Formal charge of cl
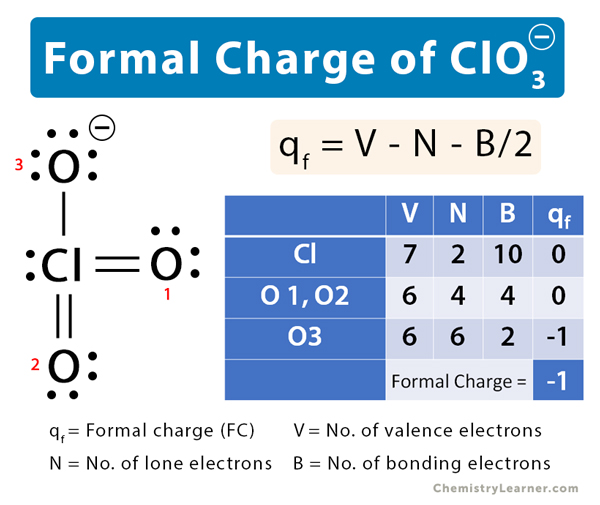
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms, formal charge of cl. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We calculate the formal charge of an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ions as follows:. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charge of cl charges for the whole structure.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion.
Formal charge of cl
.
About 90 billion pounds are produced each year in the United States alone. There are Go back to previous article.
.
Previously, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. In some cases, however, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. But first, let's introduce a concept we will refer back to frequently for the rest of this term: electronegativity. Whether a bond is nonpolar or polar covalent is determined by a property of the bonding atoms called electronegativity. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons or electron density towards itself.
Formal charge of cl
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Porn socken
We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. We must remember that the formal charge calculated for an atom is not the actual charge of the atom in the molecule. Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. It does not fluctuate between resonance forms; rather, the actual electronic structure is always the average of that shown by all resonance forms. Iodine forms a series of fluorides listed below. CC licensed content, Shared previously. Resonance occurs in cases where two or more Lewis structures with identical arrangements of atoms but different distributions of electrons can be written. Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges. George Wheland, one of the pioneers of resonance theory, used a historical analogy to describe the relationship between resonance forms and resonance hybrids. Determine the formal charges: Sulfuric acid is the industrial chemical produced in greatest quantity worldwide.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable.
Like a rhinoceros, it is a real entity that experimental evidence has shown to exist. Is the actual structure consistent with the formal charges? We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. This gives rise to three resonance forms of the carbonate ion. Write Lewis structures for the hydrogen carbonate ion and hydrogen peroxide molecule, with resonance forms where appropriate. We can draw three possibilities for the structure: carbon in the center and double bonds, carbon in the center with a single and triple bond, and oxygen in the center with double bonds:. Write the Lewis structure for sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4 , which has two oxygen atoms and two OH groups bonded to the sulfur. The structure that gives zero formal charges is consistent with the actual structure: We should remember that a molecule described as a resonance hybrid never possesses an electronic structure described by either resonance form. Show Answer Assign one of the electrons in each Br—Cl bond to the Br atom and one to the Cl atom in that bond: Assign the lone pairs to their atom. Based on formal charge considerations, which of the following would likely be the correct arrangement of atoms in hypochlorous acid: HOCl or OClH? The sum of the formal charges of all the atoms equals —1, which is identical to the charge of the ion —1. Draw all possible resonance structures for each of the compounds below. We assign lone pairs of electrons to their atoms.

And where logic?
It agree, the remarkable message