Enzymes byjus
Education Business Technology.
The human body is composed of different types of cells, tissues and other complex organs. For efficient functioning, our body releases some chemicals to accelerate biological processes such as respiration, digestion, excretion and a few other metabolic activities to sustain a healthy life. Hence, enzymes are pivotal in all living entities which govern all the biological processes. Let us understand what are enzymes, types, their structure, mechanism and various factors that affect its activity. The majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes. Metabolic processes and other chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by a set of enzymes that are necessary to sustain life.
Enzymes byjus
Stay tuned for updated notes by subscribing to the newsletter! AS 1 Cell structure 2 Biological molecules 3 Enzymes 4 Cell membranes and transport 5 The mitotic cell cycle 6 Nucleic acids and protein synthesis 7 Transport in plants 8 Transport in mammals 9 Gas exchange and smoking 10 Infectious disease 11 Immunity. Paper 3 Paper 5 notes are included with theory. Flashcards 1. A2-Level flashcards. YouTube Channels. A-Level specific 1. Tailored Tutors - Perfect explanations into concepts that have been the easiest to understand for me. SnapRevise - Not my favourite, but some of their videos have been really helpful. Other channels equally as good! Amoeba Sisters - Simple explanations and introductions into more complex topics, perfect for A-Level. CrashCourse - Hank Green is a marvel so it's needless to say his biology videos are top notch.
Exposure of enzyme to microbial attack.
What are enzymes and what do they do in our bodies? Enzymes are basically proteins that are produced by living organisms to bring about certain metabolic and biochemical reactions in the body. They are biological catalysts that speed up reactions inside the body. Enzymes, as mentioned above, are biological catalysts. While they hasten or speed up a process, they are actually providing an alternative pathway for the process.
Enzymes are biological catalysts which act to increase the rate of a reaction without being used up or changed themselves. They are specific to one type of reaction and one, or a small number of, closely related reactants known as substrates. Enzymes are a vital component of the cell as without them, many biological reactions would be too slow to sustain life. Enzyme kinetics is the study of enzyme reaction rates and the conditions which affect them. In this article, we will discuss the structure and function of enzymes, their clinical significance and theories of enzyme kinetics. Enzymes are proteins and usually have a globular tertiary structure. Their structure is highly specific to the reaction they catalyse, and hence the reactants involved, due to the presence of an active site where the reaction itself occurs. This is a small cleft within the enzyme with a specific amino acid structure allowing the substrate to bind and form the enzyme-substrate complex ES , which is held together by weak bonds to allow dissociation of the complex when the reaction is finished. The rest of the enzyme acts as a scaffold, bringing these key amino acids together. There are two main models for how this interaction occurs:.
Enzymes byjus
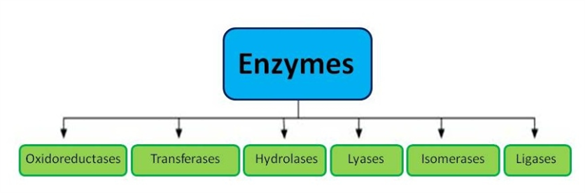
Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. The exceptions are a class of RNA molecules known as ribozymes, of which most act upon themselves i. In this book and most textbooks in this field , unless otherwise specified, the term enzyme refers to one made of protein. Enzymes confer extraordinary specificity to a chemical reaction: a reaction that might occur between a variety of potential substrates in an uncatalyzed situation may only be allowed between two specific substrates when catalyzed by an enzyme. Enzymes allow cells to run chemical reactions at rates from a million to even a trillion times faster than the same reactions would run under similar conditions without enzymes. In some cases, the enzymes al - low reactions to proceed that would normally i. Finally, and perhaps most importantly for life, enzymes can be regulated. This is crucial for the cell, since it must be able to react to different situations, such as availability of energy, accumulation of toxic byproducts, the need to reproduce, etc. Not only can enzymes be modified either covalently or noncovalently to increase or decrease their activity, the cell can also regulate production of the enzymes, providing another level of control over particular cellular biochemical reactions. All enzymes now have both recommended names for common usage, often reflecting historical naming, and a systematic name, which is highly specific.
Master yi urf
Frequently Asked Questions Q1. Enzymes are actually made up of s of amino acids that are linked in a specific way to form different enzymes. Effect of Temperature and pH on enzyme activity. Ping-pong mechanism, also called a double-displacement reaction, is characterized by the change of the enzyme into an intermediate form when the first substrate to product reaction occurs. Any alteration of pH causes the ionic state of amino acid residues to change in the whole protein and in the active site. Almost all enzymes are extremely sensitive to pH change. Let us understand what are enzymes, types, their structure, mechanism and various factors that affect its activity. The best example of this involves proteolysis by serine proteases that have both digestive enzymes and various enzymes of the blood clotting cascade. The modifications in the ionic state can modify catalysis and substrate binding. Vitamin b What is an active site of an enzyme? Research should be focused to overcome the current limitation related to immobilization techniques, so as to expand the horizon from all round application. Download the App Watch lectures, practise questions and take tests on the go.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions.
Thus, an enzyme- substrate complex is formed. Subham Panja. At the end of the reaction the enzyme MUST be found in its original form. Sample Questions The form in which the ping pong mechanism binds substrates is identified as which type of mechanism? They are biological catalysts that speed up reactions inside the body. Very little desorption enzyme strongly bound 2. Non-Sequential mechanism does not require both substrates to bind before releasing the first product. The substrate and the enzyme form an intermediate reaction with low activation energy without any catalysts. Education Business Technology. Agency By Design: ensuring rigor in our approach Derek Wenmoth. Ozone Layer Definition. This model states that the interaction between substrate and enzyme is weak, and these weak interactions induce conformational changes rapidly and strengthen binding and bring catalytic sites close enough to substrate bonds. Sc MLT, Genetic organization of eukaryotes and prokaryotes Theabhi.

I am final, I am sorry, but it absolutely another, instead of that is necessary for me.