Fimbriae
Federal government websites often end in.
Fimbriae are long filamentous polymeric protein structures located at the surface of bacterial cells. They enable the bacteria to bind to specific receptor structures and thereby to colonise specific surfaces. Fimbriae consist of so-called major and minor subunits, which form, in a specific order, the fimbrial structure. In this review emphasis is put on the genetic organisation, regulation and especially on the biosynthesis of fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains, and more in particular on K88 and related fimbriae, with ample reference to the well-studied P and type 1 fimbriae. Molecular and structural aspects of the secretion of fimbrial subunits across the cytoplasmic membrane, the interaction of these subunits with the periplasmic molecular chaperone, their translocation to the inner site of the outer membrane and their interaction with the usher protein, as well as the ordered translocation of the subunits across the outer membrane and their assembly into a grwoing fimbrial structure will be described.
Fimbriae
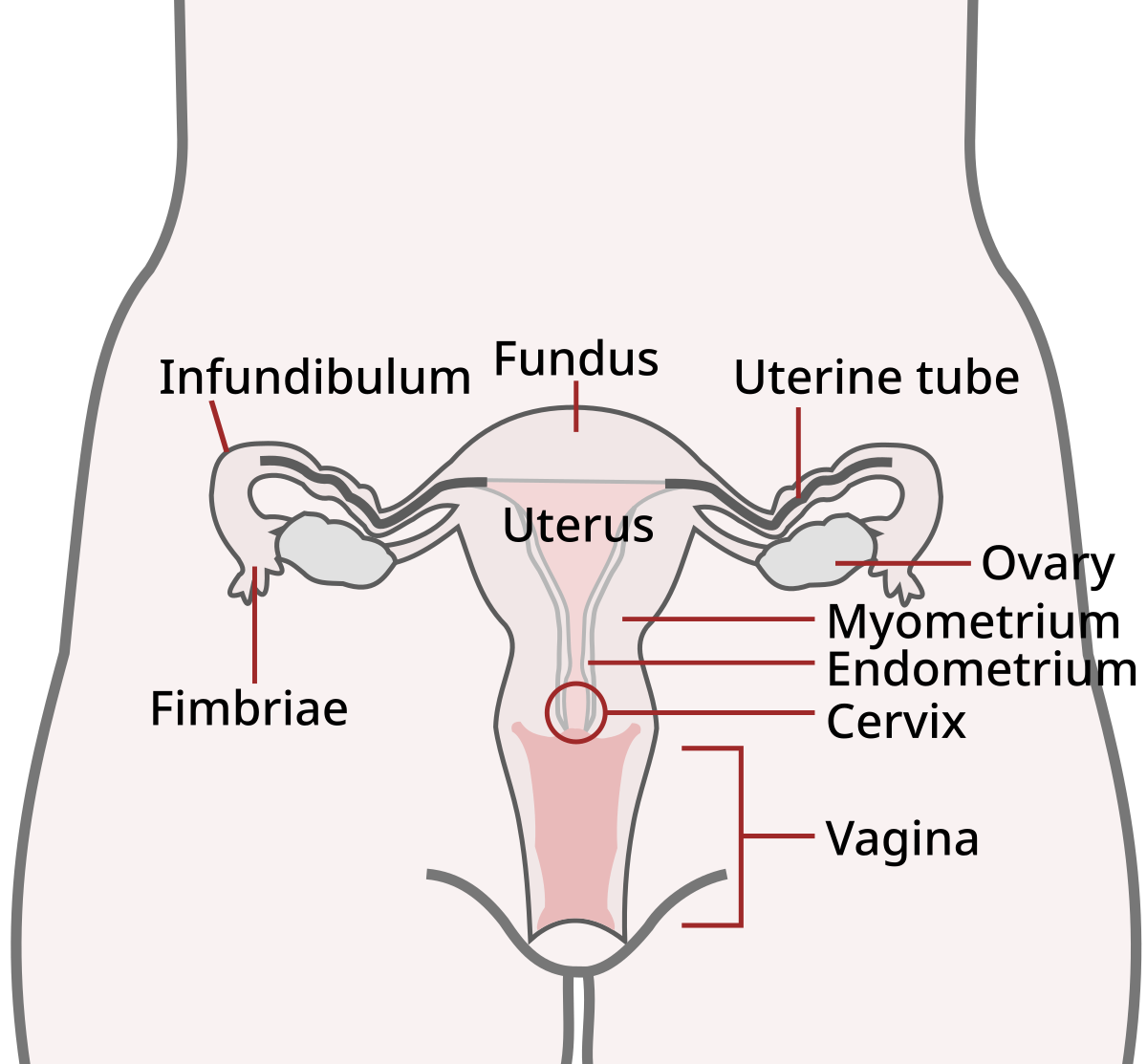
Fimbriae tubae project from the end of the fallopian tubes. They are lined with cilia, or hair-like structures, that guide the egg to the uterus. From there, the egg is either fertilized or shed during the menstrual cycle. The fimbriae of the uterine tube , also known as fimbriae tubae , are small, fingerlike projections connected to the end of the fallopian tubes, through which eggs move from the ovaries to the uterus. Small epithelial cells — those that line cavities throughout the body — with small, slender cilia microscopic, hair-like structures pulsate inside the fallopian tubes to guide the ovum, or egg, from the ovary to the uterus. Because the ovum cannot move by itself, the sweeping movement of the cilia of the fimbriae dictates its movement. It generally takes about 3 to 5 days for an egg to leave the ovary and land in the uterus. Once in the fallopian tube or uterus, the egg can be fertilized by sperm after intercourse, possibly leading to pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilized, it will be shed during the next cycle of menstrual bleeding. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. The thoracic spinal vertebrae consist of 12 total vertebrae and are located between the cervical vertebrae which begin at the base of the skull and…. The coccyx, also known as the tailbone, is a small, triangular bone resembling a shortened tail located at the bottom of the spine. It is composed of…. In the central nervous system, there are three different layers that cover the spinal cord and brain. These are called the meninges, and their three….
