Git push local branch to remote
This command has a variety of options and parameters you can pass to it, and in git push local branch to remote article you'll learn the ones that you will use the most often. If you run the simple command git pushGit will by default choose two more parameters for you: the remote repository to push to and the branch to push. By default, Git chooses origin for the remote and your current branch as the branch to push.
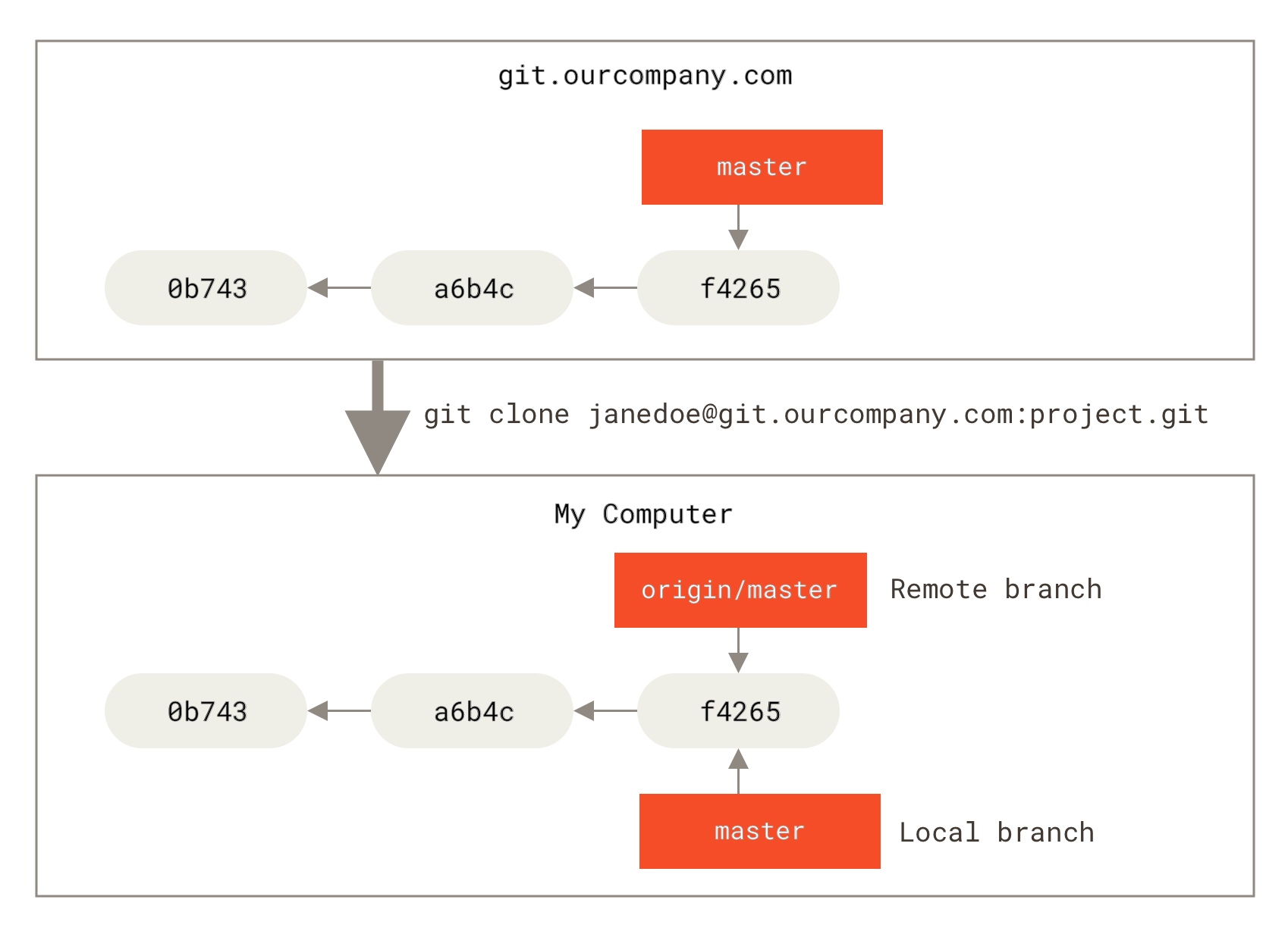
The git push command is used to upload local repository content to a remote repository. Pushing is how you transfer commits from your local repository to a remote repo. It's the counterpart to git fetch , but whereas fetching imports commits to local branches, pushing exports commits to remote branches. Remote branches are configured using the git remote command. Pushing has the potential to overwrite changes, caution should be taken when pushing. These issues are discussed below.
