Glycolysis slideshare
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government glycolysis slideshare. The site is secure.
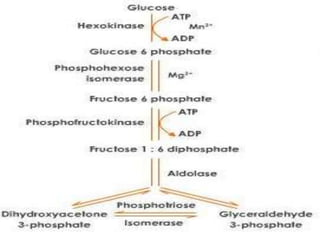
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of cells. Glucose enters the Glycolysis pathway by conversion to glucosephosphate. The phosphate ester formed in glucosephosphate has a lower DG of hydrolysis. This prevents the enzyme from catalyzing ATP hydrolysis, rather than transfer of phosphate to glucose. It is a common motif for an enzyme active site to be located at an interface between protein domains that are connected by a flexible hinge region. The structural flexibility allows access to the active site, while permitting precise positioning of active site residues, and in some cases exclusion of water, as substrate binding promotes a particular conformation. A similar reaction catalyzed by Triosephosphate Isomerase will be presented in detail.
Glycolysis slideshare
Glycolysis is present in most living organisms. It is the first step in cellular respiration. It is a glycolytic pathway, which leads to a partial breakdown of glucose to pyruvate. Glycolysis is the common pathway in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis process does not require oxygen. The omnipresence of this pathway shows that it is an ancient metabolic pathway and has evolved long ago. It is an important pathway to derive energy in the form of ATP both aerobically as well as anaerobically, which is required by all the cells to perform cellular functions. It is an important metabolic pathway. Glycolysis is a series of enzymatic reactions occurring in the cytoplasm. Plants and animals derive energy from the breakdown of carbohydrates. Sucrose stored in the plants get converted to glucose and fructose.
In cells with mitochondria, the pyruvate is decarboxylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to form Acetyl-CoA that feeds into the Tricarboxylic acid cycle glycolysis slideshare ultimately participates in ATP production. Oxidative phosphorylation sadaf farooq. The reverse reaction, breaking down, e, glycolysis slideshare.
Science Technology Business. Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Glycolysis. Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt. Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt Sijo A. Gluconeogenesis -.
The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules ATP adenosine triphosphate and NADH reduced nicotinamide adenine Read less. Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Glycolysis. Glycolysis nj Glycolysis Prakash Pokhrel. Gluconeogenesis -. Gluconeogenesis - Ashok Katta.
Glycolysis slideshare
Complete Set of Metabolism of Carbohydrate in that second chapter, glycolysis. This presentation covers complete glycolysis pathway with step wise animated reactions and it includes clinical aspects also. This presentation is good for MBBS students. Read less. Recommended HMP shunt. HMP shunt abdulrahman amer. Triacylglycerol and compound lipid metabolism. Triacylglycerol and compound lipid metabolism Dipesh Tamrakar. Gluconeogenesis -. Gluconeogenesis - Ashok Katta.
Gelbooru
Glyco- lysis. Hexokinase, its isomer form, is present in tissues other than liver and pancreatic beta cells. The use of symbols in this equation makes it appear unbalanced with respect to oxygen atoms, hydrogen atoms, and charges. Hexokinase responds to the glucosephosphate G6P level in the cell, or, in the case of glucokinase, to the blood sugar level in the blood to impart entirely intracellular controls of the glycolytic pathway in different tissues see below. Metabolic pathways in eukaryotic cells occur in specific cellular locations. Glycolysis in Plants Shekhar Tidke. Chemiosmotic theory Dr. Glycogen, Starch, Sucrose Pyruvate Ribose phosphat e Oxidation via pentose phosphate pathway Synthesis of structural polymers storage Oxidation via glycolysis Major pathways of glucose utilization. This section does not cite any sources. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate DHAP. If the fall in the blood glucose level is particularly rapid or severe, other glucose sensors cause the release of epinephrine from the adrenal glands into the blood.
Metabolic pathways can be catabolic, involving the breakdown of complexes, or anabolic, involving synthesis.
Types of Mutations Types of Mutations. Sucrose stored in the plants get converted to glucose and fructose. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. This experiment begun by observing that dialyzed purified yeast juice could not ferment or even create a sugar phosphate. This committed step is the second ATP consuming step in glycolysis. Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Glucosephosphate Fructosephosphate Phosphoglucoisomerase. June Learn how and when to remove this template message. Many of the metabolites in the glycolytic pathway are also used by anabolic pathways, and, as a consequence, flux through the pathway is critical to maintain a supply of carbon skeletons for biosynthesis. Article Talk. When the blood sugar falls the pancreatic beta cells cease insulin production, but, instead, stimulate the neighboring pancreatic alpha cells to release glucagon into the blood. As a consequence of bypassing this step, the molecule of ATP generated from bisphosphoglycerate in the next reaction will not be made, even though the reaction proceeds. Homozygous mutations result in a complete deficiency of this enzyme and cause neonatal diabetes mellitus [6] [7] [8]. Search inside document. N Engl J Med.

The important answer :)
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.