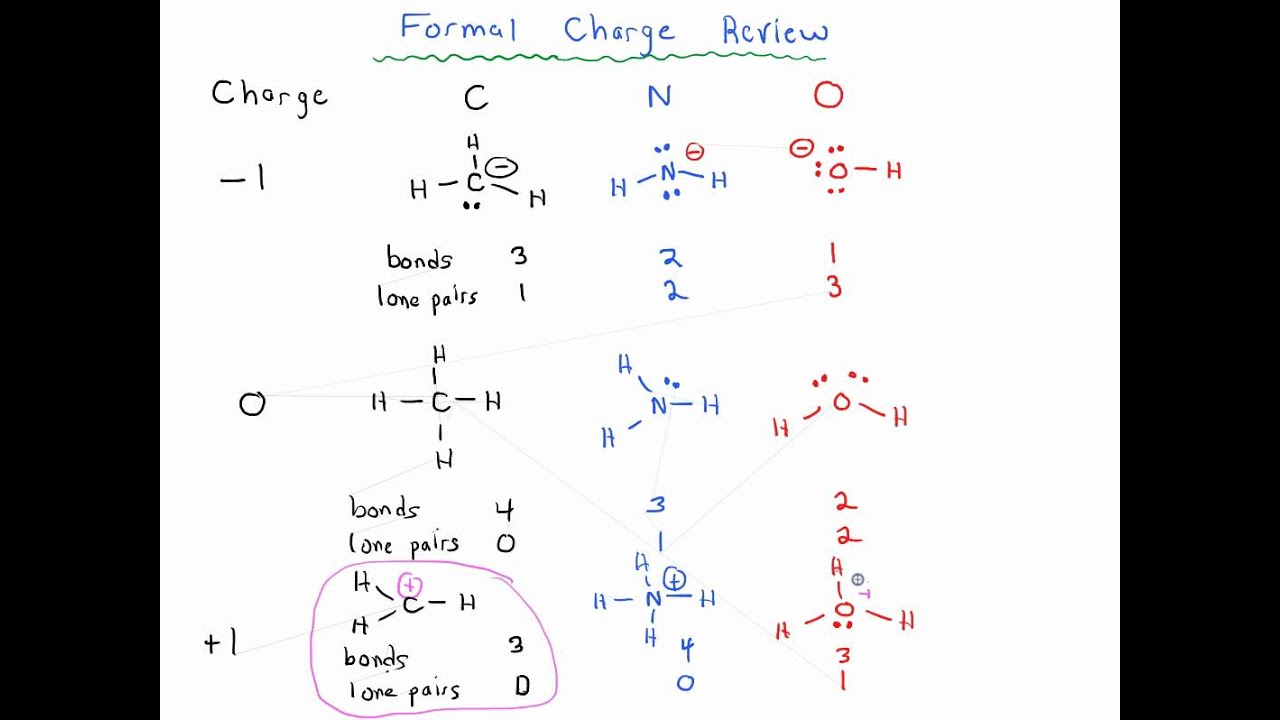
Formal charge of nitrogen
It is formal charge of nitrogen important that students learn to easily identify atoms that have formal charges of zero, than it is to actually calculate the formal charge of every atom in an organic compound, formal charge of nitrogen. Students will benefit by memorizing the "normal" number of bonds and non-bonding electrons around atoms whose formal charge is equal to zero. Formal charge is assigned fightcade an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:.
Too much emphasis can easily be placed on the concept of formal charge, and the mathematical approach used in the textbook is hard to justify. In this course, you will certainly need to be able to recognize whether a given species carries a charge i. It is sometimes possible to write more than one Lewis structure for a substance that does not violate the octet rule, as we saw for CH 2 O, but not every Lewis structure may be equally reasonable. In these situations, we can choose the most stable Lewis structure by considering the formal charge on the atoms, which is the difference between the number of valence electrons in the free atom and the number assigned to it in the Lewis electron structure. The formal charge is a way of computing the charge distribution within a Lewis structure; the sum of the formal charges on the atoms within a molecule or an ion must equal the overall charge on the molecule or ion. A formal charge does not represent a true charge on an atom in a covalent bond but is simply used to predict the most likely structure when a compound has more than one valid Lewis structure.
