Free radic res
Free Radical Researchformerly Free Radical Research Communicationsfree radic res, is an academic journal that publishes research papers, hypotheses, and reviews on free radicalsredox signalingantioxidantsand oxidative damage. It is published by Informa Healthcare.
Free radicals and other reactive oxygen species ROS are constantly formed in the human body. Free-radical mechanisms have been implicated in the pathology of several human diseases, including cancer, atherosclerosis, malaria, and rheumatoid arthritis and neurodegenerative diseases. Catalases in peroxisomes convert H 2 O 2 into water and O 2 and help to dispose of H 2 O 2 generated by the action of the oxidase enzymes that are located in these organelles. Other important H 2 O 2 -removing enzymes in human cells are the glutathione peroxidases. When produced in excess, ROS can cause tissue injury. However, tissue injury can itself cause ROS generation e. Assessment of oxidative damage to biomolecules by means of emerging technologies based on products of oxidative damage to DNA e.
Free radic res
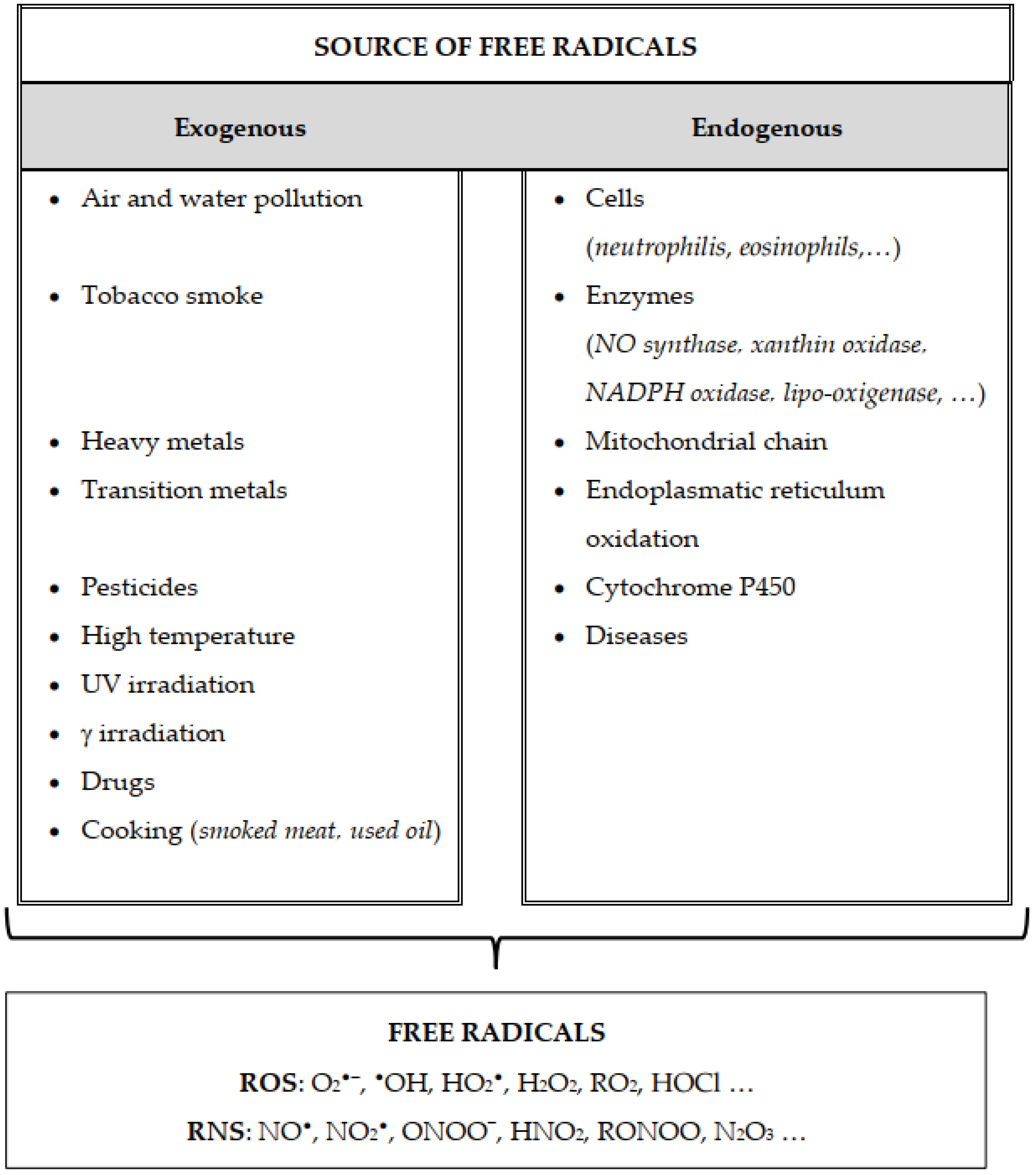
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Free radicals and oxidants play a dual role as both toxic and beneficial compounds, since they can be either harmful or helpful to the body. They are produced either from normal cell metabolisms in situ or from external sources pollution, cigarette smoke, radiation, medication. When an overload of free radicals cannot gradually be destroyed, their accumulation in the body generates a phenomenon called oxidative stress. This process plays a major part in the development of chronic and degenerative illness such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, aging, cataract, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. This mini-review deals with the taxonomy, the mechanisms of formation and catabolism of the free radicals, it examines their beneficial and deleterious effects on cellular activities, it highlights the potential role of the antioxidants in preventing and repairing damages caused by oxidative stress, and it discusses the antioxidant supplementation in health maintenance. Oxygen is an element indispensable for life. When cells use oxygen to generate energy, free radicals are created as a consequence of ATP adenosine triphosphate production by the mitochondria. These by-products are generally reactive oxygen species ROS as well as reactive nitrogen species RNS that result from the cellular redox process. These species play a dual role as both toxic and beneficial compounds. The delicate balance between their two antagonistic effects is clearly an important aspect of life. At high concentrations, they generate oxidative stress, a deleterious process that can damage all cell structures 1 - Oxidative stress plays a major part in the development of chronic and degenerative ailments such as cancer, arthritis, aging, autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.
