Glycogen synthase
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 GSK3 may be the busiest kinase in most cells, with over known substrates to deal with. How does GSK3 maintain control to selectively phosphorylate each substrate, and why was it evolutionarily favorable for GSK3 glycogen synthase assume such a large responsibility? GSK3 must be particularly adaptable for incorporating new substrates into its repertoire, glycogen synthase, and we discuss the distinct properties of GSK3 that may contribute to its capacity to fulfill its roles in multiple signaling pathways, glycogen synthase. The mechanisms regulating GSK3 predominantly post-translational modifications, substrate priming, cellular trafficking, protein complexes have been reviewed previously, so here we focus on newly identified complexities in these mechanisms, how each of these regulatory mechanism contributes to the ability of GSK3 to select which substrates to phosphorylate, and how these mechanisms may glycogen synthase contributed to its adaptability as new substrates evolved.
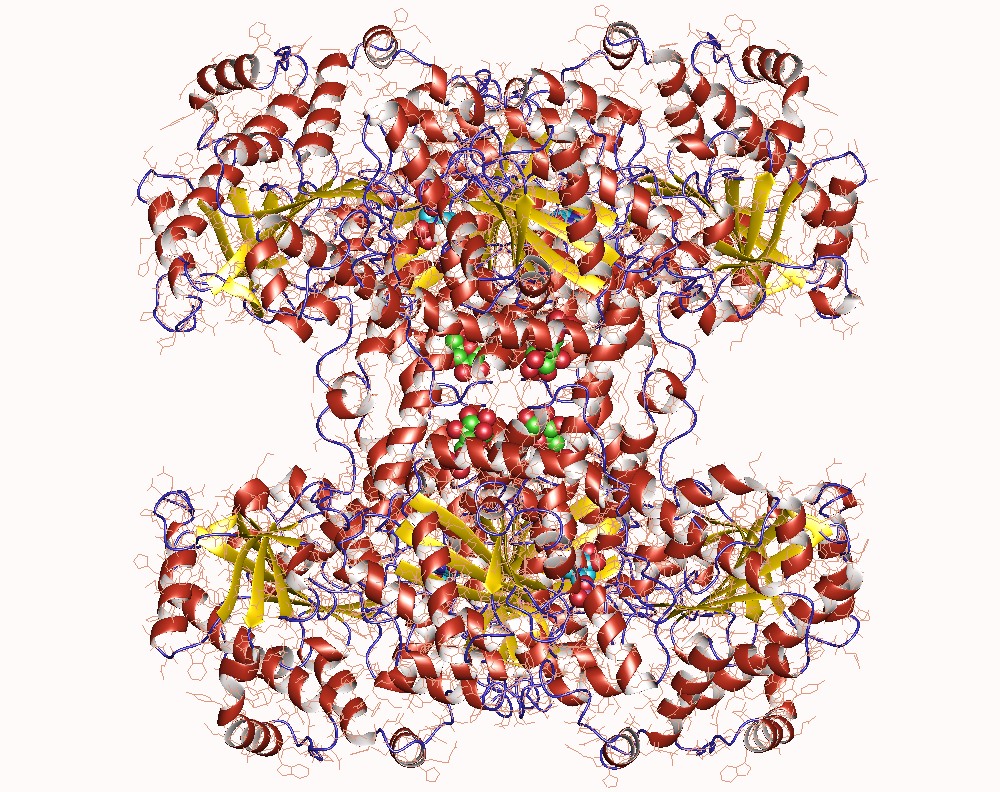
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen synthase GYS1 is the central enzyme in muscle glycogen biosynthesis. GYS1 activity is inhibited by phosphorylation of its amino N and carboxyl C termini, which is relieved by allosteric activation of glucosephosphate Glc6P. We present cryo-EM structures at 3.
