orbitals. These sp hybridized orbitals of the carbon atom then overlap with the p orbitals of the oxygen atoms, forming 2 sigma bonds.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Oxygen has the 1s2 2s2 2p4 electron configuration of the ground state. Purchase Now.
The carbon dioxide or CO2 has sp type hybridisation. This type of hybridisation occurs as an outcome of the carbon being bound to two different atoms. The atom of the carbon comprises 2 double bonds, i. However, this is not sufficient for creating bonds involving the oxygen. Therefore, one electron from the 2s orbital shifts from the 2s level to 2p level, which leads to the creation of 2 hybrid orbitals. These hybridised sp orbitals belonging to the carbon atoms extend beyond 2p orbitals that belong to the atoms of oxygen for creating two sigma bonds. A pi-bond is formed between the 2 leftover p electrons.
To determine the hybridization of carbon dioxide, let us take the carbon atom first. The carbon atom has two double bonds, or two effective pairs exist in it. However, this is not enough to produce bonds with oxygen. So, then, one electron from 2s orbital moves from the 2s level to the 2p level that results in the formation of two hybrid orbitals. Now, these hybridized sp orbitals of carbon atoms overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to produce 2 sigma bonds. They are used to form a pi bond as for the two remaining p electrons. In the carbon dioxide molecule, oxygen also hybridizes its orbitals to produce three sp2 hybrid orbitals.
Hybridization of carbon in co2
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the carbon dioxide molecule or CO2. Lewis structures, also known as electron dot diagrams, were introduced by Gilbert N. Lewis in They play a crucial role in visualizing the arrangement of valence electrons among atoms in a molecule, helping us predict its physical and chemical properties. A Lewis structure is a type of shorthand notation that scientists use to describe the distribution of electrons in molecules. Lewis structures are a foundational tool in chemistry, allowing us to visualize how atoms share or transfer electrons to form molecules. When creating the Lewis structure for carbon dioxide, we start with the central carbon atom, which forms double bonds with two oxygen atoms on either side. This process highlights the importance of understanding valence electrons as they determine how each atom interacts and forms bonds. Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Felicia vox
Particularly, note down the number of single, double, and triple bonds made by each atom. Now, these hybridized sp orbitals of carbon atoms overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to produce 2 sigma bonds. To determine the hybridization of carbon dioxide, let us take the carbon atom first. We can consider one of the 2s electrons to be excited to fill the other empty 2p orbital to provide a 1s2 2s1 2p3 configuration. Carbon has 6 electrons, whereas Oxygen has 8 electrons. Steps in the Ring Closure. So, place the Carbon in the middle and then keep the oxygen either side of that! This geometric shape is mainly due to the presence of a sigma bond and valence electron pairs repelling each other where they are forced to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom. Conclusion The hybridisation of carbon dioxide concludes how to find out the hybridisation of CO2. The formation of CO 2 consists of two particles: Oxygen and Carbon. Two of the 2p orbitals, for example, the 2px and 2pz, only hold one electron. We also learn the importance of XeF6 molecular geometry and bond angles importance and much more about the topic in detail. Last updated on Jul 31, If we talk about its uses, these are as follows:. Enthalpy of Neutralisation.
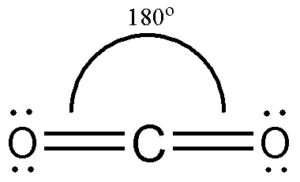
First, we need to draw the Lewis structure of CO 2.
However, out of these three sp hybrid orbitals, only one will be used to produce a bond with the carbon atom. Out of the three sp hybrid orbitals, only one is used to form a bond with the carbon atom. As a result, the carbon atom acquires such a linear molecular shape with symmetric charge distribution. Determine the overall hybridisation of the molecule by finding out the same for the atom present in the centre. Oxygen has 1s2 2s2 2p4 configuration of electrons that belong to the ground state. Hybridization of Carbon in CO 2. However, only 1 sp hybrid orbital will be used from these 3 sp hybrid orbitals to make a bond with carbon atoms. JEE Examination Scheme. Here, if it is bonded with four atoms, then it is Did not receive OTP?

I confirm. I join told all above. We can communicate on this theme.
It is simply excellent idea
Rather excellent idea and it is duly