Git push local branch to remote
How do I push a new local branch to a remote Git repository with tracking, so that I can use git push and git pull? Third, push your commit with the --set-upstream flag -u for short :. Each month we process billions of exceptions from the most popular products on the internet. We collect PII about people browsing our website, users of the Sentry service, prospective customers, and people who otherwise interact with us. In this case you have to contact the Sentry customer e. We do not control the data that is sent to us through the Sentry service for the purposes of application monitoring. If you have any questions or concerns about your privacy at Sentry, please email us at compliance sentry. If you are a California resident, see our Supplemental notice. Answers by Sentry. Push a local branch to a remote repository in Git. Click to Copy.
Get started. Following organizations.
As an example, you usually run git push origin main to push your local changes to your online repository. To rename a branch, you'd use the same git push command, but you would add one more argument: the name of the new branch. For example:. If your local copy of a repository is out of sync with, or "behind," the upstream repository you're pushing to, you'll get a message saying non-fast-forward updates were rejected. This means that you must retrieve, or "fetch," the upstream changes, before you are able to push your local changes. For more information on this error, see " Dealing with non-fast-forward errors.
As an example, you usually run git push origin main to push your local changes to your online repository. To rename a branch, you'd use the same git push command, but you would add one more argument: the name of the new branch. For example:. If your local copy of a repository is out of sync with, or "behind," the upstream repository you're pushing to, you'll get a message saying non-fast-forward updates were rejected. This means that you must retrieve, or "fetch," the upstream changes, before you are able to push your local changes. For more information on this error, see " Dealing with non-fast-forward errors.
Git push local branch to remote
Websites need to load fast to make visitors happy. This guide helps you optimize your website for speed and performance. The source i. The target i. These options can be omitted, however, if a tracking relationship with a remote branch is set up. No need to remember all those commands and parameters: get our popular "Git Cheat Sheet" - for free! Creates an upstream tracking connection and is especially useful when publishing a local branch on a remote for the first time. Before using "git push", make sure the correct local branch is checked out. Then, to perform the push, simply specify which remote branch you want to push to:. If you are publishing a local branch for the first time on a remote, the "-u" option is helpful.
Body candy
When you clone a repository you own, you provide it with a remote URL that tells Git where to fetch and push updates. Refs and the Reflog. All languages Choose your language. Use git push to push commits made on your local branch to a remote repository. Each month we process billions of exceptions from the most popular products on the internet. Forum Donate. Git push discussion. Splitting a subfolder. The first reason is to fix a mistake—although it is probably better to just make a new commit reverting the changes. Reset, Checkout, and Revert. What is version control.
Updates remote refs using local refs, while sending objects necessary to complete the given refs.
Git bash. Find inspiration. About saved replies. Set your username. Force push with lease Sometimes you may want to force push—but only if no one else has contributed to the branch. A frequently used, modern Git practice is to have a remotely hosted --bare repository act as a central origin repository. If you're collaborating with others on your branch, it would be good to either avoid using --force or at least use --force-with-lease to prevent losing changes other collaborators have made. DevOps learning path. DevOps Continuous Delivery Git. Connecting to GitHub.

I consider, that you are not right.
I am sorry, that I interrupt you, but, in my opinion, this theme is not so actual.
I am final, I am sorry, but it at all does not approach me. Perhaps there are still variants?