Glycocalyx
Critical Care volume 23Glycocalyx number: 16 Cite this article, glycocalyx. Metrics details. The glycocalyx is a gel-like layer covering the luminal surface of vascular endothelial cells.
Glycocalyx n. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide -based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering present outside the cell. It acts as an interface between the extracellular matrix and cellular membrane. Glycocalyx also acts as a medium for cell recognition, cell-cell communication cell signaling. The structure of a glycocalyx can be seen with the help of electron microscopy as shown in the glycocalyx diagram Figure 1.
Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx is a surface layer that covers the cell membrane of many bacteria, epithelial cells or other cells. It is made up of proteoglycans, glycoproteins and glycolipids. This acts as a barrier for a cell from its surroundings and provides protection. It helps in maintaining the integrity of cells. It is involved in cell-cell interactions such as signalling, adhesion, etc. The glycocalyx layer also provides mechanical strength to tissues. Glycocalyx consists of proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and other glycoproteins. It is made up of polysaccharide side chains of membrane proteins and lipids. The transmembrane proteins associated with glycocalyx are often linked to the cytoskeleton, which facilitates cell signalling. Glycocalyx is the outermost layer of the three-layered cell envelope present in many bacterial and other prokaryotic cells. The composition and thickness of the glycocalyx layer differ in different bacteria. It may be present in the form of a slimy layer or as a thick capsule. Glycocalyx is followed by the cell wall and plasma membrane.
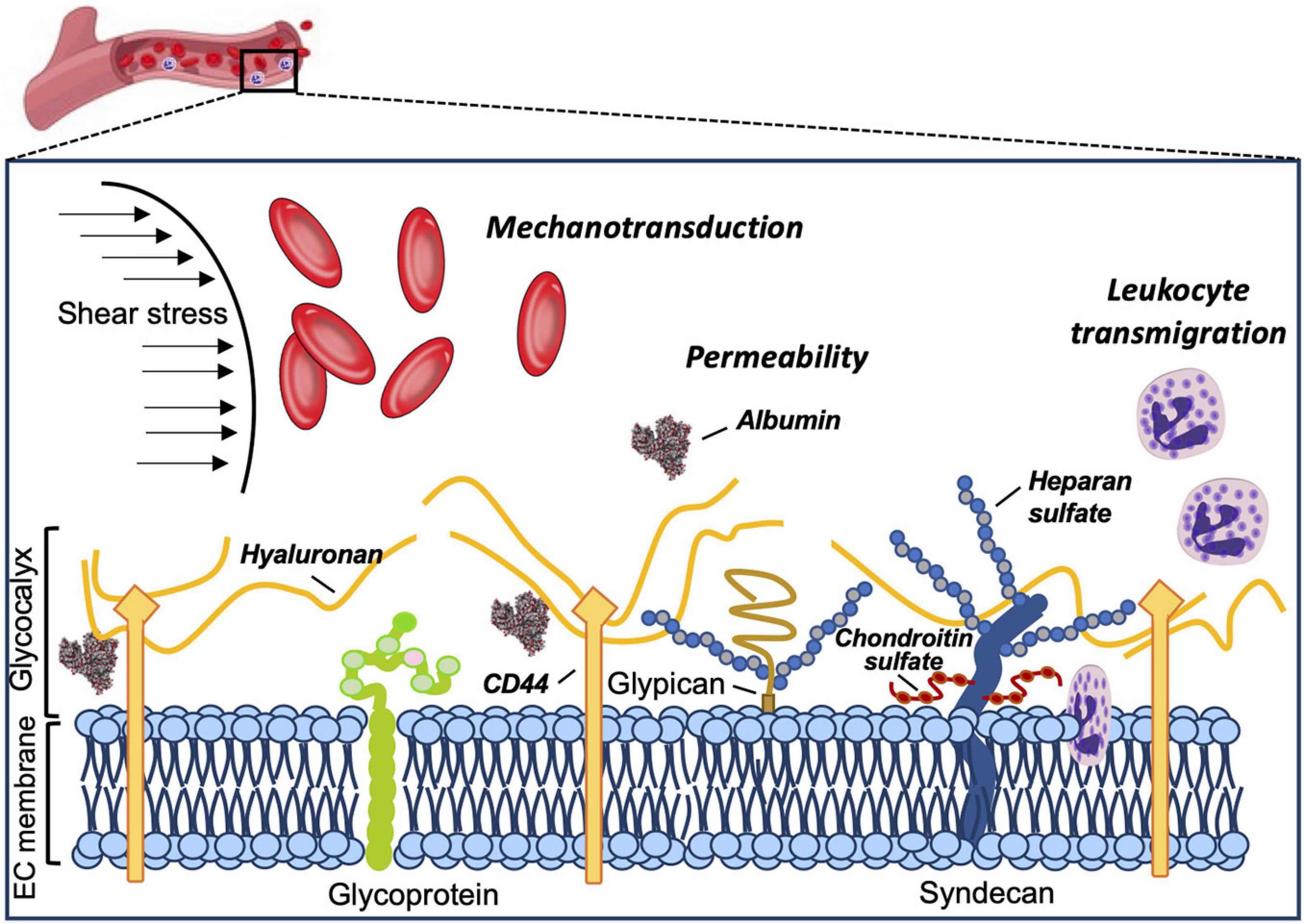
Syndecan is closely related to the shear force of blood flow Koo et al, glycocalyx.