Glycogen synthase
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen is the major glucose reserve in eukaryotes, and defects in glycogen metabolism and structure lead to disease. Glycogenesis involves interaction of glycogenin GN with glycogen synthase GS , where GS is activated by glucosephosphate G6P and inactivated by phosphorylation. We describe the 2. This work therefore provides insights into glycogen synthesis regulation and facilitates studies of glycogen-related diseases. Glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose that functions as the primary energy store in eukaryotes. Glycogen is stored predominantly in the muscle and liver cells, and to a lesser extent in other organs and tissues including kidney, brain, fat and heart 1. Glycogen is synthesised through the cooperative action of three enzymes: glycogenin GN , glycogen synthase GS and glycogen branching enzyme GBE 2. Known in vivo phosphorylation sites of GS are shown in red and are labelled with residue number and classical nomenclature in bold. GN tyrosine that becomes auto-glucosylated and was mutated to a phenylalanine YF in this study is indicated.
T mmelting temperature. GSK3 has been implicated in repression glycogen synthase gluconeogenic enzymes such as phosphoenolpuruvate carboxy kinase and glucose 6 phosphatase that reduces hepatic glucose production and helps in modulating glucose homeostasis Lochhead et al.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 GSK3 , a constitutively acting multi-functional serine threonine kinase is involved in diverse physiological pathways ranging from metabolism, cell cycle, gene expression, development and oncogenesis to neuroprotection. GSK3 has been implicated in various diseases such as diabetes, inflammation, cancer, Alzheimer's and bipolar disorder. GSK3 negatively regulates insulin-mediated glycogen synthesis and glucose homeostasis, and increased expression and activity of GSK3 has been reported in type II diabetics and obese animal models. Consequently, inhibitors of GSK3 have been demonstrated to have anti-diabetic effects in vitro and in animal models. However, inhibition of GSK3 poses a challenge as achieving selectivity of an over achieving kinase involved in various pathways with multiple substrates may lead to side effects and toxicity.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen is the major glucose reserve in eukaryotes, and defects in glycogen metabolism and structure lead to disease.
Glycogen synthase
Although glucose is the primary fuel for cells, it is not an efficient molecule for long-term storage in complex i. Therefore, in both plants and animals, the glucose molecules are linked together to form polysaccharides known as glucans. The average size of a glycogen unit is a cytoplasmic granule containing over glucose molecules. The addition of a glucosephosphate to another or to a glycogen chain is energetically unfavorable, so it must be coupled with a sufficiently exergonic reaction to proceed.
Hampton inn and suite
The focus of this review is the recent advances and the challenges surrounding GSK3 as an anti-diabetic therapeutic target. In addition, we could detect human GS site 2 S8 phosphorylation by mass spectrometry for the first time in a recombinant enzyme preparation. Question mark indicates theoretical structures. Cryo-EM density for Glc6P is shown. Ryu, J. Berg Authors Thomas J. Search PMC articles. J Biol Chem. Cameron, J. Acta Crystallogr. Pettersen, E. Control of glycogen synthesis by glucose, glycogen, and insulin in cultured human muscle cells.
Glycogen synthase UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis , the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase EC 2. Much research has been done on glycogen degradation through studying the structure and function of glycogen phosphorylase , the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation.
Publication types Research Support, N. Insulin promotes glycogen synthesis in the absence of GSK3 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle. Browner, M. Zheng, S. Nucleic Acids Res. Dephosphorylation, performed by glycogen-associated phosphatases of type 1 PP1 , substantially alters kinetic properties of GYS, including increased affinity for UDP-glc and sensitivity to the Glc6P activator IUCrJ 6 , — Regulation of muscle glycogen synthase phosphorylation and kinetic properties by insulin, exercise, adrenaline and role in insulin resistance. Cancer Res. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition and activation of protein kinase C. Reprints and permissions. Brief report: cardiomyopathy and exercise intolerance in muscle glycogen storage disease 0. Glycogen synthase kinases 3alpha and 3beta in cardiac myocytes: regulation and consequences of their inhibition.

Can be
I consider, that you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Write to me in PM.