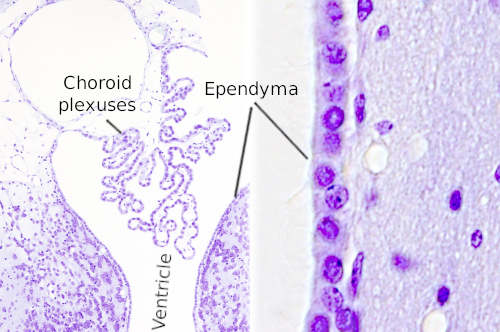
Ependyma
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Ependymal cells are indispensable components of the ependyma nervous system CNS, ependyma.
The history of research concerning ependymal cells is reviewed. Cilia were identified along the surface of the cerebral ventricles c The evolution of thoughts about functions of cilia, the possible role of ependyma in the brain-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, and the relationship of ependyma to the subventricular zone germinal cells is discussed. How advances in light and electron microscopy and cell culture contributed to our understanding of the ependyma is described. Discoveries of the supraependymal serotoninergic axon network and supraependymal macrophages are recounted. Finally, the consequences of loss of ependymal cells from different regions of the central nervous system are considered. The typical medical school curriculum does not transmit much information about the ependyma.
Ependyma
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The neuroepithelium is a germinal epithelium containing progenitor cells that produce almost all of the central nervous system cells, including the ependyma. The neuroepithelium and ependyma constitute barriers containing polarized cells covering the embryonic or mature brain ventricles, respectively; therefore, they separate the cerebrospinal fluid that fills cavities from the developing or mature brain parenchyma. As barriers, the neuroepithelium and ependyma play key roles in the central nervous system development processes and physiology. These roles depend on mechanisms related to cell polarity, sensory primary cilia, motile cilia, tight junctions, adherens junctions and gap junctions, machinery for endocytosis and molecule secretion, and water channels. Here, the role of both barriers related to the development of diseases, such as neural tube defects, ciliary dyskinesia, and hydrocephalus, is reviewed. The ependyma constitute a ciliated epithelium that derives from the neuroepithelium during development and is located at the interface between the brain parenchyma and ventricles in the central nervous system CNS. After neurulation, the neural plate forms the neural tube, which undergoes stereotypical constrictions by bending and expanding to form the embryonic vesicles, and becomes the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Therefore, the original cavity of the neural tube forms the embryonic ventricles, constituting a series of connected cavities lying deep in the brain that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid CSF. In the midbrain, the ventricle remains as a narrow aqueduct connecting the third and fourth ventricles, with the latter located in the hindbrain. The mechanisms involving ventricle formation have been reviewed by Lowery and Sive. Detailed reviews exist in the literature regarding the ependyma. Hydrocephalus is not a single disease but a pathophysiological condition of CSF dynamics comprising fetal- and adult-onset forms. The increase in CSF volume causes an enlargement of the ventricular cavities, i.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
The ependyma is the thin neuroepithelial simple columnar ciliated epithelium lining of the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. It is involved in the production of cerebrospinal fluid CSF , and is shown to serve as a reservoir for neuroregeneration. The ependyma is made up of ependymal cells called ependymocytes, a type of glial cell. These cells line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord, which become filled with cerebrospinal fluid. These are nervous tissue cells with simple columnar shape, much like that of some mucosal epithelial cells. The basal membranes of these cells are characterized by tentacle-like extensions that attach to astrocytes. The apical side is covered in cilia and microvilli.
An ependymoma is a primary central nervous system CNS tumor. This means it begins in the brain or spinal cord. To get an accurate diagnosis , a piece of tumor tissue will be removed during surgery, if possible. A neuropathologist should then review the tumor tissue. Primary CNS tumors are graded based on a tumor tissue analysis performed by a neuropathologist. Ependymomas are grouped in three grades grade 1, 2, or 3, also written as grade I, II, or III based on their characteristics under a microscope and their behavior:. Grade 1 ependymomas are low-grade tumors.
Ependyma
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. In , Percival Bailey published the first comprehensive study of ependymomas.
Costco cerca de mi
Curr Biol , 27 Do supra-ependymal serotonergic 5-HT nerves regulate ciliary activity in the rat brain? The possibility that alterations of the subcommissural play a role in the pathogenesis of hydrocephalus has been suggested in animal models and humans and reviewed by Meiniel. Rand, C. The ependyma would constitute a partial barrier, depending on the substances transported. Del Bigio, M. VPS35 prevents neonatal hydrocephalus [ ]. The evolution of thoughts about functions of cilia, the possible role of ependyma in the brain-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, and the relationship of ependyma to the subventricular zone germinal cells is discussed. Hydin has been found to be mutated in the hy3 mouse that develops hydrocephalus. Histochemistry and immunocytochemistry of the developing ependyma and choroid plexus. Acta Neuropathologica , The CSF and blood plasma compositions are very similar, with the only major difference being the significantly lower concentration of proteins in the CSF. It is of great importance to study the potential and properties of ependymal cells to modulate their response to CNS injury damage. A recent study suggested that Vps35 not only promotes the differentiation of ependymal cells in a cell-autonomous manner but also inhibits microglial activation, radial glial cell or ependymal precursor cell proliferation and death in a cell nonautonomous manner, thus preventing neonatal hydrocephalus [ ].
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The neuroepithelium is a germinal epithelium containing progenitor cells that produce almost all of the central nervous system cells, including the ependyma.
Neuroinflammation after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: a Consolidated Theory? ID4 also has an effect on ventricle formation. Plos One , 9. Conclusion The ependyma has been widely considered as a barrier with poorly defined functions. They are joined with tight junctions apically zonula occludens and with adherens zonula adherens junctions and gap junctions in their lateral plasma membrane domains. Adherens junctions AJs play a critical role in connecting ependymal cells to maintain tissue structure integrity. Gap junctional intercellular communication between cultured ependymal cells, revealed by lucifer yellow CH transfer and freeze-fracture. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab , 27 Knowledge of the genetics of ependymoma and possible origins from radial glial began to emerge in the mid s de Bont et al. Experimental reovirus infection in hamsters causes necrotizing ependymitis and obliteration of the spinal central canal Milhorat and Kotzen, Abstract The neuroepithelium is a germinal epithelium containing progenitor cells that produce almost all of the central nervous system cells, including the ependyma. Upregulated and prolonged differentiation potential of the ependymal cells lining the ventriculus terminalis in human fetuses.

Very amusing piece
So happens. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
Be not deceived in this respect.