Electron pair geometry of sf4
The process of mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom of slightly different energies so that a redistribution of energy takes place between electron pair geometry of sf4 resulting in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape is called hybridization. The new orbitals in this form are known as hybrid orbitals. Like pure orbitals the hybrid orbitals are used in Bond formation.
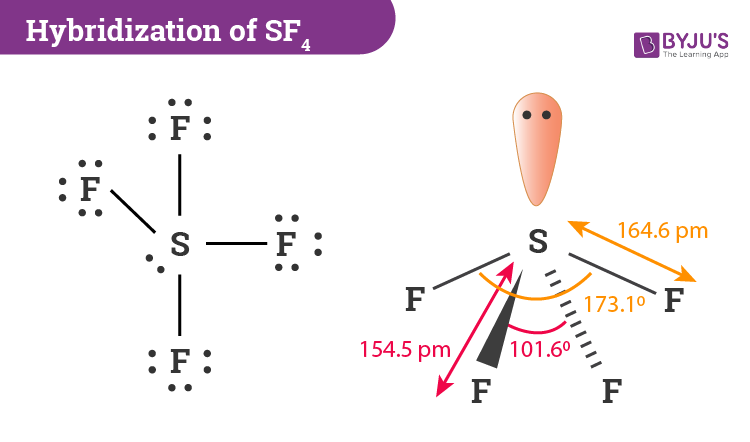
Let us learn about the SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
The molecular formula of sulfur tetrafluoride SF 4 indicates that the compound has one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms. Sulfur is located in Group 16 of the periodic table and has six valence electrons. Fluorine is located in Group 17 and has seven valence electrons. Fluorine requires one electron to complete its octet and achieve the electron configuration of its nearest neighbor, neon. Sulfur and fluorine will combine to form four S-F single bonds. Sulfur will use four valence electrons to bond with the four fluorine atoms. Hence, it will have one lone pair of electrons, while each fluorine atom will have six []. Lewis structure is used to show the bond formation in sulfur tetrafluoride. Sulfur is the least electronegative of the two. So, it will lie at the center of the molecule. Dash lines represent the four S-F single covalent bonds.
Download Important Formulas pdf. Crystalline Polymer. Sulfur and fluorine will combine to form four S-F single bonds.
.
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space Figure 7. A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees. A bond distance or bond length is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms along the straight line joining the nuclei. Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory VSEPR theory enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
One needs to know some basic properties of the given compound and its Lewis structure to understand its molecular geometry, polarity, and other such properties. SF4 is a chemical formula for Sulfur Tetrafluoride. It is a colorless corrosive gas that is used in the synthesis of several organofluorine compounds. SF4 is a rather hazardous compound but is used widely in chemical and pharmaceutical companies. It is easy to understand the molecular geometry of a given molecule by using the molecular formula or VSEPR model. A molecular formula helps to know the exact number and type of atoms present in the given compound. Here there is one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms in the compound, which makes it similar to the molecular formula of AX4E. Molecules having a molecular formula of AX4E have trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry.
Jtwc
What is SF4's molecular geometry? Lines represent bonds created between two atoms, whereas dots represent valence electrons that do not make any bonds. Learn more. SF4 is polar in nature and features sp3d hybridisation. The molecular formula of sulfur tetrafluoride SF 4 indicates that the compound has one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves. To know if the molecule is either polar or nonpolar, observe the sulfur tetrafluoride molecular geometry. It will also help in determining the hybrid orbitals count used by the atom by knowing the steric number. In SF 4 , a nonbonding sulphur lone electron pair replaces one of these ligands, while the rest are fluorines. What is the SF4 Hybridization? Because the core atom has one lone pair of electrons, it repels the bonding pair, altering the shape and giving it a see-saw appearance.
SF4 or sulfur tetrafluoride is a compound that has a distinct odor of sulfur or rotten eggs. This compound is generally identified as being a colorless gas. The molecular weight of this compound is calculated to be
Molecular Formula. Temporary Hardness of Water. SF4 is polar in nature and features sp3d hybridisation. Enthalpy of Neutralisation. The reason behind this is that the lone pair prefers one of the equatorial positions. JEE Application Process. As a result, we can identify five distinct electron density zones. The electron geometry of SF 4 is trigonal bipyramidal. Download Important Formulas pdf. Ans : Not all ligands peripheral groups in trigonal bipyramidal molecules or complexes are equidi Fluorine is located in Group 17 and has seven valence electrons. SF 4 isomerised temperature- or solvent-dependently, switching between states in which the nonbonding electron pair is equatorial with two fluorines and states in which the electron pair and one fluorine are axial. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. Ans : Draw the SF

0 thoughts on “Electron pair geometry of sf4”