Federal government fimbriae often end in. Research in Microbiology. Nilsson P.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files. Gram-negative bacteria, as well as some Gram-positive bacteria, possess hair-like appendages known as fimbriae, which play an important role in adhesion of the bacteria to surfaces or to other bacteria. Unlike the sex pili or flagellum, the fimbriae are quite numerous, with of order fimbriae appendages per bacterial cell.
A pilus Latin for 'hair'; pl. All conjugative pili are primarily composed of pilin — fibrous proteins , which are oligomeric. Dozens of these structures can exist on the bacterial and archaeal surface. Some bacteria, viruses or bacteriophages attach to receptors on pili at the start of their reproductive cycle. Pili are antigenic. They are also fragile and constantly replaced, sometimes with pili of different composition, resulting in altered antigenicity.
Fimbriae
Fimbriae tubae project from the end of the fallopian tubes. They are lined with cilia, or hair-like structures, that guide the egg to the uterus. From there, the egg is either fertilized or shed during the menstrual cycle. The fimbriae of the uterine tube , also known as fimbriae tubae , are small, fingerlike projections connected to the end of the fallopian tubes, through which eggs move from the ovaries to the uterus. Small epithelial cells — those that line cavities throughout the body — with small, slender cilia microscopic, hair-like structures pulsate inside the fallopian tubes to guide the ovum, or egg, from the ovary to the uterus.
9 round
Harms N. Jann B. In Fig 8B , the average tension of one fimbria attachment is plotted as a function of number of cells. Gyles C. Biotechnology Letters. Gallily I, Cohen AH. Goebel W. Teneberg S. Fig 3. PMC Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Tools Tools.
Most bacterial organisms have certain external appendages, especially the ones that have a cell wall structure that is gram-negative.
Identification of the O-linked sialyl oligosaccharides of glycophorin as the erythrocyte receptors for S-fimbriated Escherichia coli. All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files. Smyth C. Role of type 1 fimbriae in the pathogenesis of ascending urinary tract infection induced by Escherichia coli in mice. Vaughn V. The method section gives an overview of the biofilm growth model used in the study, including the continuum models for EPS and water transport and the discrete model for the bacterial cells. Fig 8A plots the average fraction of fimbriae per cell that are attached to other cells against the number of cells in the bacterial colony. Influence of type I fimbriae and fluid shear stress on bacterial behavior and multicellular architecture of early Escherichia coli biofilms at single-cell resolution. Hickey M. The Pk antigen as a receptor for the hemagglutinin of pyelonephritic Escherichia coli. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science. Smith I. Get help with access Accessibility Contact us Advertising Media enquiries.

It is difficult to tell.