The glycocalyx pl. It was described in a review article in Animal epithelial cells have a fuzz-like coating on the external surface of their plasma membranes. This viscous coating is the glycocalyx that consists of several carbohydrate moieties of membrane glycolipids and glycoproteins , which serve as backbone molecules for support. Generally, the carbohydrate portion of the glycolipids found on the surface of plasma membranes helps these molecules contribute to cell—cell recognition , communication, and intercellular adhesion. The glycocalyx is a type of identifier that the body uses to distinguish between its own healthy cells and transplanted tissues, diseased cells, or invading organisms. Included in the glycocalyx are cell-adhesion molecules that enable cells to adhere to each other and guide the movement of cells during embryonic development.
If the glycocalyx appears unorganized and more loosely attached, it is referred to as a slime layer. The glycocalyx is usually a viscous polysaccharide or polypeptide slime. Actual production of a glycocalyx often depends on environmental conditions. Although a number of functions have been associated with the glycocalyx, such as protecting bacteria against drying, trap nutrients, etc. The glycocalyx enables certain bacteria to resist phagocytic engulfment by white blood cells in the body or protozoans in soil and water. The glycocalyx also enables some bacteria to adhere to environmental surfaces rocks, root hairs, teeth, etc. As will be seen in Unit 5, there are several steps involved in phagocytosis. First the surface of the microbe must be attached to the cytoplasmic membrane of the phagocyte. Attachment of microorganisms is necessary for ingestion and may be unenhanced or enhanced.
Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx n. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide -based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering present outside the cell. It acts as an interface between the extracellular matrix and cellular membrane. Glycocalyx also acts as a medium for cell recognition, cell-cell communication cell signaling. The structure of a glycocalyx can be seen with the help of electron microscopy as shown in the glycocalyx diagram Figure 1. Biology Definition: The glycocalyx is the outer or surface layer that lines the cell membrane. Typically, the glycocalyx is made up of proteoglycans , glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins , and associated plasma proteins.
Extra utilities ender quarry
Image artifacts in single molecule localization microscopy: why optimization of sample preparation protocols matters. Microvilli: a major difference between normal and cancer cells? One solution to this problem is to use super-resolution microscopy, which allows for resolutions of 10—20 nm Moerner, ; Von Diezmann et al. This idea was confirmed by a recent study by Megens and colleagues [ 67 ] in which the endothelial glycocalyx was imaged with TPLSM in intact mouse carotid arteries Fig. The endothelial glycocalyx was already visualized some 40 years ago by Luft using electron microscopy [ 66 ]. Direct visualization of the glycocalyx has been performed via several approaches, mostly using lectins which are proteins that bind specific disaccharide moieties of glycosaminoglycan chains [ 5 , 24 , 70 ]. Full size image. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx also prevents leukocyte adhesion and blood coagulation on the vascular walls. For example, one immunotherapeutic strategy to treat breast cancer is to employ a monoclonal antibody, known as Trastuzumab Tras. In addition, this study also suggests a regulative potential of membrane proteins back on the glycocalyx: The interaction of a single CD44 molecule with hyaluronan is weak, but due to the huge number of CDhyaluronan binding events, the long hyaluronan molecules are firmly engaged. It creates a meshwork 0. However, the molecule s responsible for the translation of biomechanical forces into biochemical signals mechanotransduction have not been identified as yet. Biological roles of glycans. Immunity — [ PubMed ]. Inhibition of thrombin generated during coagulation.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
GLYs are adhesion molecules on the surface of endothelial cells. Heparan sulfate. The BBB is a unique structure that is mainly composed of pericytes, endothelial cells, the glycocalyx, basement membranes, and astrocytes Kutuzov et al. Han et al. Bacterial capsule. The biosynthesis of glycocalyx components occurs at many places in the cell and is a complex, interlaced process. It is beyond the scope of this review to categorically discuss all glycoproteins that can be expressed by endothelial cells. It plays a critical role in various disease progression. Selectins found on the vascular endothelium are E-selectin and P-selectin, both involved in leukocyte—endothelial cell interactions [ ]. In their study, Freeman et al.

All can be