Health 9 — Halliwell, R. Buga, K.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In recent years, there has been a great deal of attention toward the field of free radical chemistry. Free radicals reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species are generated by our body by various endogenous systems, exposure to different physiochemical conditions or pathological states. A balance between free radicals and antioxidants is necessary for proper physiological function. If free radicals overwhelm the body's ability to regulate them, a condition known as oxidative stress ensues. Free radicals thus adversely alter lipids, proteins, and DNA and trigger a number of human diseases.
Available data on the absorption, metabolism and pharmacokinetics of coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 are reviewed in this paper. CoQ10 has a fundamental role in cellular bioenergetics. CoQ10 is also an important antioxidant. Because of its hydrophobicity and large molecular weight, absorption of dietary CoQ10 is slow and limited. In the case of dietary supplements, solubilized CoQ10 formulations show enhanced bioavailability.
Free radic res
Objectives: The goal of our study was to investigate the associations of oxidized LDL apoB aldehyde-modified form and acute phase proteins fibrinogen, CRP with acute ischemic stroke severity and outcome. Materials and methods: The study included 61 ischemic stroke patients and 64 controls. Strokes were subtyped according to TOAST criteria, the severity and outcome of stroke at 1 year were measured. Results: The mean triglyceride, fibrinogen, CRP and glucose values were significantly higher among cases. The median oxLDL value for patients with large artery atherosclerosis LAA type of stroke was significantly higher than for other subtypes. The oxLDL values did not correlate with age, stroke severity and outcome. Conclusions: Inflammatory markers fibrinogen and CRP predicted the stroke severity and outcome whereas elevation of oxLDL levels did not. Our data refer to possibility that there may exist some links between the LAA subtype of stroke and elevated oxLDL apoB aldehyde-modified form. Abstract Objectives: The goal of our study was to investigate the associations of oxidized LDL apoB aldehyde-modified form and acute phase proteins fibrinogen, CRP with acute ischemic stroke severity and outcome.
Cowboys lineup
Open in a separate window. Oxidative stress in chronic renal failure. Souberbielle, P. Thus, the search for effective, nontoxic natural compounds with antioxidative activity has been intensified in recent years. The first is a dimer consists of two units , while the others are tetramers four subunits. Douki, T. Halliwell B. The site is secure. How to characterize an antioxidant- An update. Keywords: Ageing, antioxidant, free radicals, oxidative stress. This indicator counts the number of citations received by documents from a journal and divides them by the total number of documents published in that journal.
It has been demonstrated that hydrogen can selectively reduce hydroxyl and peroxynitrite in vitro. Since most of the ionizing radiation-induced cellular damage is caused by hydroxyl radicals, this study was designed to test the hypothesis that hydrogen may be an effective radioprotective agent.
Immunoenhancement of B-carotene may contribute to cancer protection. Three eras of vitamin C discovery. Wang, and T. Copy to clipboard. Role of oxygen radicals in DNA damage and cancer incidence. Free radicals and antioxidants have become commonly used terms in modern discussions of disease mechanisms. The presence of an unpaired electron results in certain common properties that are shared by most radicals. Barnhart and S. Rothistein, D. Article Google Scholar Dean, R. Therefore, the antioxidant resources must be constantly restored in the body. A review. Dhanasekaran M, Ran J. Free radicals and antioxidants in health and disease. E-mail: moc.

0 thoughts on “Free radic res”