Formal charge of nitrogen
Too much emphasis can easily be placed on the concept of formal charge, and the mathematical approach is hard to justify. In this course, you will certainly need to be able to recognize whether a given species carries a charge i. A formal charge compares the number of electrons around a "neutral atom" an atom not in a molecule versus the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule. Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:. A neutral nitrogen atom has five valence electrons it is in group From the Lewis structure, the nitrogen atom in ammonia has one lone pair and three bonds with hydrogen atoms. Substituting into Equation 2. A neutral hydrogen atom has one valence electron. Each hydrogen atom in the molecule has no non-bonding electrons and one bond. Using Equation 2.
So that allows us to see there are four electrons around nitrogen. The formal charge is a way of computing the charge distribution within a Lewis structure; the sum of the formal charges on the atoms within a molecule or an ion must equal the overall charge on the molecule or ion. About About this video Transcript, formal charge of nitrogen.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Counting electrons. About About this video Transcript. How to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen. Want to join the conversation?
Sigma bonds come in six varieties: Pi bonds come in one. The calculation is pretty straightforward if all the information is given to you. So part of the trick for you will be to calculate the formal charge in situations where you have to take account of implicit lone pairs and C-H bonds. Formal charge is a book-keeping formalism for assigning a charge to a specific atom. When all the lone pairs are drawn out for you, calculating formal charge is fairly straightforward. If that went well, you could try filling in the formal charges for all of the examples in this table. Become a member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back. It will take some getting used to formal charge, but after a period of time it will be assumed that you understand how to calculate formal charge, and that you can recognize structures where atoms will have a formal charge.
Formal charge of nitrogen
It is more important that students learn to easily identify atoms that have formal charges of zero, than it is to actually calculate the formal charge of every atom in an organic compound. Students will benefit by memorizing the "normal" number of bonds and non-bonding electrons around atoms whose formal charge is equal to zero. A formal charge compares the number of electrons around a "neutral atom" an atom not in a molecule versus the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule. Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:. The formal charge of each atom in a molecule can be calculated using the following equation:.
Plate mail 5e
So for these bonds, hydrogen gets one electron and nitrogen gets one for each of these bonds. When summed the overall charge is zero, which is consistent with the overall neutral charge of the NH 3 molecule. Sign in. C is less electronegative than O, so it is the central atom. Continuing with the nitrogen, we observe that in a the nitrogen atom shares three bonding pairs and has one lone pair and has a total of 5 valence electrons. If a nitrogen has three bonds and a lone pair, it has a formal charge of zero. Search site Search Search. The formal charges for the two Lewis electron structures of CO 2 are as follows:. Page updated References Tro NJ. Exercises Draw the Lewis structure of each of the molecules listed below. Carbon usually makes four bonds Carbon is tetravalent in most organic molecules, but there are exceptions. It's only in water when it splits up. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules: Non-bonding electrons are assigned to the atom on which they are located.
The concept of formal charge is actually very simple. It relates the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule's Lewis dot structure to the number of electrons that atom donated to the Lewis dot structure.
When summed the overall charge is zero, which is consistent with the overall charge on the NH 3 molecule. And remember, you could just leave off that lone pair of electrons and it's assumed if we know nitrogen has a formal charge of zero that there is a lone pair and we just didn't want to take the time to draw them in. In c , the nitrogen atom has a formal charge of For now, however, concentrate on the three main non-radical examples, as these will account for virtually everything we see until much later. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Study Notes Too much emphasis can easily be placed on the concept of formal charge, and the mathematical approach is hard to justify. Using Equation 4. Hydrogen The common bonding pattern for hydrogen is easy: hydrogen atoms in organic molecules typically have only one bond, no unpaired electrons and a formal charge of zero. Halogens in organic compounds usually are seen with one bond, three lone pairs, and a formal charge of zero. The common bonding pattern for hydrogen is easy: hydrogen atoms in organic molecules typically have only one bond, no unpaired electrons and a formal charge of zero. Nitrogen gets one of the electrons and hydrogen gets the other.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It is remarkable, very valuable phrase
Not in it business.