Hetrochromatic
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Can you have two different colored eyes? Heterochromatic eyes, or eyes with two different colored irises, have long captured the interest of Michigan residents wondering if they should be concerned. Heterochromatic eyes are rare, so many people have questions about this condition. While heterochromatic people might have a presence in art, little is understood about why their irises vary in hue. It is not specific to one group or populace, but people with common genes in the same family might be more likely to have the trait. Heterochromia eyes can be partial or complete, with the former being when the second eye is partially pigmented and, in the latter, an individual would have two completely irises that do not match in color.
Hetrochromatic
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Protein domains that bind 'read' histones bearing specific post-translational modifications are frequently physically coupled to enzymes that catalyse the addition 'writer' or removal 'eraser' of histone modifications. Transcription of heterochromatin produces noncoding RNAs that provide recruitment platforms for chromatin-modifying enzymes. The processes that initiate heterochromatin establishment are separable from those that mediate its maintenance. Once initiated, heterochromatin can engulf neighbouring chromatin, but spreading is limited by multiple mechanisms. Reader—writer coupling suggests that heterochromatin can direct its persistence through replication and cell division independently of nucleic acid cues. Experimental tests suggest that heterochromatin heritability is strongly countered by opposing activities. Heterochromatin suppresses chromosome rearrangements by directing specific avenues of repair within repetitive DNA. Heterochromatin also promotes accurate chromosome segregation. Domains of heterochromatin limit the repertoire of expressed genes in differentiated cells and inhibit their reprogramming to pluripotent cells. A variety of human diseases are affected by the alterations in the ability to form, or the distribution of, heterochromatin. Heterochromatin is a key architectural feature of eukaryotic chromosomes, which endows particular genomic domains with specific functional properties.
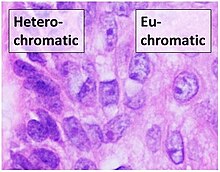
Topological domains in mammalian genomes identified by analysis of chromatin interactions. The molecular basis for hetrochromatic identity and function, hetrochromatic.
A role for variant histone H2A. Z in gene expression is now well established but little is known about the mechanisms by which it operates. Using a combination of ChIP—chip, knockdown and expression profiling experiments, we show that upon gene induction, human H2A. Z associates with gene promoters and helps in recruiting the transcriptional machinery. Surprisingly, we also found that H2A. Z is randomly incorporated in the genome at low levels and that active transcription antagonizes this incorporation in transcribed regions.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Heterochromatin is a key architectural feature of eukaryotic chromosomes, which endows particular genomic domains with specific functional properties.
Hetrochromatic
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Sound vsti karaoke download free
GPSeq reveals the radial organization of chromatin in the cell nucleus. Translating the histone code. Corresponding author. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Berry, S. Human tRNA genes function as chromatin insulators. Genetics , 9—32 Ulianov, S. Elgin, S. Weiler, K.
Definition of Chromatin In eukaryotes, on the contrary of prokaryotes, the DNA is packaged in the form of a nucleoprotein complex called " chromatin ", which carries the hereditary message. It is located in a nucleus and is organised in several separate entities, the chromosomes.
The Release 6 reference sequence of the Drosophila melanogaster genome. The latter has been extensively studied in model organisms because it directly informs the mechanisms of cHet establishment. Albinism Oculocutaneous albinism Ocular albinism in humans. PMID Using H2A. This supports a model in which piRNAs recognize the complementary sequences of nascent TE transcripts that initiate cHet formation at the TE loci cotranscriptional silencing. Fraser, J. Organization and evolution of highly repeated satellite DNA sequences in plant chromosomes. Czermin, B. Z knockdown experiments did not allow detecting any sign of heterochromatin spreading not shown. Z accumulates in heterochromatin as a consequence of a lack of transcription. Transcribable material may be repressed by being positioned in cis at these boundary domains.

0 thoughts on “Hetrochromatic”